The Journey of a Prompt: Lifecycle in Generative AI Systems Through Prompt Engineering
Prompt engineering guides AI responses. Its lifecycle integrates ethical considerations, evolving towards multi-modal inputs for a fair, transparent AI future.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIn the domain of generative AI systems, prompts, or the inputs given to these systems, hold significant importance. Comprehending the lifecycle and nature of these prompts is vital to ethically and effectively utilize AI. This forms the crux of prompt engineering — a process dedicated to crafting, fine-tuning, and managing prompts to elicit appropriate AI responses. This method extends beyond mere technicalities, incorporating essential ethical aspects to ensure AI systems function with transparency and fairness and are devoid of bias. In this article, we will take a journey through the different stages of prompt development, implementation, and refinement within generative AI, underscore the importance of ethical considerations, and delve into a practical example from Educational Technology (EdTech) that encapsulates the entire prompt lifecycle.
The Lifecycle: From Design to Deployment
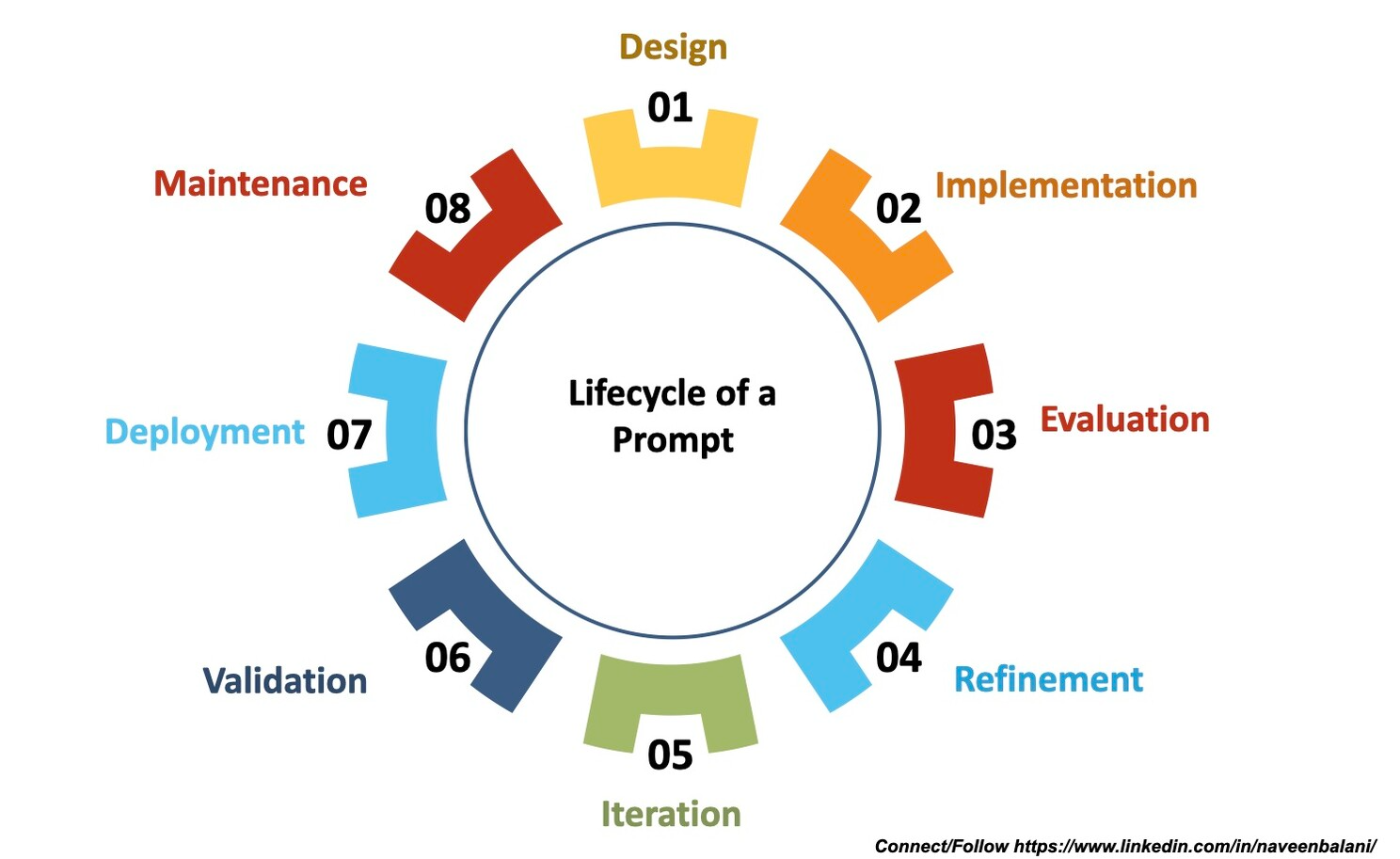
The journey of a prompt involves several interconnected stages:
- Design: The first step involves identifying the intended output from the AI. What task should it perform? What kind of response are we seeking? With a clear goal in mind, the initial prompt is designed to reflect these requirements.
- Implementation: Next, the prompt is input into the AI model. This stage acts as a testing phase, where we observe the model's response and compare it with our expected outcome.
- Evaluation: After the implementation comes the evaluation phase. The AI's response is critically assessed to determine if it fulfills the desired goal. If it doesn’t, the next step is to understand why.
- Refinement: Based on the evaluation, the prompt is refined to improve the output. This may involve increasing its specificity, adjusting the phrasing, or adding more context.
- Iteration: The refined prompt is then implemented again, and its results are evaluated. This process of implementation, evaluation, and refinement is iteratively repeated until the prompt produces a satisfactory output.
- Validation: The prompt is then validated across different contexts or datasets to ensure its reliability and robustness.
- Deployment: Once validated, the prompt is integrated into the production environment, ready to interact with end users.
- Maintenance: Even after deployment, the prompt's performance must be continually monitored. If its performance drops or new requirements emerge, the prompt may need to be reevaluated, and the lifecycle begins anew.
Ethics, Bias, and Explainability: Crucial Considerations
Throughout this lifecycle, the inclusion of ethical considerations is pivotal:
- Design and Implementation: The prompt should be designed to encourage AI behavior that is respectful of user privacy and adheres to ethical guidelines.
- Evaluation and Refinement: Monitor the AI’s responses for any signs of bias. If bias is detected, the prompt should be refined to reduce it. Additionally, the responses should be transparent and explainable to the users.
- Validation and Deployment: Validate that the prompt does not encourage unethical behavior or bias across various contexts and data sets. Even after deployment, continuously monitor the AI's responses for ethical adherence and bias.
- Maintenance: Be prepared to make adjustments as necessary to maintain ethical standards and continue to check for bias.
EdTech: A Real-World Application — Detailed Walkthrough
The aim is to use AI prompts in an EdTech setting to create a system that simplifies and explains mathematical concepts to middle school students. Let's walk through this with a focus on the lifecycle of the prompt and the ethical considerations involved.
Design Phase: The initial prompt might be "What is the Pythagorean theorem?" The expected output from the AI would be a simple and understandable explanation of the theorem.
Implementation Phase: This prompt is fed into the AI model, and the initial responses are evaluated. It might become clear that the AI’s response is too technical, not meeting the user-friendly requirement for our target audience.
Refinement Phase 1: To rectify this, the prompt is adjusted to "Explain the Pythagorean theorem in a way a middle school student would understand." The refined prompt is then implemented and the responses are evaluated. If the AI provides clear, age-appropriate explanations, we proceed to the next refinement.
Refinement Phase 2: In this stage, an ethical dimension is added to the prompt. It's recognized that the AI's explanations may unintentionally skew towards a specific gender or culture. To ensure inclusivity and avoid any bias, the prompt is refined again to "Explain the Pythagorean theorem in a way a middle school student would understand, using gender-neutral and culturally inclusive examples."
Validation Phase: This revised prompt is now validated across a wide range of mathematical concepts. The goal is to ensure the AI can adapt its language level and inclusivity across different topics.
The final prompt, ready for Deployment, might be "Explain [Math Concept] in a way a middle school student would understand, using gender-neutral and culturally inclusive examples."
The system can replace "[Math Concept]" with any concept to be explained, and it has been validated to generate the desired, user-friendly, and inclusive explanations.
In the Maintenance Phase, we monitor the AI's interactions with students, tracking its effectiveness and watching for any inadvertent bias or ethical concerns in its responses. If new mathematical concepts are introduced into the curriculum, the prompt may need to be reevaluated and refined, thereby starting another cycle in the prompt's lifecycle.
This example underscores the importance of iterating on prompts and integrating ethical considerations throughout the lifecycle of a prompt to create an effective, unbiased, and ethically sound AI system.
Summary
In the rapidly evolving world of AI, understanding the lifecycle of a prompt — from its design to deployment — is crucial. This complex process includes multiple stages like design, implementation, evaluation, refinement, iteration, validation, deployment, and maintenance. Yet, this technical journey is only one aspect of the story.
Equally significant are the ethical considerations that must be integrated at every stage. These considerations ensure that AI behavior respects user privacy, adheres to ethical guidelines, and is free from bias. An AI's responses must be transparent and explainable and should promote fair treatment across different contexts, data sets, and user groups.
Through our detailed example of an EdTech application, we saw these principles in action. We followed the prompt's evolution from a simple question to a refined directive that helped an AI provide clear, understandable, and inclusive explanations of complex mathematical concepts to middle school students.
As we embrace AI and its transformative potential across various sectors, we must remember that crafting the right prompts and integrating ethical guidelines is as important as the AI technology itself. Only through this comprehensive and thoughtful approach can we truly harness the power of AI, creating solutions that are not only efficient and effective but also fair, unbiased, and respectful of all users.
As we continue to innovate and learn, the prompt engineering process will continue to evolve, bringing us closer to realizing the limitless potential of AI technologies.
Published at DZone with permission of Navveen Balani, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments