5 Key Steps for a Successful Cloud Migration Strategy
Applying the right strategy is essential when moving a company from on-premises to the cloud or from one cloud to another.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIf you have not remodeled your business to the cloud, you have stayed behind your competitors. The first step towards optimizing business strategy is cloud migration. 80% of companies, from small to large, have shifted their services to the cloud.
Cloud migration can enhance data security, functionality, scalability, and customer service and reduce costs. Businesses can store their data, software applications, and more components in the cloud. However, migration from one cloud to another or from local data centers to the cloud requires the right strategy to be considered.
Before diving into the five steps of a migration strategy, let’s first unwrap the knowledge about cloud migration.
What Is Cloud Migration?
Cloud migration is transforming all an organization's digital assets, including IT resources, databases, services, and applications, from on-premise infrastructure to a public cloud like AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure. Cloud-to-cloud migration, on the other hand, is the process of moving from one cloud to another.
Implementing a cloud-based environment in your business setup can put you ahead of the game. Migrating from on-premise to the cloud moves your data and analytics workload and resolves common issues by providing virtual services over the internet. Let us take a look at cloud migration strategies and steps for successfully migrating your business to the cloud.
Cloud Migration Strategy
Planning, design, migration, operation, and maintenance are the five stages of cloud migration, also known as cloud transformation. These stages involve the efficient and uninterrupted migration of the company's workload and data.
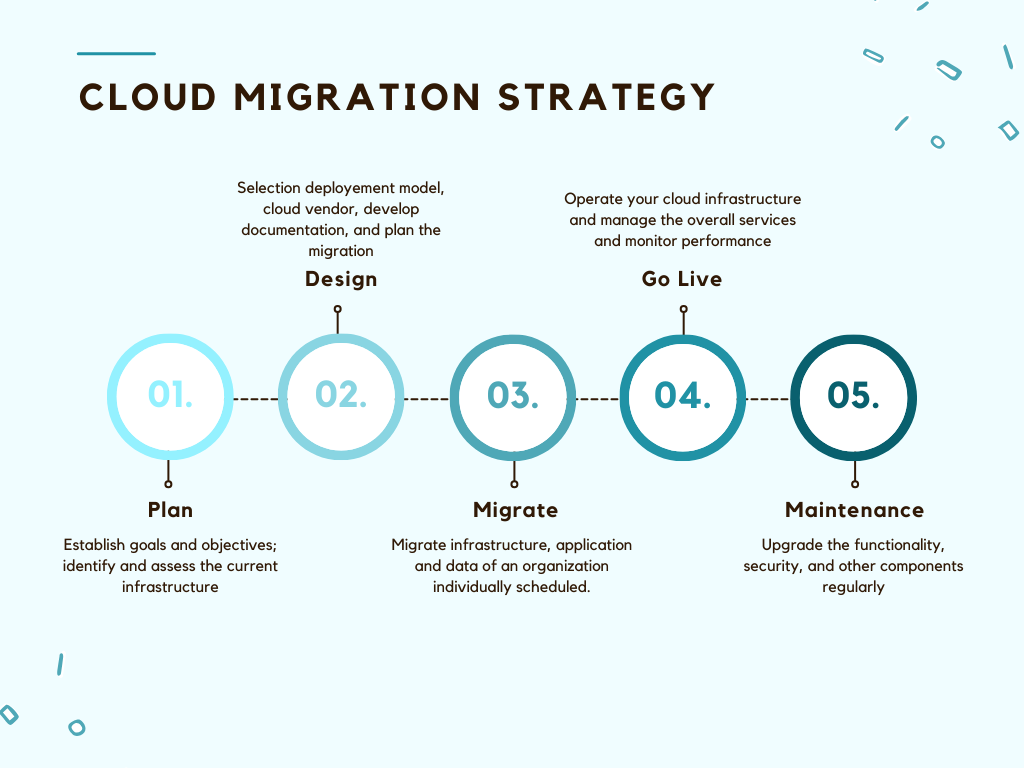
1. Plan
Planning, assessing, and learning are the main goals of the first phase of the cloud migration strategy. Companies establish their objectives for cloud migration, including increasing agility, scalability, cost savings, and improved performance. Organizations analyze the gaps and strengths of their IT services for successful cloud migration. The planning phase is further broken down into four steps:
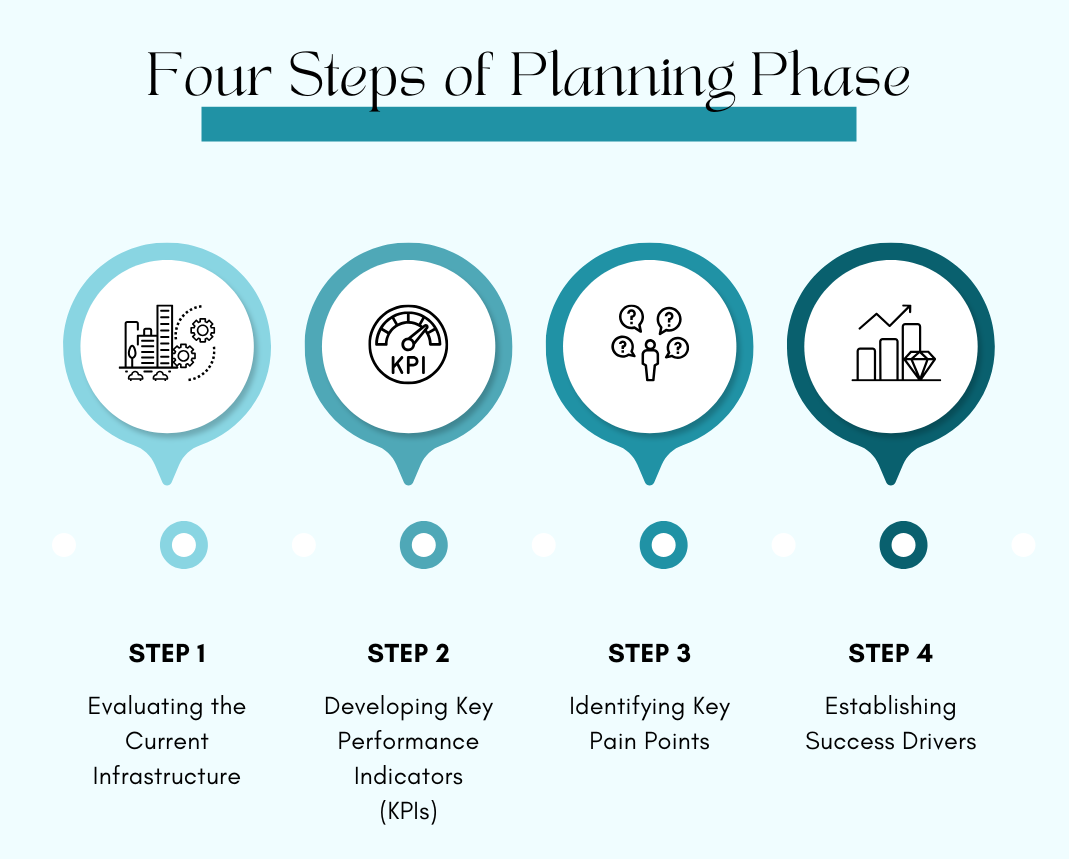
Step 1: Assessing the Present Infrastructure
Consider and analyze the present infrastructure of your organization to identify the challenges and opportunities before migration. Analyze the existing application, resources, software, hardware, security, and networking. You can utilize automated tools and work with experts to develop the picture of infrastructure for applications and requirements.
Step 2: Establishing KPIs
Key performance indicators (KPIs) measure the overall performance of the current infrastructure of your organization. The current environment and the project's future needs can be evaluated. KPIs can monitor the general operation and advancement of the migration, both during and after it is finished.
Step 3: Identifying Key Pain Points
Understand key pain points by working with the expert team and analyze the future requirements of the organization. The legacy of underperformance that has been identified can be used to focus future efforts.
Step 4: Creating Success Motivators
Identify the main reasons and points for the migration of your business to a cloud-based platform. The success of your cloud migration depends on combining these points with the KPIs and pain points. After designing the cloud infrastructure, creating success drivers can lower costs and ROI, improve data security, and make data sharing easier.
2. Design
After analyzing the current infrastructure and understanding the key pain points and needs, another step is the road map of the migration. Evaluate your current setup's environment, taking into account critical and legacy data as well as application interoperability factors.
The design for migration may step down into the deployment model selection, vendor selection, and documentation and migration plan.
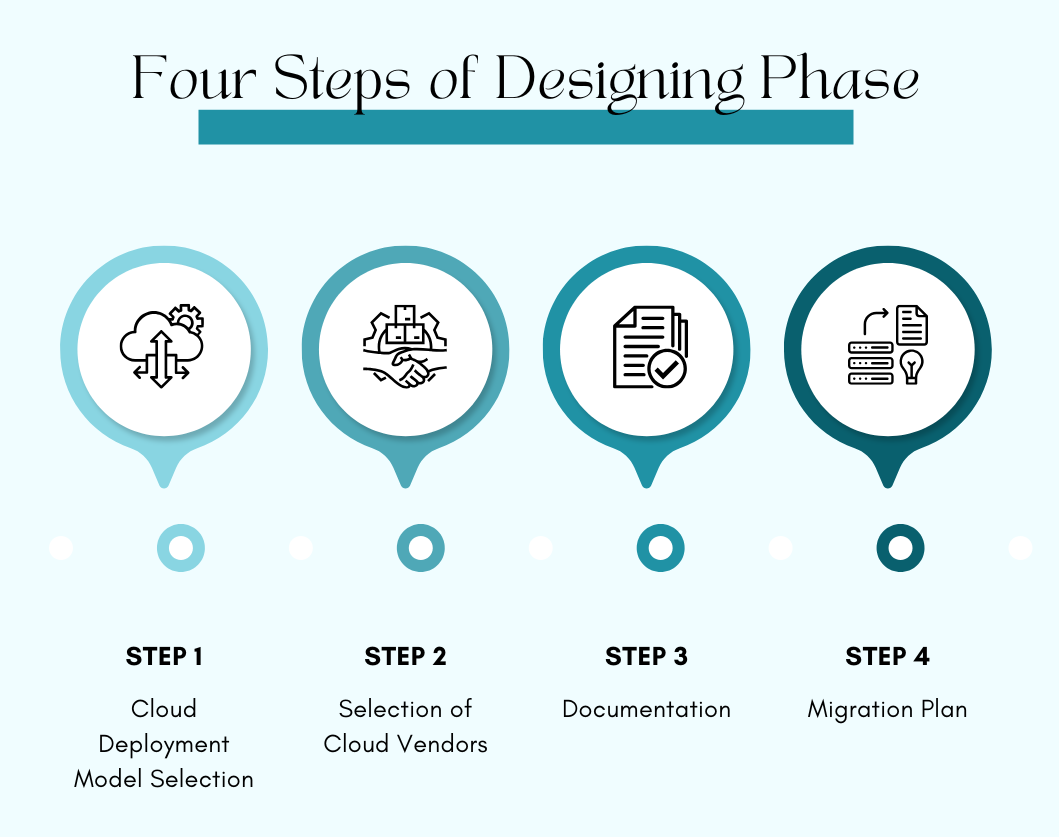
Step 1: Cloud Deployment Model
The organization’s computing, security, and networking requirements have been analyzed in the planning phase. The cloud deployment model determines the workload and who will oversee the organization's infrastructure. Goals and objectives can be achieved through any of the following models:
- Hybrid cloud
- Community cloud
- Public cloud
- Private cloud
Before selecting one model of the above, identify their advantages and disadvantages and select the one that can fulfill your organization’s requirements.
Step 2: Vendor Selection
Moving forward, it’s time to choose a vendor that aligns best with your needs and requirements, which you have analyzed in the previous steps. Evaluate the potential vendors for the surety of customer service and other components. Cloud service experts can help you select the best models and vendors.
Step 3: Documentation
On the completion of analysis and selection, the documentation of infrastructure architecture is necessary. An implementation and migration roadmap is included in the infrastructure documentation. The documentation allows you to keep tabs on developments and keep stakeholders informed. Infrastructure documentation will contain applications, software, and cloud resources of the organization.
Step 4: Migration Plan
Migration planning will specify how and when each migration event will take place. Determine whether all of the infrastructure and applications can be moved to their current state or if they require modification.
The migration plan sets the order of each application migration, establishes baselines for KPIs, modifies the necessary documents and applications, provides deadlines, and minimizes downtime and disruptions during migration.
3. Migration
Migration is the process of transferring data, infrastructure, and applications to the cloud. The most important and crucial part of migration is moving the data. This step contains different techniques to move the workloads, data, and applications that include as-is shifting, shifting after modifying, or rebuilding the applications.
Ensuring the transfer from one environment to another is critical for the planned migration without any disruptions. Shift individually and conduct testing after each migration to avoid data loss or disruptions during the transformation process.
4. Going Live
Once workloads are migrated to the cloud-based environment and the system is set up, it’s time to operate or go live. Cloud experts manage the workloads, including monitoring, maintaining security, and managing resources. After rigorous planning, designing, and implementation, there can be snags, errors, and downtime.
In order to address errors, ensure compliance, and troubleshoot problems simultaneously, an IT team should be present. Downtime should be kept to a minimum so that the system can operate concurrently.
5. Maintenance
As you go live, the company may get feedback and complaints regarding the performance of the cloud operation. Organizations may look for ways to improve performance, streamline cloud operations, implement more cloud-native features, and cut costs.
Continuous infrastructure and application testing, monitoring cloud performance, and managing workloads can ensure greater performance of the cloud. The health of the cloud must be assessed by the IT team.
Conclusion
Digital revolutionization made it necessary for businesses to move to cloud services from local centers to enhance their performance and infrastructure. Cloud migration can keep your business ahead in the market and increase the growth of a business. The right strategy is the key to the successful cloud migration of your business.
Set your goals and identify your business needs, design the roadmap and plan the migration through the requirements, migrate the infrastructure, applications, and data to the cloud individually with approval carefully, go live and operate, optimize and maintain the overall system regularly.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments