The State of Data Streaming for Energy and Utilities in 2023
Use cases, architectures, and case studies for Apache Kafka in the energy and utilities industry, including IoT, AI, blockchain, and cybersecurity.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeThis blog post explores the state of data streaming for the energy and utilities industry in 2023. The evolution of utility infrastructure, energy distribution, customer services, and new business models requires real-time end-to-end visibility, reliable and intuitive B2B and B2C communication, and integration with pioneering technologies like 5G for low latency or augmented reality for innovation. Data streaming allows integrating and correlating data in real-time at any scale to improve most workloads in the energy sector.
I look at trends in the utilities sector to explore how data streaming helps as a business enabler, including customer stories from SunPower, 50hertz, Powerledger, and more. A complete slide deck and on-demand video recording are included.
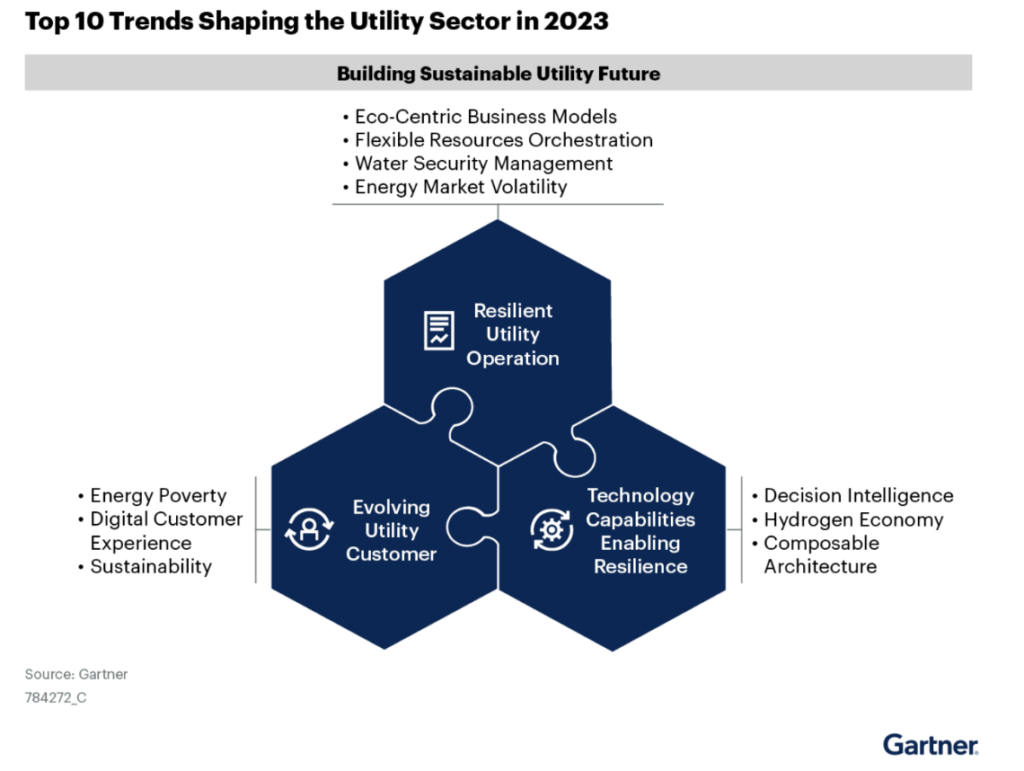
General Trends in the Energy and Utilities Industry
The energy and utilities industry is fundamental for a sustainable future. Garter explores the Top 10 Trends Shaping the Utility Sector in 2023: "In 2023, power and water utilities will continue to face a variety of forces that will challenge their business and operating models and shape their technology investments.
Utility technology leaders must confidently compose the future for their organizations in the midst of uncertainty during this energy transition volatile period — the future that requires your organizations to be both agile and resilient."
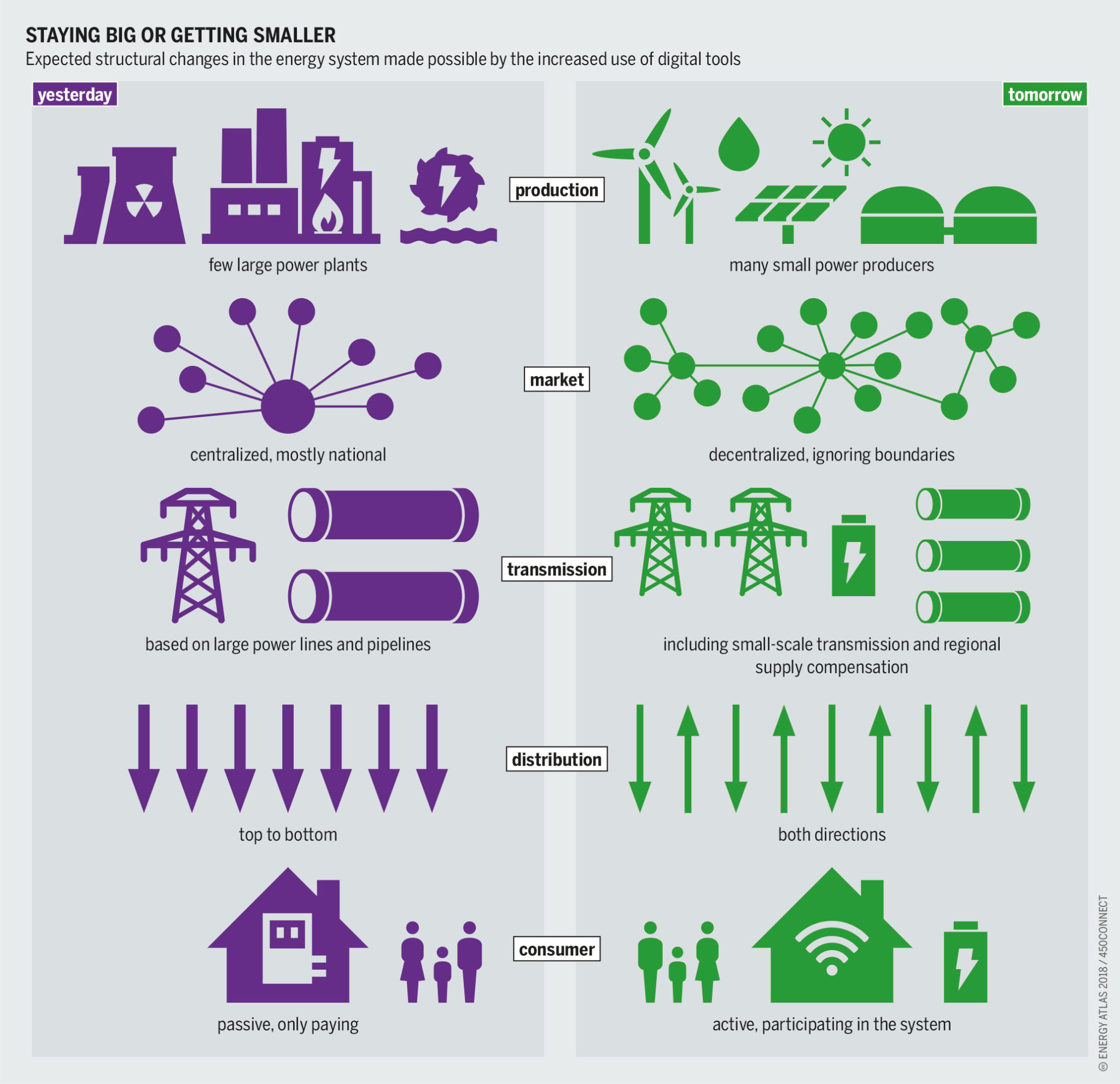
From System-Centric and Large to Smaller-Scale and Distributed
The increased use of digital tools makes the expected structural changes in the energy system possible:
Energy AI Use Cases
Artificial Intelligence (AI) with technologies like Machine Learning (ML) and Generative AI (GenAI) is a hot topic across all industries. Innovation around AI disrupts many business models, tasks, business processes, and labor.
NVIDIA created an excellent diagram showing the various opportunities for AI in the energy and utilities sector. It separates the scenarios by segment: upstream, midstream, downstream, power generation, and power distribution.
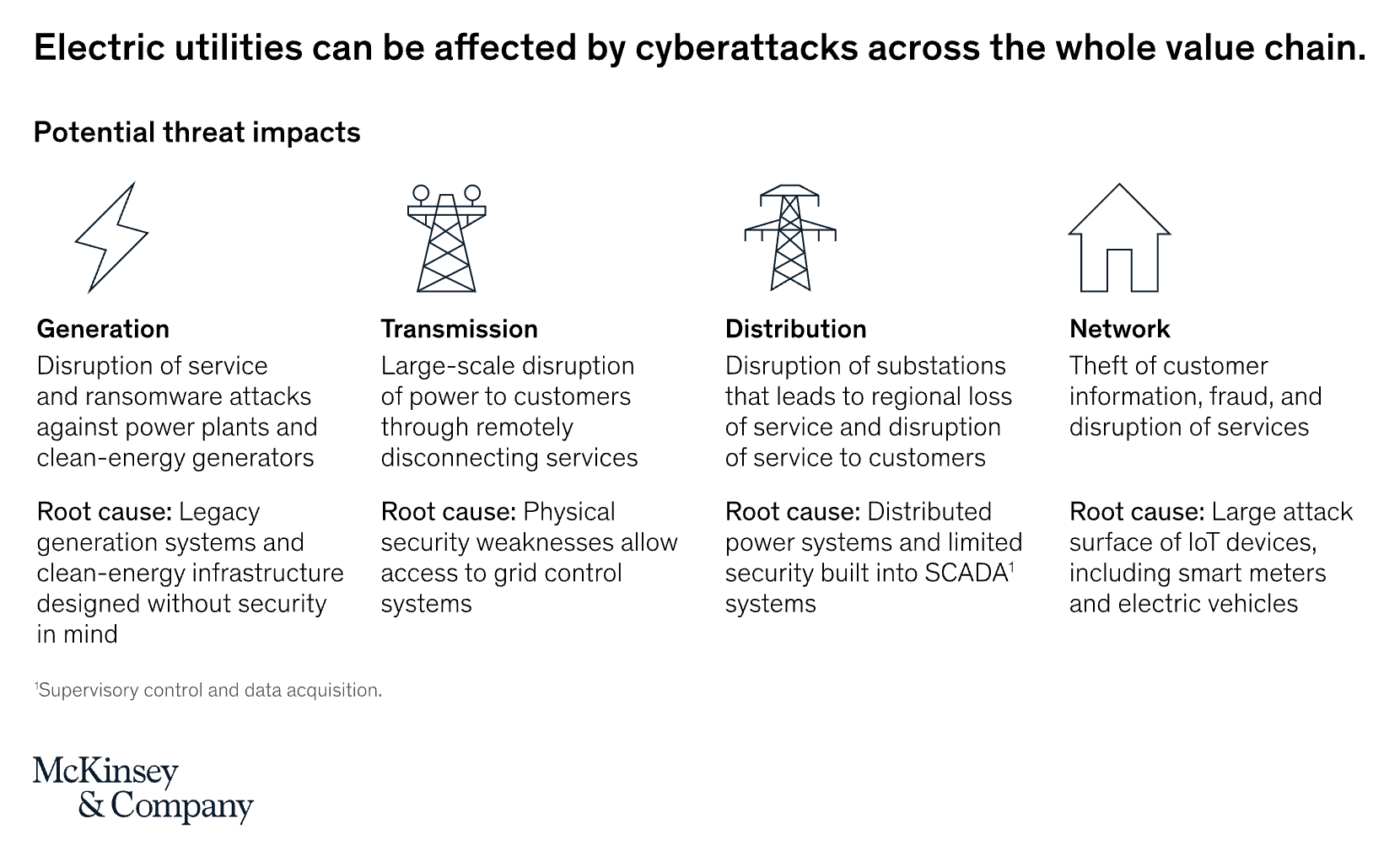
Cybersecurity: The Threat Is Real!
McKinsey & Company explains that "the cyber threats facing electric-power and gas companies include the typical threats that plague other industries: data theft, billing fraud, and ransomware. However, several characteristics of the energy sector heighten the risk and impact of cyber threats against utilities:"
Data Streaming in the Energy and Utilities Industry
Adopting trends like predictive maintenance, track and trace, proactive sales and marketing, or threat intelligence is only possible if enterprises in the energy sector can provide and correlate information at the right time in the proper context. Real-time, which means using the information in milliseconds, seconds, or minutes, is almost always better than processing data later (whatever later means):
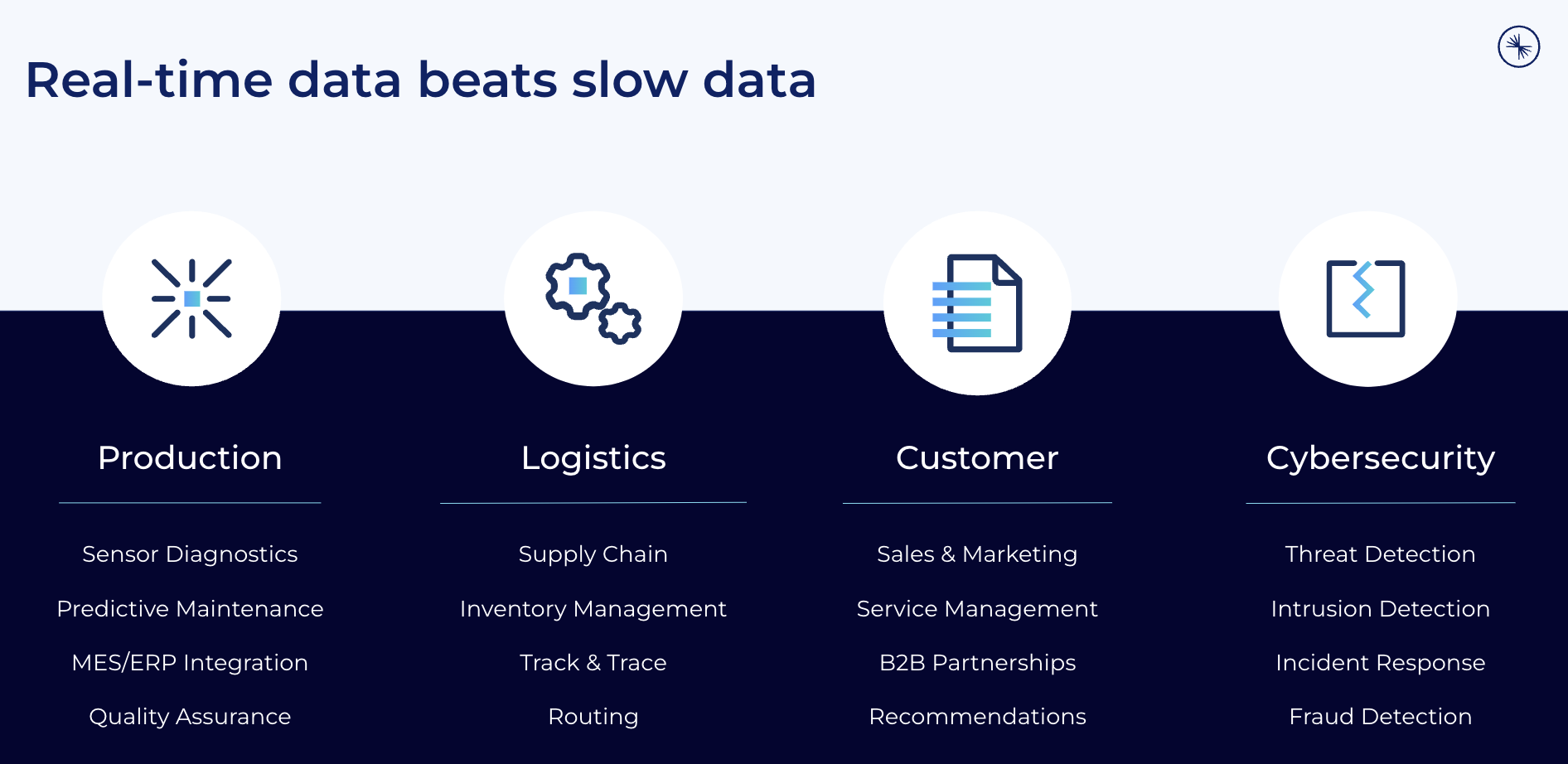
Data streaming combines the power of real-time messaging at any scale with storage for true decoupling, data integration, and data correlation capabilities.
5 Ways Utilities Accomplish More With Real-Time Data
“After creating a collaborative team that merged customer experience and digital capabilities, one North American utility went after a 30 percent reduction in its cost-to-serve customers in some of its core journeys.”
As the Utilities Analytics Institute explains: "Utilities need to ensure that the data they are collecting is high quality, specific to their needs, preemptive in nature, and, most importantly, real-time." The following five characteristics are crucial to add value to real-time data:
- High-Quality Data
- Data Specific to Your Needs
- Make Your Data Proactive
- Data Redundancy
- Data is Constantly Changing
Real-Time Data for Smart Meters and Common Praxis
Smart meters are a perfect example of increasing business value with real-time data streaming. As Clou Global confirms: "The use of real-time data in smart grids and smart meters is a key enabler of the smart grid."
Possible use cases include:
- Load Forecasting
- Fault Detection
- Demand Response
- Distribution Automation
- Smart Pricing
Processing and correlating events from smart meters with stream processing is just one IoT use case.
Cloud Adoption in Utilities and Energy Sector
Accenture points out that 84% use Cloud SaaS solutions and 79% use Cloud PaaS Solutions in the energy and utilities market for various reasons:
- New approach to IT
- Incremental adoption
- Improved scalability, efficiency, agility, and security
- Unlock most business value.
This is a general statistic, but this applies to all components in the data-driven enterprise, including data streaming. A company does not just move a specific application to the cloud; this would be counter-intuitive from a cost and security perspective. Hence, most companies start with a hybrid architecture and bring more and more workloads to the public cloud.
Architecture Trends for Data Streaming
The energy and utilities industry applies various trends for enterprise architectures for cost, flexibility, security, and latency reasons. The three major topics I see these days at customers are:
- Global data streaming
- Edge computing and hybrid cloud integration
- OT/IT modernization
Let's look deeper into some enterprise architectures that leverage data streaming for energy and utilities use cases.
Global Data Streaming Across Data Centers, Clouds, and the Edge
Energy and utilities require data infrastructure everywhere. While most organizations have a cloud-first strategy, there is no way around running some workloads at the edge outside a data center for cost, security, or latency reasons.
Data streaming is available everywhere:
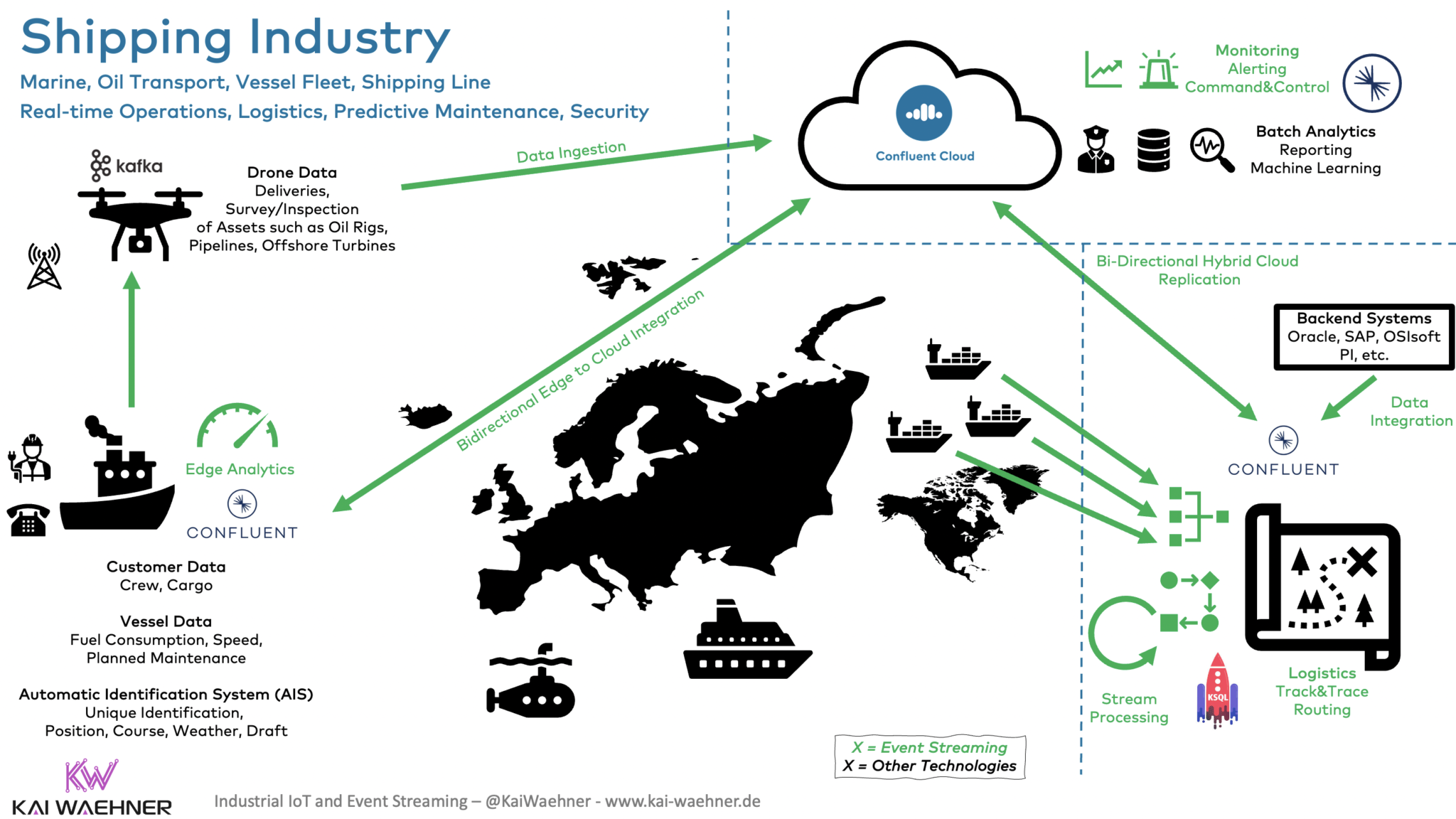 Data synchronization across environments, regions, and clouds is possible with open-source Kafka tools like MirrorMaker. However, this requires additional infrastructure and development/operations efforts. Innovative solutions like Confluent's Cluster Linking leverage the Kafka protocol for real-time replication. This enables much easier deployments and significantly reduced network traffic.
Data synchronization across environments, regions, and clouds is possible with open-source Kafka tools like MirrorMaker. However, this requires additional infrastructure and development/operations efforts. Innovative solutions like Confluent's Cluster Linking leverage the Kafka protocol for real-time replication. This enables much easier deployments and significantly reduced network traffic.
Edge Computing and Hybrid Cloud Integration
Kafka deployments look different depending on where it needs to be deployed.
Fully managed serverless offerings like Confluent Cloud are highly recommended in the public cloud to focus on business logic with reduced time-to-market and TCO.
In a private cloud, data center, or edge environment, most companies deploy on Kubernetes today to provide a similar cloud-native experience.
Kafka can also be deployed on industrial PCs (IPC) and other industrial hardware. Many use cases exist for data streaming at the edge. Sometimes, a single broker (without high availability) is good enough.
No matter how you deploy data streaming workloads, a key value is the unidirectional or bidirectional synchronization between clusters. Often, only curated and relevant data is sent to the cloud for cost reasons. Also, command and control patterns can start a business process in the cloud and send events to the edge.
![Edge Computing and Hybrid Cloud Integration]() OT/IT Modernization With Data Streaming
OT/IT Modernization With Data Streaming
The energy sector operates many monoliths, inflexible and closed software and hardware products. This is changing in this decade. OT/IT modernization and digital transformation require open APIs, flexible scale, and decoupled applications (from different vendors).
Many companies leverage Apache Kafka to build a postmodern data historian to complement or replace existing expensive OT middleware:
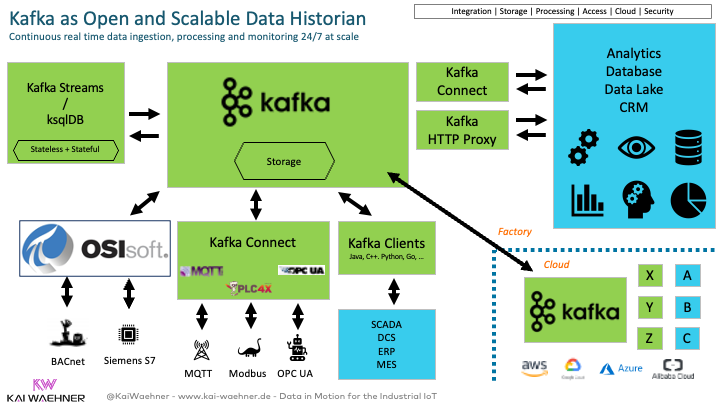
Just to be clear: Kafka and any other IT software like Spark, Flink, Amazon Kinesis, and so on are NOT hard real-time. It cannot be used for safety-critical use cases with deterministic systems like autonomous driving or robotics. That is C, Rust, or other embedded software.
However, data streaming connects the OT and IT worlds. As part of that, connectivity with robotic systems, intelligent vehicles, and other IoT devices is the norm for improving logistics, integration with ERP and MES, aftersales, etc.
New Customer Stories for Data Streaming in the Energy and Utilities Sector
So much innovation is happening in the energy and utilities sector. Automation and digitalization change how utilities monitor infrastructure, build customer relationships, and create completely new business models.
Most energy service providers use a cloud-first approach to improve time-to-market, increase flexibility, and focus on business logic instead of operating IT infrastructure. Elastic scalability gets even more critical with all the growing networks, 5G workloads, autonomous vehicles, drones, and other innovations.
Here are a few customer stories from worldwide energy and utilities organizations:
- 50hertz: A grid operator modernization of the legacy, monolithic, and proprietary SCADA infrastructure to cloud-native microservices and a real-time data fabric powered by data streaming.
- SunPower: Solar solutions across the globe where 6+ million devices in the field send data to the streaming platform. However, sensor data alone is not valuable! Fundamentals for delivering customer value include measurement ingestion, metadata association, storage, and analytics.
- aedifion: Efficient management of the real estate to operate buildings better and meet environmental, social, and corporate governance (ESG) goals. Secure connectivity and reliable data collection are implemented with Confluent Cloud (and deprecated the existing MQTT-based pipeline).
- Ampeers Energy: Decarbonization for the real estate. The service provides district management with IoT-based forecasts and optimization and local energy usage accounting. The real-time analytics of time-series data is implemented with OPC-UA, Confluent Cloud, and TimescaleDB.
- Powerledger: Green energy trading with blockchain-based tracking, tracing, and trading of renewable energy from rooftop solar power installations and virtual power plants. Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) representing renewable energy certificates (RECs) in. A decentralized rather than the conventional unidirectional market. Confluent Cloud ingests data from smart electricity meters.
Resources To Learn More
This blog post is just the starting point. Learn more about data streaming in the energy and utilities industry in the following on-demand webinar recording, the related slide deck, and further resources, including pretty cool lightboard videos about use cases.
On-Demand Video Recording
The video recording explores the telecom industry's trends and architectures for data streaming. The primary focus is the data streaming case studies.
Slides
If you prefer learning from slides, check out the deck used for the above recording:
Slide Deck: The State of Data Streaming for Energy & Utilities in 2023
Case Studies and Lightboard Videos for Data Streaming in the Energy and Utilities Industry
The state of data streaming for energy and utilities in 2023 is fascinating. New use cases and case studies come up every month. This includes better data governance across the entire organization, real-time data collection and processing data across hybrid edge and cloud infrastructures, data sharing and B2B partnerships for new business models, and many more scenarios.
We recorded lightboard videos showing the value of data streaming simply and effectively. These five-minute videos explore the business value of data streaming, related architectures, and customer stories. Stay tuned; I will update the links in the next few weeks and publish a separate blog post for each story and lightboard video.
And this is just the beginning. Every month, we will talk about the status of data streaming in a different industry. Manufacturing was the first. Financial services second, then retail, telcos, gaming, and so on... Check out my other blog posts.
Let’s connect on LinkedIn and discuss it! Join the data streaming community and stay informed about new blog posts by subscribing to my newsletter.
Published at DZone with permission of Kai Wähner, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

 OT/IT Modernization With Data Streaming
OT/IT Modernization With Data Streaming
Comments