AI Agents: Future of Automation or Overhyped Buzzword?
AI Agents perceive, decide, and act independently, continuously learning and adapting to automate complex tasks with minimal human intervention.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIn a world obsessed with artificial intelligence, there's a new player in town — AI agents. But before you roll your eyes and think, "Great, another tech term to pretend I understand at meetings," let’s break it down.
What the Heck Are AI Agents?
Imagine you have a really smart assistant — not just one that tells you the weather or suggests a new Netflix show — but one that thinks, plans, and acts without you having to spell everything out. That’s what AI agents are all about. Unlike simple chatbots or automation scripts that follow rigid, predefined paths, AI agents are designed to be autonomous. They don’t just react; they perceive, decide, and take action based on goals.
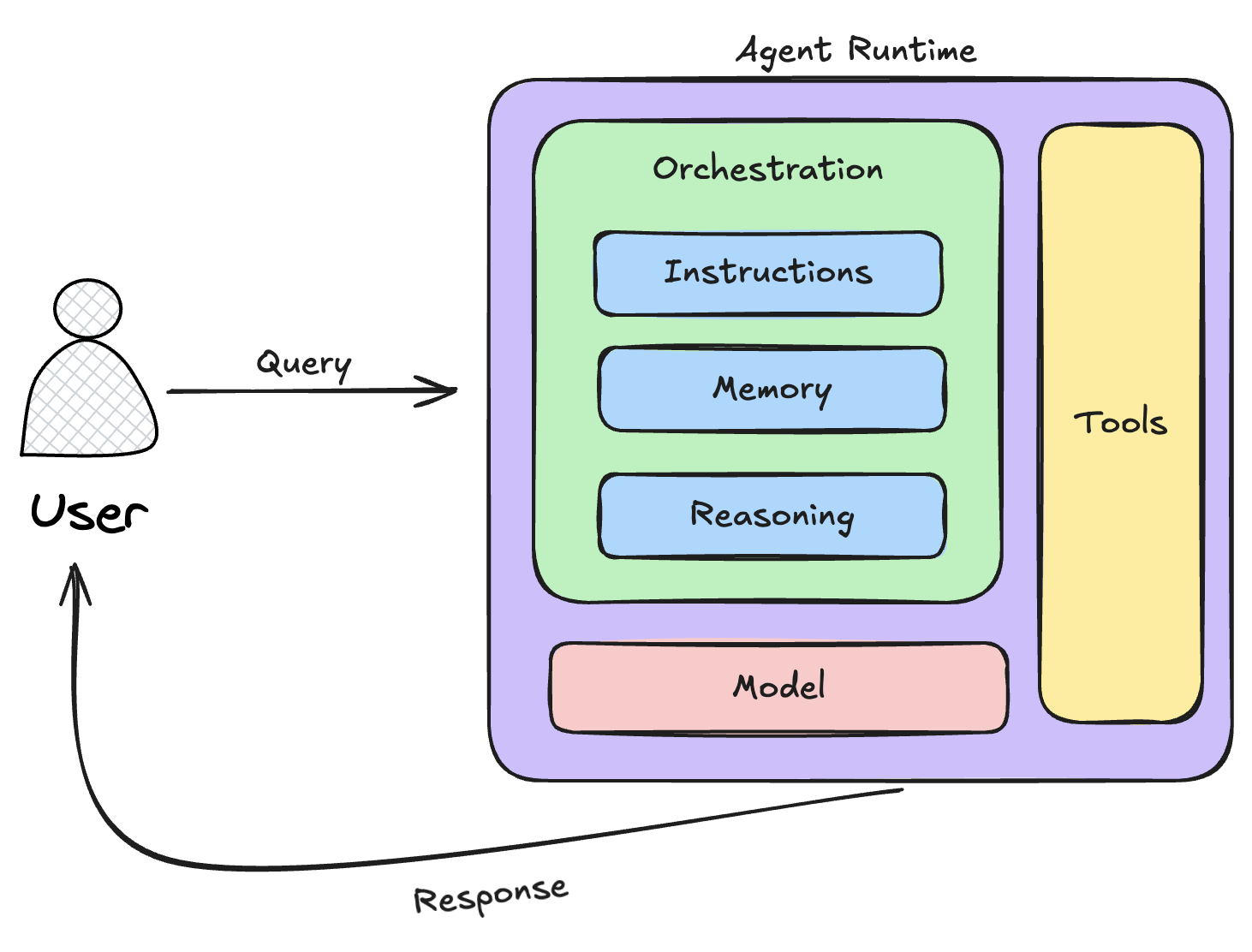
At their core, AI agents have three main components:
- A model. The brain behind the agent, often powered by a language model (like GPT) or a combination of AI techniques.
- Tools. The “hands” of the agent, allowing it to interact with databases, APIs, and external systems.
- An orchestration layer. This governs how the agent perceives its environment, plans, and acts.
Think of an AI agent as a chef in a high-end restaurant. It looks at the ingredients available (perception), decides what to cook (reasoning), and then actually prepares the dish (action). This cycle repeats and improves over time, making the agent more efficient and effective.
Not Everything That Talks Back Is an AI Agent
Here’s where we need to clear up some confusion. Just because something is labeled as “AI” doesn’t make it an agent.
A large language model, like the ones behind your favorite chatbots, is an impressive text generator. It predicts words based on patterns it has learned but doesn’t actually understand what it’s saying. It’s like a parrot that repeats words convincingly but doesn’t grasp their meaning. Similarly, chatbots and automated customer service assistants might give helpful responses, but they’re simply regurgitating predefined scripts — they don’t make decisions or adapt dynamically.
AI agents, on the other hand, are goal-oriented problem solvers. They don’t just answer questions; they analyze real-time data, make informed decisions, and adapt their behavior to achieve complex objectives. Imagine hiring a new employee — one that doesn’t just do what they’re told but also figures out what needs to be done, identifies the best way to do it, and improves over time. That’s the difference between a basic chatbot and an AI Agent.
How Are AI Agents Built?
AI agents are not just simple programs following a script; they are complex systems built with multiple interdependent components. Their architecture can be broken down into three fundamental parts:
The Model
This is the core decision-making unit of an AI agent. It typically consists of machine learning models, including large language models (LLMs), neural networks, and other AI techniques. These models process input data, generate predictions, and make informed decisions based on patterns and learned behaviors.
The Tools
AI agents extend their capabilities through external tools such as APIs, databases, search engines, or specialized functions. These tools allow agents to retrieve real-time information, interact with digital systems, and even execute specific tasks beyond their initial training data.
The Orchestration Layer
This governs the entire operational cycle of an AI agent. It includes mechanisms for perception (input processing), reasoning (decision-making), and action (executing tasks). The orchestration layer ensures the agent dynamically adapts to new inputs and refines its responses over time.
Cognitive Architecture: The Brain of AI Agents
The cognitive architecture of an AI agent defines how it processes information, reasons through problems, and interacts with its environment. This architecture typically includes the following:
1. Perception Module
The agent collects raw data from its surroundings, which can include structured databases, real-time web scraping, or even IoT sensor inputs.
2. Memory and Knowledge Graphs
AI agents store and retrieve relevant information to maintain context over time. This includes both short-term memory (session-based interactions) and long-term memory (historical learning and pattern recognition).
3. Decision-Making and Planning
Agents use frameworks such as Chain-of-Thought (CoT) or Tree-of-Thought (ToT) reasoning to break complex tasks into manageable steps, analyze multiple solutions, and select the best course of action.
4. Action Execution
Once a decision is made, the agent interacts with its environment using predefined tools, API calls, or even physical actuators in robotics-based implementations.
5. Feedback Loop and Continuous Learning
AI agents refine their decision-making process over time through reinforcement learning, self-supervised learning, or user feedback mechanisms.
Think of an AI agent like a self-driving car. The model is the brain that makes driving decisions, the tools include sensors and navigation systems to interact with the road, and the orchestration layer ensures all these components work in sync to drive safely and efficiently. The cognitive architecture enables the car to not only drive but also learn from past trips, anticipate potential obstacles, and adapt to new routes dynamically.
Why Should You Care?
AI agents are not just an evolution of AI; they are a fundamental shift in IT operations and decision-making. These agents are being increasingly integrated into Predictive AIOps (Artificial Intelligence for IT Operations), where they autonomously manage, optimize, and troubleshoot systems without human intervention. Unlike traditional automation, which follows pre-defined scripts, AI agents dynamically predict, adapt, and respond to system conditions in real time.
Some key benefits of AI agents include:
- Proactive issue resolution. AI agents in AIOps identify potential failures before they occur, reducing downtime and ensuring system resilience.
- Autonomous decision-making. They optimize system performance, allocate resources, and resolve errors without waiting for human input.
- Scalability and adaptability. AI agents continuously learn from system data, adjust in real time, and enhance operational efficiency without requiring frequent manual updates.
- Enhanced IT autonomy. By leveraging reinforcement learning and predictive analytics, AI agents create self-sustaining IT ecosystems, minimizing operational risks and human workload.
Okay, so AI agents sound cool, but what can they actually do?
- Adaptive and self-sustaining AI systems. AI agents are transforming IT management and operational resilience. Instead of just replacing workflows, they now optimize and predict system health, automatically mitigating risks and reducing downtime. Whether it's self-repairing IT infrastructure, real-time cybersecurity monitoring, or orchestrating distributed cloud environments, AI Agents are pushing technology toward self-governing, intelligent automation.
- Dynamic decision-making. AI agents continuously analyze complex systems in real time, using advanced cognitive architectures to make decisions without predefined rules. This allows them to detect anomalies, mitigate security risks, and reconfigure environments autonomously.
- Autonomous systems in IT and cybersecurity. AI agents are not just digital assistants but active participants in managing IT infrastructure. They autonomously allocate resources, detect vulnerabilities, and adapt to emerging threats, enhancing system resilience without human oversight.
- Self-learning and predictive adaptation. AI agents employ reinforcement learning techniques, meaning they refine their behavior based on past experiences. Whether it’s optimizing system performance, predicting potential failures, or automating complex workflows, these agents continuously improve without requiring manual intervention.
What’s Next for AI Agents?
The future of AI agents is both thrilling and terrifying. Companies are investing in large action models (LAMs) — next-gen AI that doesn’t just generate text but actually does things. We’re talking about AI that can manage entire business processes or run a company’s operations without human intervention.
But with great power comes great responsibility, right? AI agents will also need governance, ethical considerations, and built-in safeguards to prevent them from going rogue (because, let’s face it, we’ve all seen Terminator).
Final Thoughts: Hype or Reality?
AI agents aren’t just another tech buzzword — they represent a fundamental shift in how AI interacts with the world. Sure, we’re still in the early days, and there’s a lot of fluff in the market, but make no mistake: AI agents will change the way we work, live, and do business.
The question is: Are you ready for them, or will you be left scrambling to catch up?
Further Reading and Sources
For those interested in diving deeper into the world of AI agents and their applications, I highly recommend exploring the research behind Predictive AIOps and cognitive AI architectures. The insights presented in Agentic AI in Predictive AIOps: Enhancing IT Autonomy and Performance provide a strong foundation for understanding how AI agents are transforming IT operations and decision-making processes.
Additionally, the whitepaper Agents explores the intricate details of AI agent architectures, including cognitive reasoning, decision-making models, and integration with external tools. This paper highlights how AI agents bridge the gap between foundational models and real-world applications, extending their utility far beyond simple automation.
If you're curious about the frameworks and methodologies that power AI agents, both of these sources will help you gain a more comprehensive understanding of the technology and its implications.
AI agents are not just a futuristic concept; they are already reshaping industries. The key question remains — will you be a passive observer or an active participant in this revolution?
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments