Implementing Serverless Microservices Architecture on AWS
In this article, we will explain how enterprises can implement serverless microservices architectures using AWS Cloud.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeMicroservices are an architectural approach for software that is designed to speed up development cycles and support scalability. In this approach, the software is composed of small independent services that communicate over well-architected APIs.
In this article, we will explain how enterprises can implement serverless microservices architecture using the AWS Cloud.
Monolithic vs. Microservices Architecture
In a monolithic architecture, all the components are tightly coupled and run as a single service. Here, the entire architecture has to be scaled if any one component of the application experiences a spike in demand. This architecture type increases the difficulty level to implement new ideas in the application.
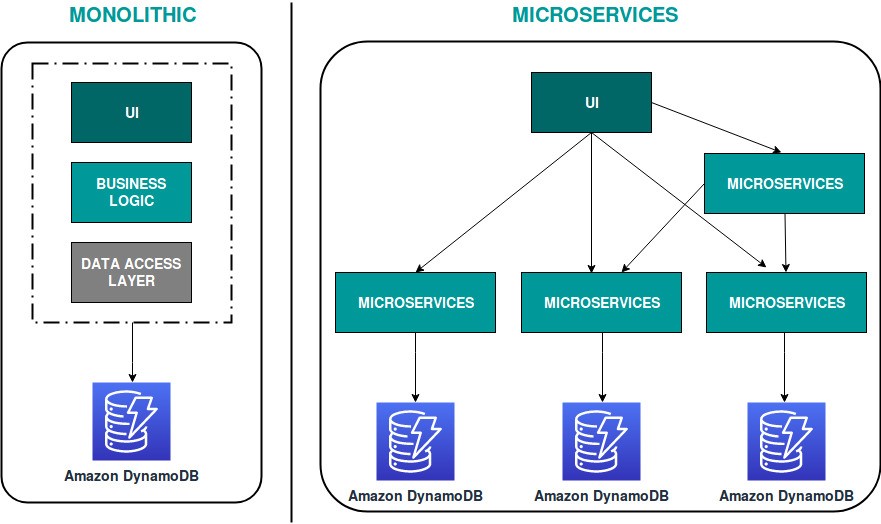
Fig 1. Monolithic vs. Microservices Architecture
In a microservices architecture, each component is a small application that has its own hexagonal architecture. It is an architectural style that structures an application as a collection of services that are loosely coupled and independently deployable.
Features of Microservices Architecture
Independent
In a microservices architecture, each component can be changed, upgraded, or replaced individually without affecting the functionality of other components.
Decentralized
Microservices architecture follows the decentralized data management, where each service has its own view on data models.
Autonomous
In a microservices architecture, there is no need to share any of the component code or implementation with other components. Any communication between components can be done via well-defined APIs.
Black Box
Microservices architecture behaves like a black box because each component hides the details of complexity from other components.
Advantages of Microservices Architecture
Quality
Microservices architecture can also improve the quality of code as the whole application is running into small and well-defined components
Scalability
In a microservices architecture, each component is properly decoupled so it can be scaled horizontally and independently from each other and it never faces the downtime during the scaling process because in horizontal scaling more components are added to the existing pool instead of increasing the capacity of each component
Easy Development
Microservices architecture makes it easy to try out new ideas and roll it back with the help of continuous integration and continuous delivery if something undesired happens.
Resilience
With a microservices architecture, applications can handle total service failure by degrading the functionality instead of crashing the entire application.
Challenges of Microservices Architecture
Migration
The process of migration from a monolithic architecture to a microservices architecture is complex and requires to release code dependencies going down to the database layer.
Testing
In a microservices environment, testing is complex due to different services and their integrations.
Monitoring
In a microservices architecture, the application is broken down into small components. It is difficult to find the root cause of the problem when something goes wrong because the issue may not lie within the component that fails, but a dependency.
Serverless Microservices Architecture
The diagram below shows the serverless microservices architecture where the complete solution is built without managing any server. This also eliminates the operational efforts of running and monitoring the servers.
Lambda will handle everything required to run and scale the execution to meet actual demand with high availability. Lambda supports several programming languages and it can be called directly from any web or mobile applications.
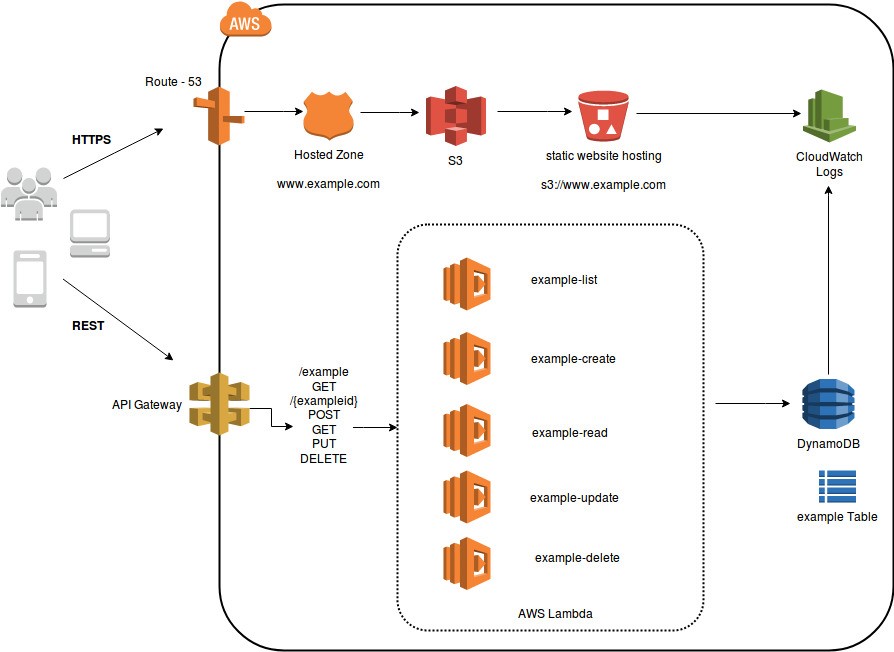
Fig 2. Serverless Microservices Architecture
In the architecture diagram, Lambda is integrated with API Gateway. Synchronous calls from API gateway to AWS Lambda enables the application to operate as serverless. AWS Lambda will store all the data in a fully managed NoSQL database called DynamoDB and all the static data will be stored in S3 Bucket.
It can be said that microservices architecture is designed to overcome the challenges of traditional monolithic architectures seen in enterprise applications. It allows collaboration between operations and development teams of any organization leading to DevOps and is a preferred choice nowadays.
AWS offers multiple managed services that can help engineers build microservice architectures and minimize architectural and operational complexity.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments