Configuring a Main Class in Spring Boot
In this article, see a tutorial that explains how to configure a main class in Spring Boot.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeSpringApplication.run(Classname.class, args) bootstraps a spring application as a stand-alone application from the main method. It creates an appropriate ApplicationContext instance and load beans.
By default, if the main class isn’t explicitly specified, Spring will search for one in the classpath at compile time and fail to start if none or multiple of them are found.
Let’s see how we can Configure a Main Class in Spring Boot.
xxxxxxxxxx
public class SpringBootMainClassApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootMainClassApplication.class, args);
}
}
This is the main class of our application form which the Spring Boot application will get executed. Now let’s create one homepage controller to open the home page of the application.
xxxxxxxxxx
public class HomeController {
("/")
public String goToHomePage () {
return "<h1>This is the Home page</h1>";
}
}
You may also be interested in: Hibernate 5 Java Configuration Example
Below is the POM.xml file for our Spring Boot project.
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.1.9.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath></relativePath> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.dailycodebufffer.example</groupId>
<artifactId>Spring-Boot-Main-Class</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>Spring-Boot-Main-Class</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>11</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
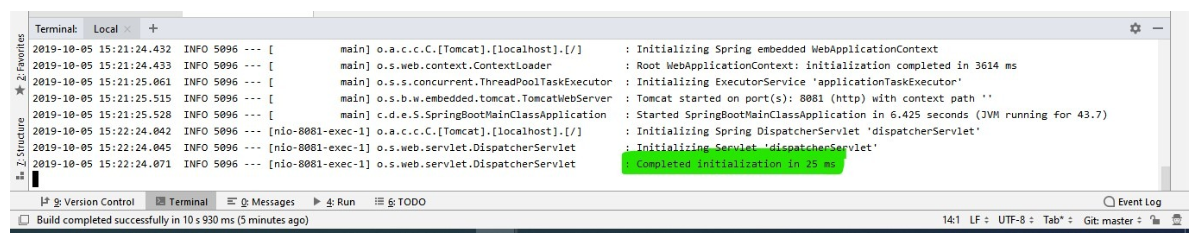
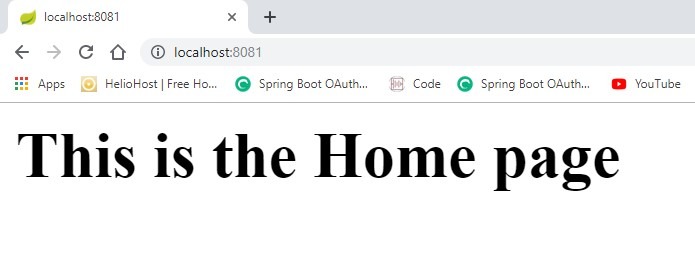
Now, when you run the application with mvn spring-boot:run command in Terminal, the Spring Boot application will get started in port 8081 as configured in the application.properties file. Check out the below screenshot for the build success and home page of the application.
Now, let’s create a new Spring Main class in the application. After the creation of this class, we will have two new main classes with two public static void main(String args[]) methods.
xxxxxxxxxx
public class SpringBootMainClassApplication2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootMainClassApplication2.class, args);
}
}
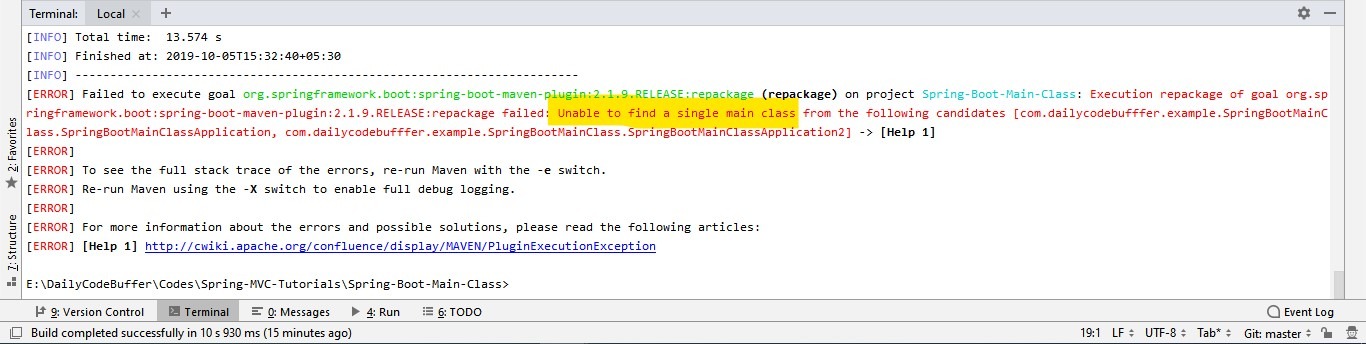
As we know from Java basics, we can only have one main method in a Java application. When we try to build this application, it will throw an exception as below.
How Do We Solve This?
Spring Boot allows us to define the Main class in the configuration when we have multiple main classes declared in the application. As we are using a MAVEN build, we have to configure the POM.xml for Spring Boot to identify the main class of the application.
Below are the changes required in the POM.xml file:
xxxxxxxxxx
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<mainClass>com.dailycodebufffer.example.SpringBootMainClass.SpringBootMainClassApplication</mainClass>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
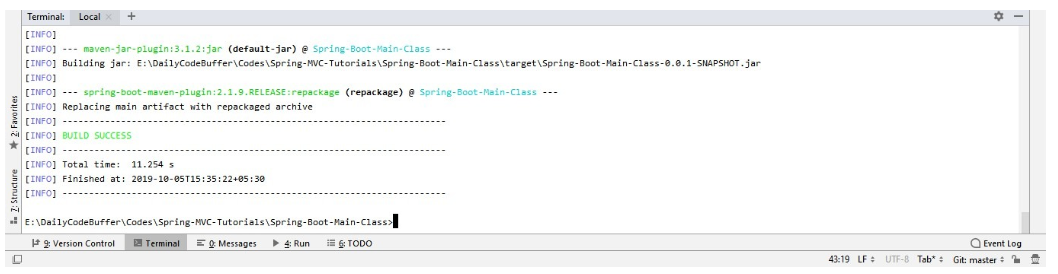
Voila! We can define any of the main classes in the configuration. Below, check out the successful build of our Spring Boot application.
Using CLI to Configure the Main Class in Spring Boot
We can also specify a main class via the command-line interface.
Spring Boot’s org.springframework.boot.loader.PropertiesLauncher comes with a JVM argument to let you override the logical main-class called loader.main:
xxxxxxxxxx
java -cp Spring-Boot-Main-Class-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar -Dloader.main=com.dailycodebufffer.example.SpringBootMainClass.SpringBootMainClassApplication org.springframework.boot.loader.PropertiesLauncher
Conclusion
There are more than a few ways to specify the entry point to a Spring Boot application. It’s important to know that all these configurations are just different ways to modify the manifest of a JAR or WAR file.
As always, you can find the code on GitHub.
Further Reading
The @SpringBootApplication Annotation Example in Java + Spring Boot
Spring Boot Configuration: Overriding Built-In Configuration
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments