Use AWS Glue To Migrate RDS Data To Amazon Redshift
For those seeking to migrate their databases to Amazon Redshift, this tutorial provides steps on how to do so using AWS Glue.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeMoving large amounts of data is always a cumbersome task to do, especially when there are adjustments to be made along the way. However, sticking with a more traditional way of storing data or running database services isn’t efficient either.
If you are building a data lake, for example, moving from Amazon RDS to Amazon Redshift is a logical decision to make. Redshift integrates well with other AWS services and is itself a fully managed, petabyte-scale data warehouse service in the cloud. So, it works optimally in handling petabytes of structured and semi-structured data. Regardless of the size of the data set, Amazon Redshift can provide fast query performance by using other SQL-based tools and business intelligence applications.
Among those tools, to help you fully take advantage of the data warehouse platform, is AWS Glue; which you can use to migrate your data from RDS to Redshift. AWS Glue is a fully managed ETL service (extract, transform, and load) for moving and transforming data between your data stores.
NOTE: It can read and write data from the following AWS services.
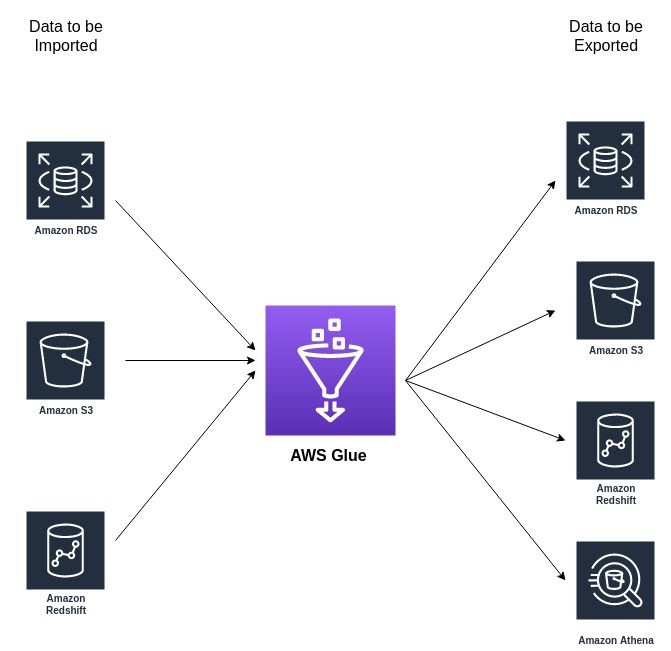
AWS Glue: Copy And Unload
Moving data to and from Amazon Redshift is something best done using AWS Glue. Glue is an ETL service that can also perform data enriching and migration with predetermined parameters, which means you can do more than copy data from RDS to Redshift in its original structure.
For example, Glue supports FindMatches ML Transform, and it works with Apache Spark. You can run multiple Spark ETL jobs in an efficient way, plus you have the ability to create bookmarks at any point. Bookmarks act as points to which you can rewind your Glue jobs.
What you want to do first is establish ETL runtime for extracting data stored in Amazon RDS. Configure the AWS Glue Crawlers to collect data from RDS directly, and then Glue will develop a data catalog for further processing.
To do this, go to AWS Glue and add a new connection to your RDS database. While you are at it, you can configure the data connection from Glue to Redshift from the same interface. The next step is creating the data catalog; you need a data catalog for RDS and Redshift.
Adding a crawler is a matter of identifying schemes for data copying and unloading, although you have to make sure that crawlers have sufficient access to collect the data. Assign sufficient access level to crawlers using IAM.
Creating Migration Jobs
Glue Jobs are actionable runtimes that perform specific tasks. When you create a Glue Job, you define how data needs to be gathered, processed and transferred. This is the core of Glue ETL; it does the extraction, transformation, and loading of data.
You can use Python or Scala as your ETL language. When configuring Jobs, however, you want to be specific with your data mapping, including the data types for each column. You can add security configurations, additional scripts or job parameters as needed.
Glue will generate codes for the process and display a diagram of how the process flows. If you are happy with the results, you can execute the code to start migrating data from RDS to Redshift. You can immediately try a query in Redshift once the process is completed.
For larger data sets, you want to be careful with how you define the columns you’re migrating. Be specific and make sure you define the column type for each set to avoid unnecessary errors and problems with the process.
Steps To Move Data From Rds To Redshift Using AWS Glue
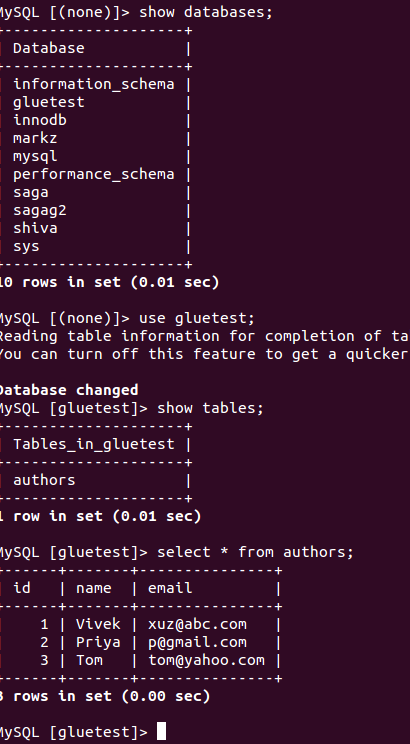
Create A Database In Amazon RDS:
Create an RDS database and access it to create tables.
Create tables in the database as per below.
Creating A Cluster In Amazon Redshift
Create a Redshift cluster.
Create a table in the Redshift cluster as per the below image.
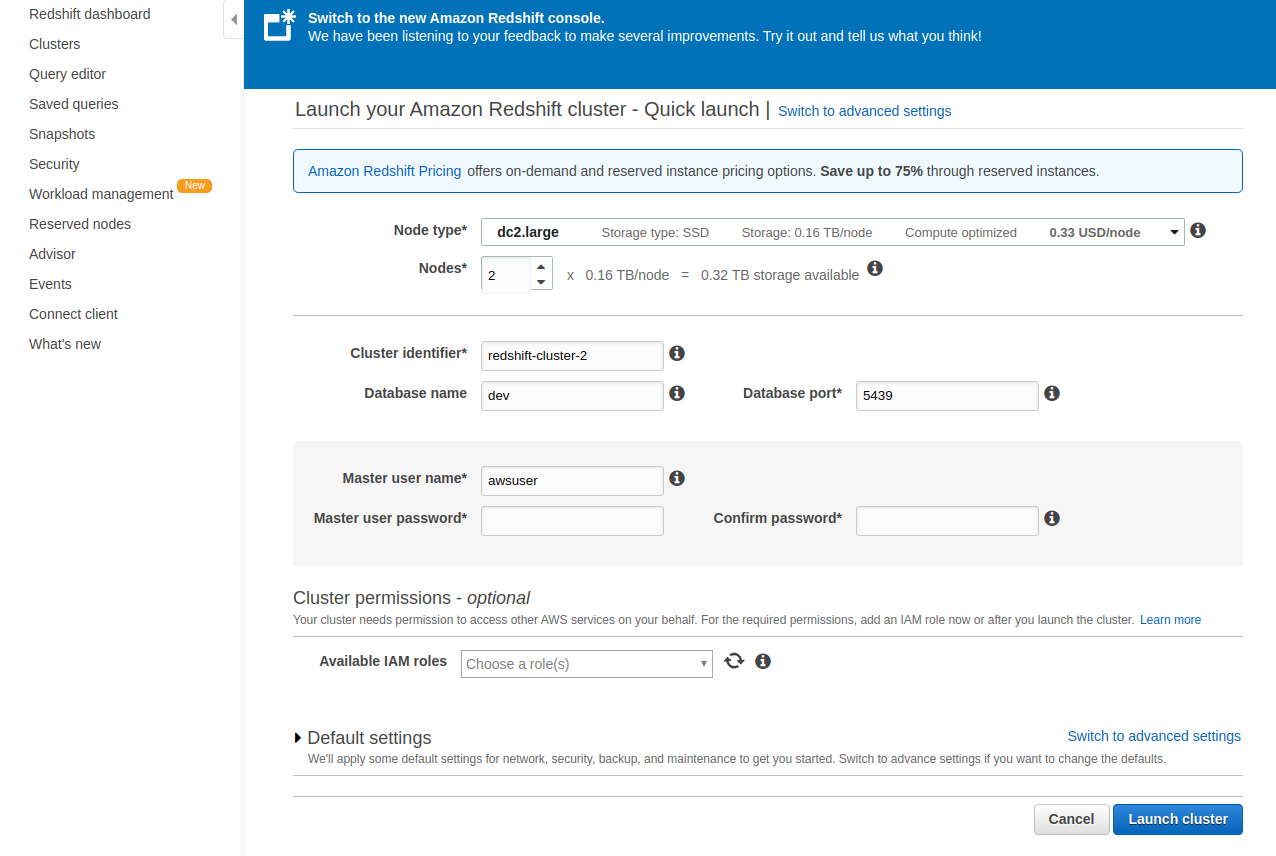
Next, launch your Amazon Redshift cluster with the Quick launcher and add details like cluster name, database name, username, and password.
In the query editor, specify the db details and run queries.
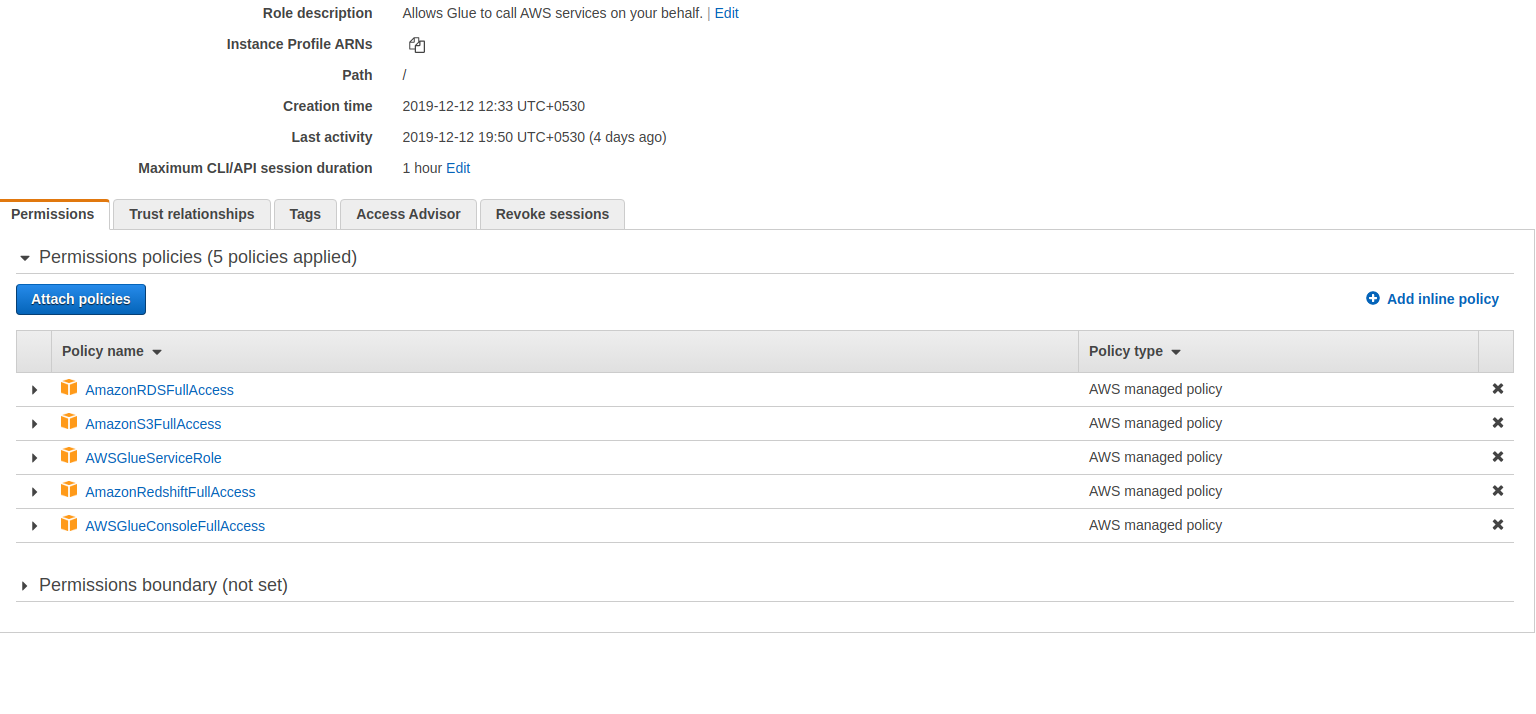
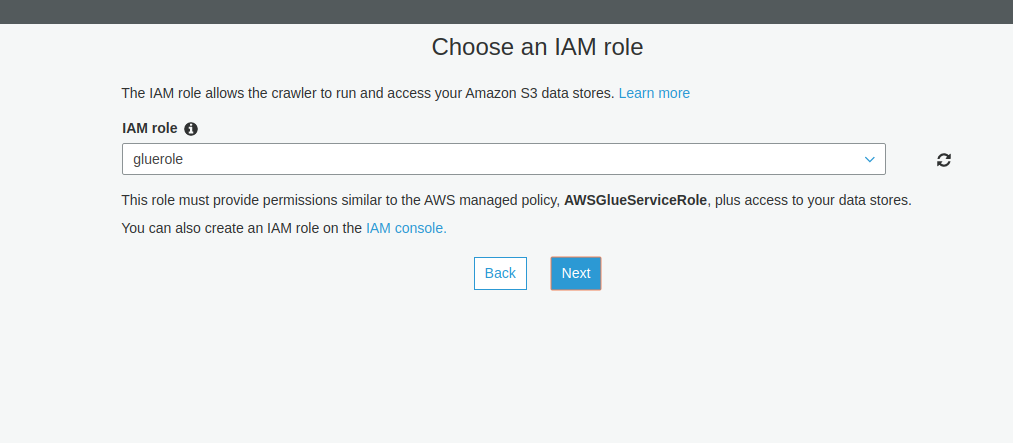
Create An IAM Role
Create a role in IAM for AWS Glue to access your RDS db, Redshift warehouse, and S3 store.
Setting Up The Connections And Jobs In AWS Glue
Create a connection between Redshift and RDS.
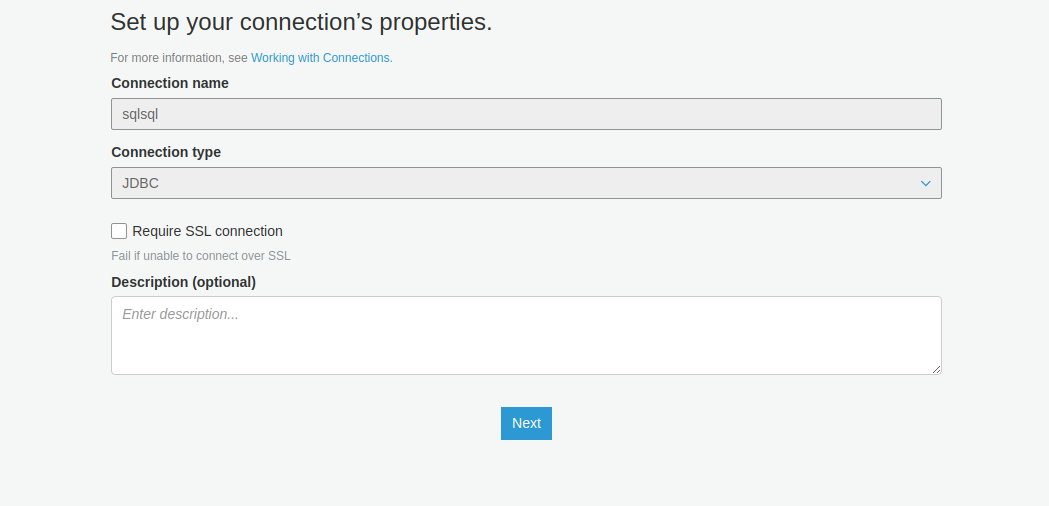
Specify the JDBC-URL as created from Redshift. Specify the user name and password of your MySQL RDS DB, and choose your VPC and subnets.
Next, go to Redshift, select your cluster, and click on that cluster.
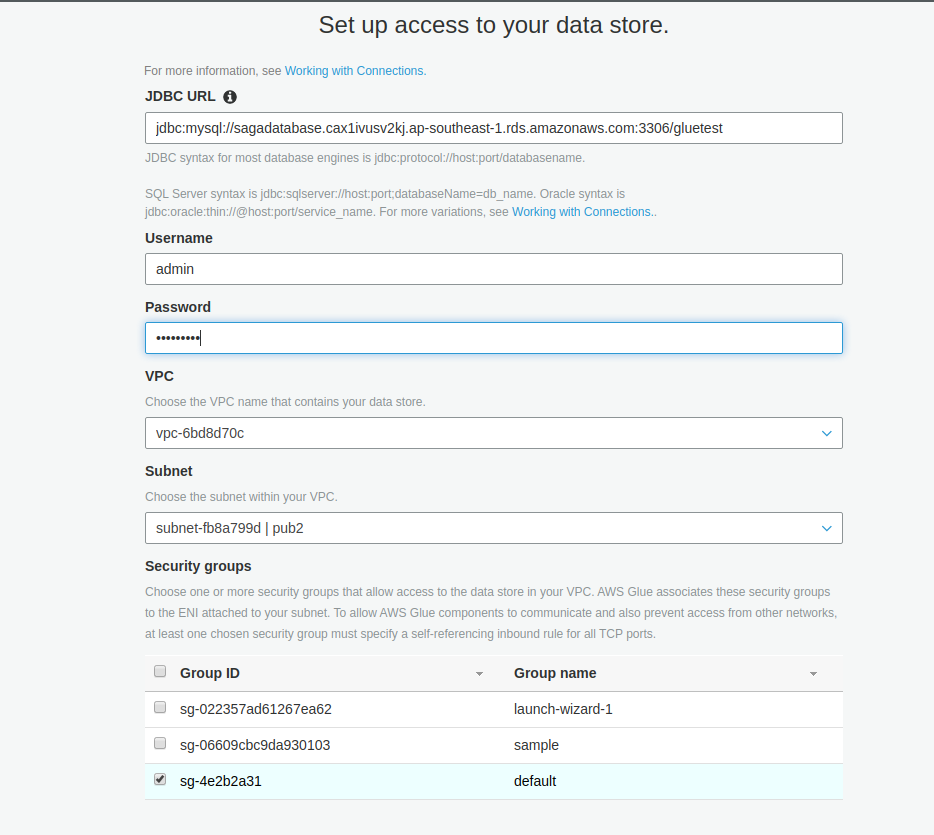
Review and finish the setup.
Similarly, add in the connection details for Redshift into Glue using a similar approach.
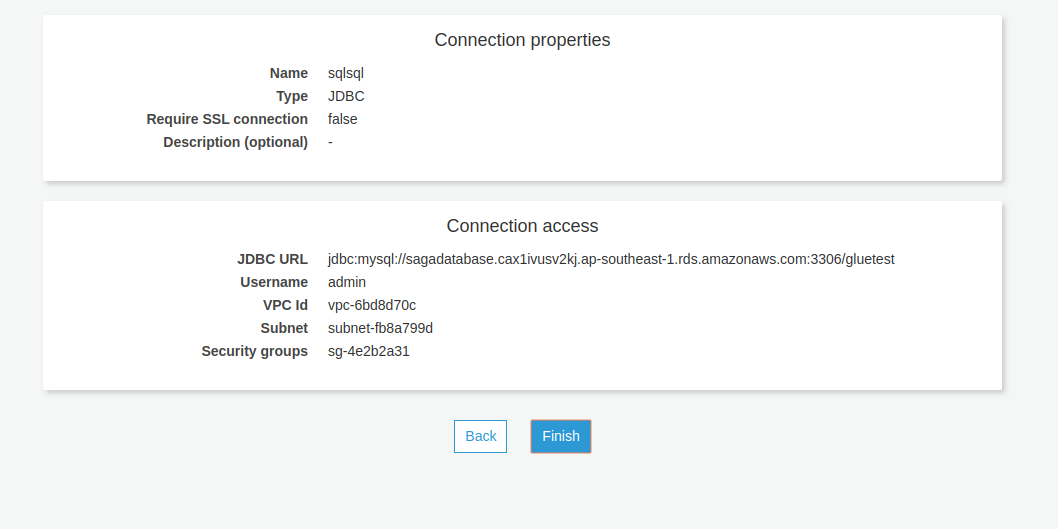
After a successful connection, make a test connection using the IAM role that you have already created.
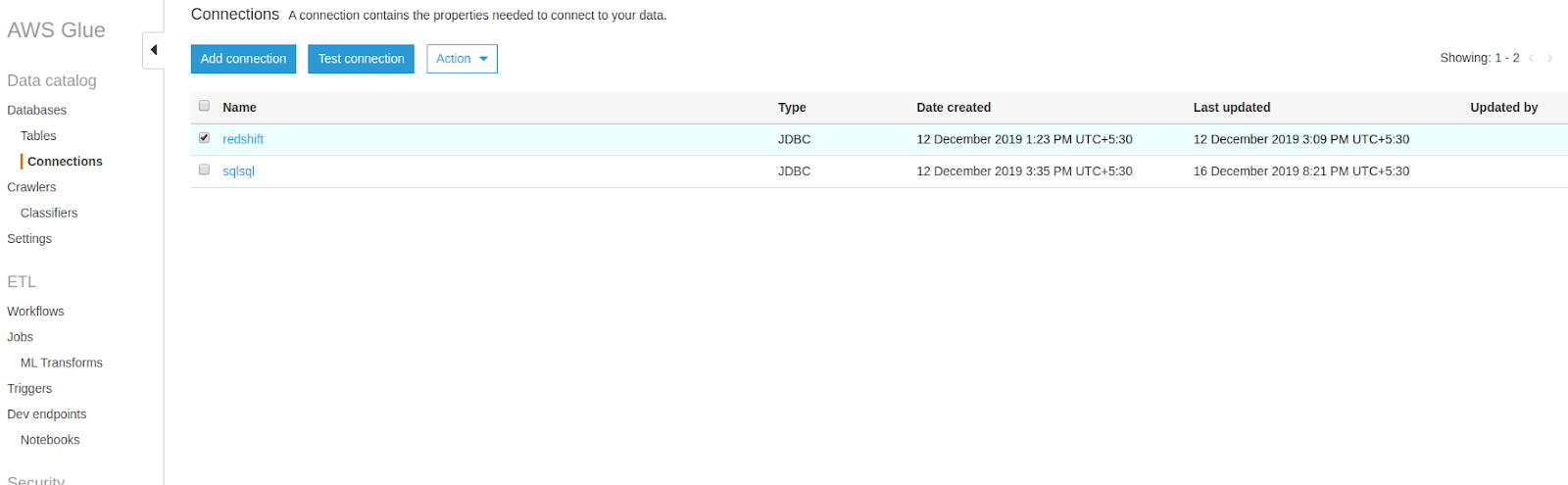
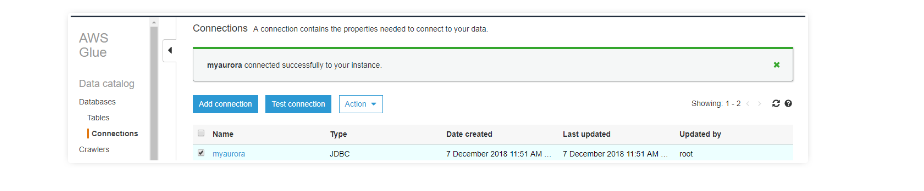
Note: While creating connection details for RDS you may get a "found error for connection" message. Use this link to clear your connection errors.
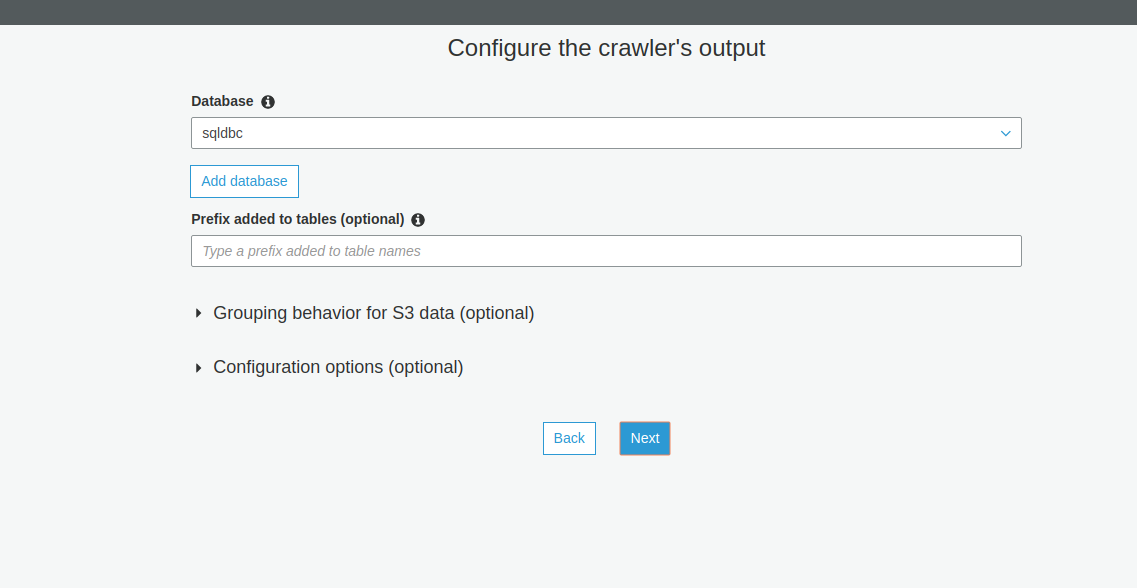
Once your connection details are created, create a data catalog (crawlers) for Redshift MySQL, MS SQL, MariaDB, Aurora, PostgreSQL, and OracleDB. Any database type.
Here "include path" indicates the database name of your RDS DB.
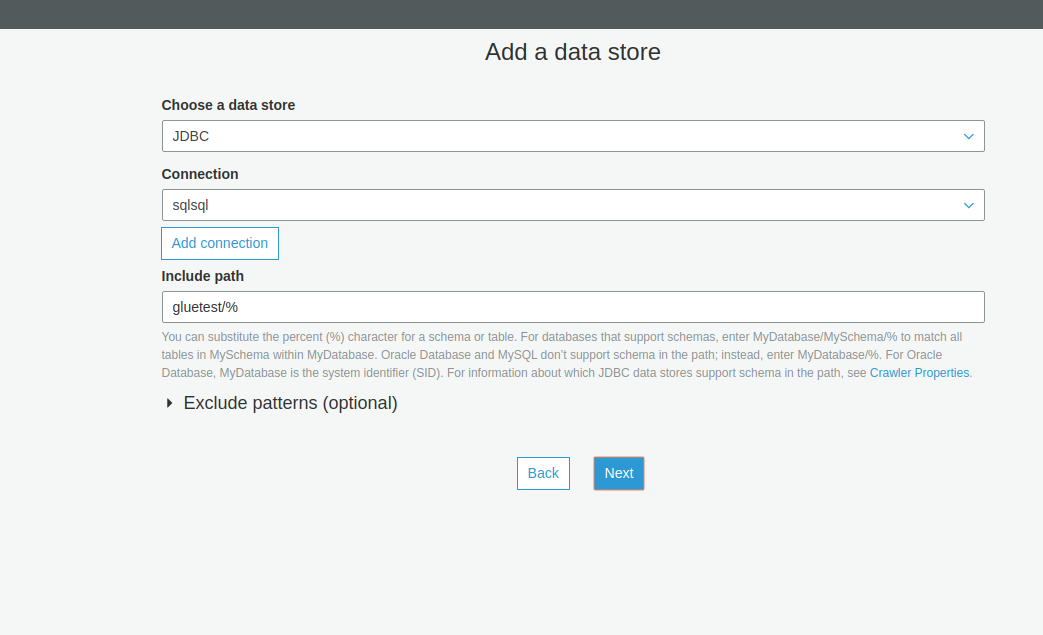
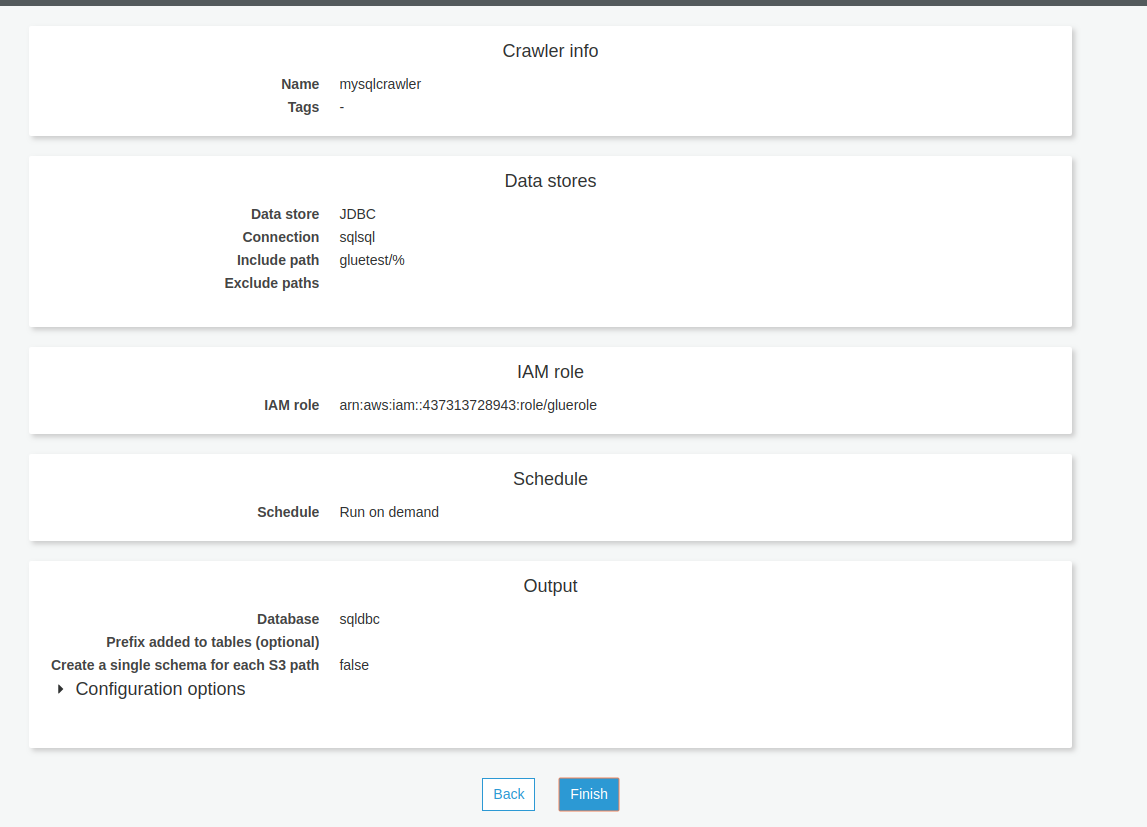
Review and finish the details. Once the crawler is configured, the output will look as per the image below.
Similarly, create a data catalog (crawler) for Redshift.
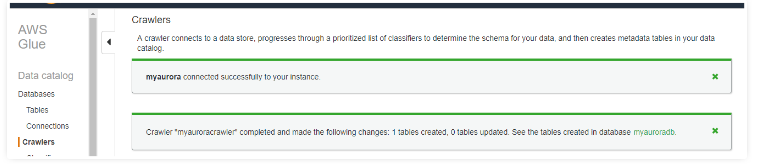
Once both the data catalog and data connections are ready, run the crawlers for RDS and Redshift to visualize the database tables in the table dashboard.
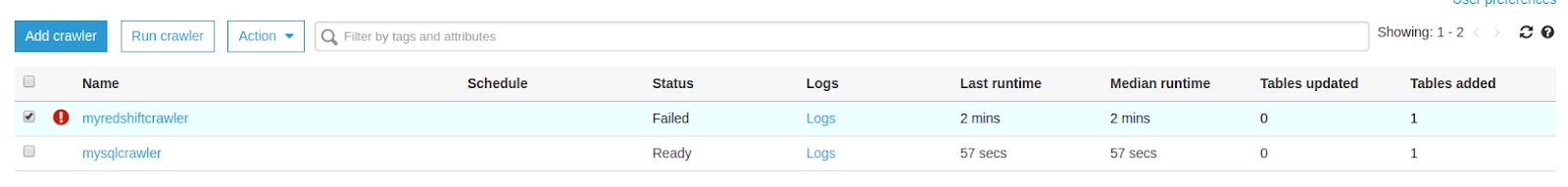
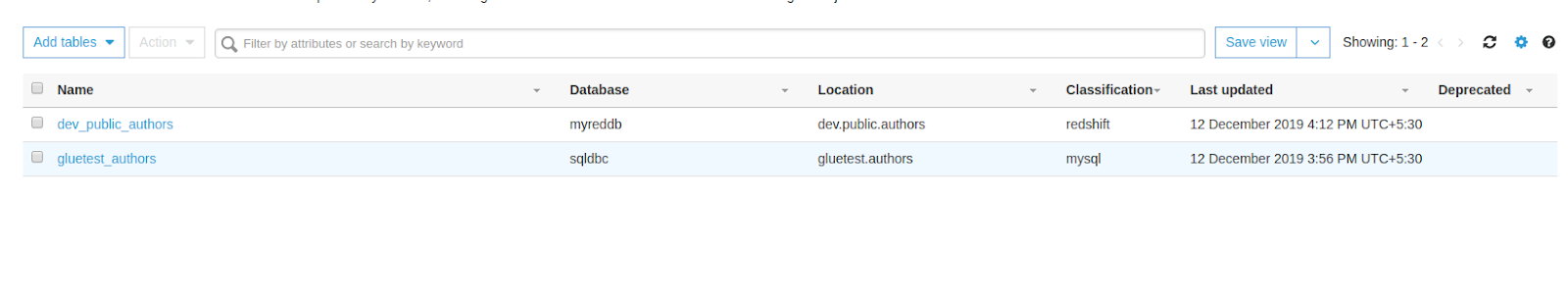
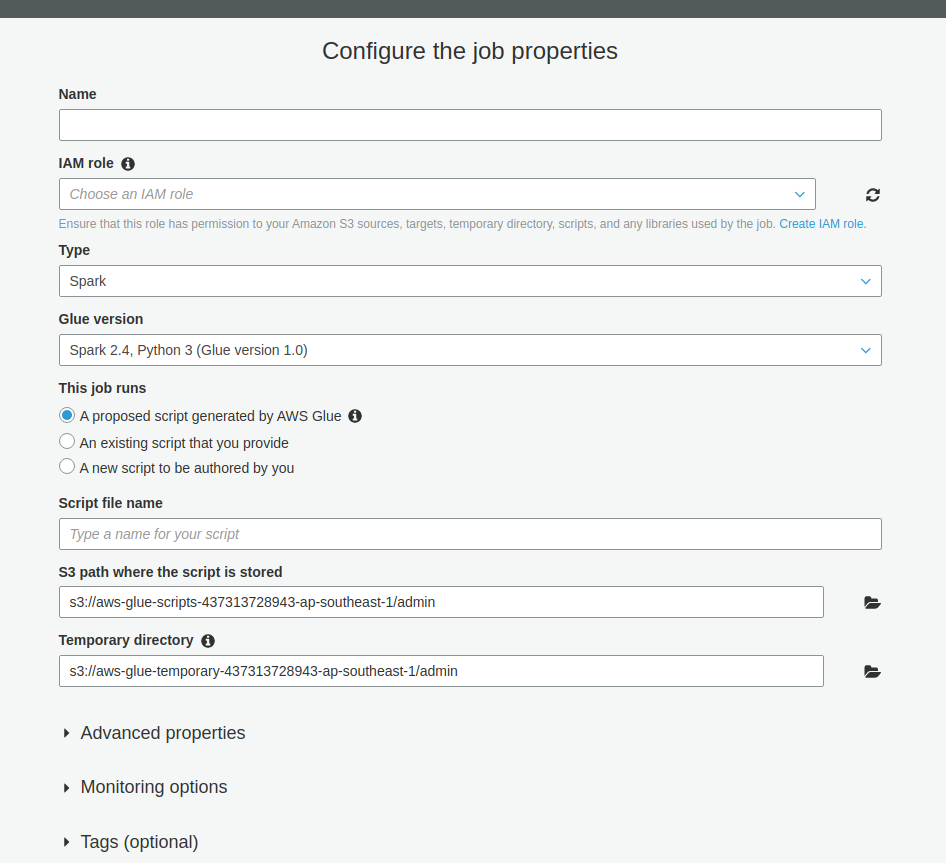
Upon successful implementation of the data catalog (crawlers), data connections, and tables, you can now start creating a job to export all your data from your RDS DB to Redshift. Simply specify the job name and role in AWS Glue and review, finish, and run it.
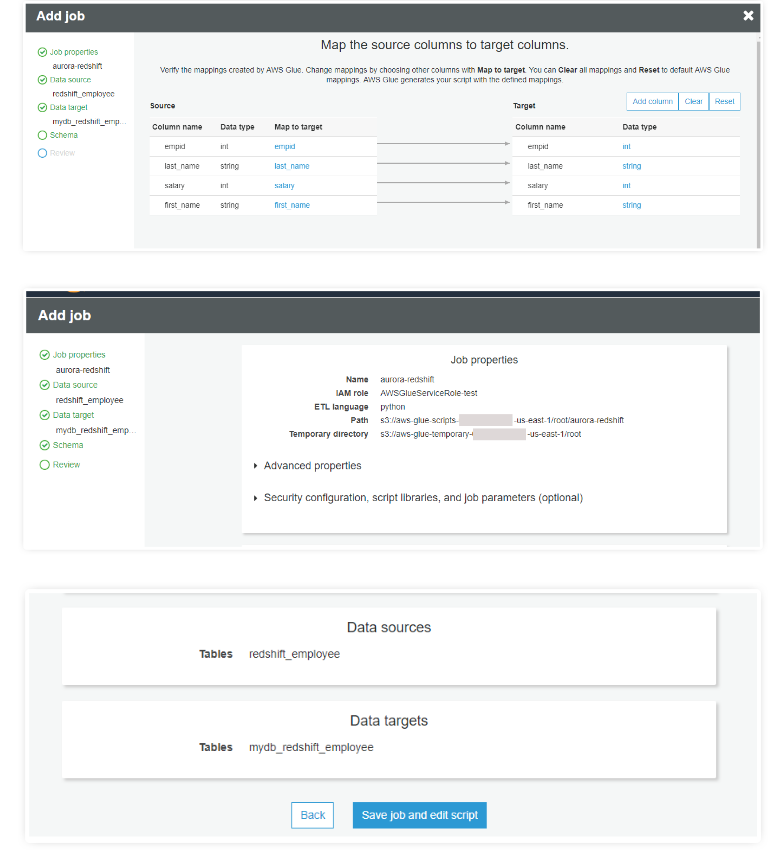
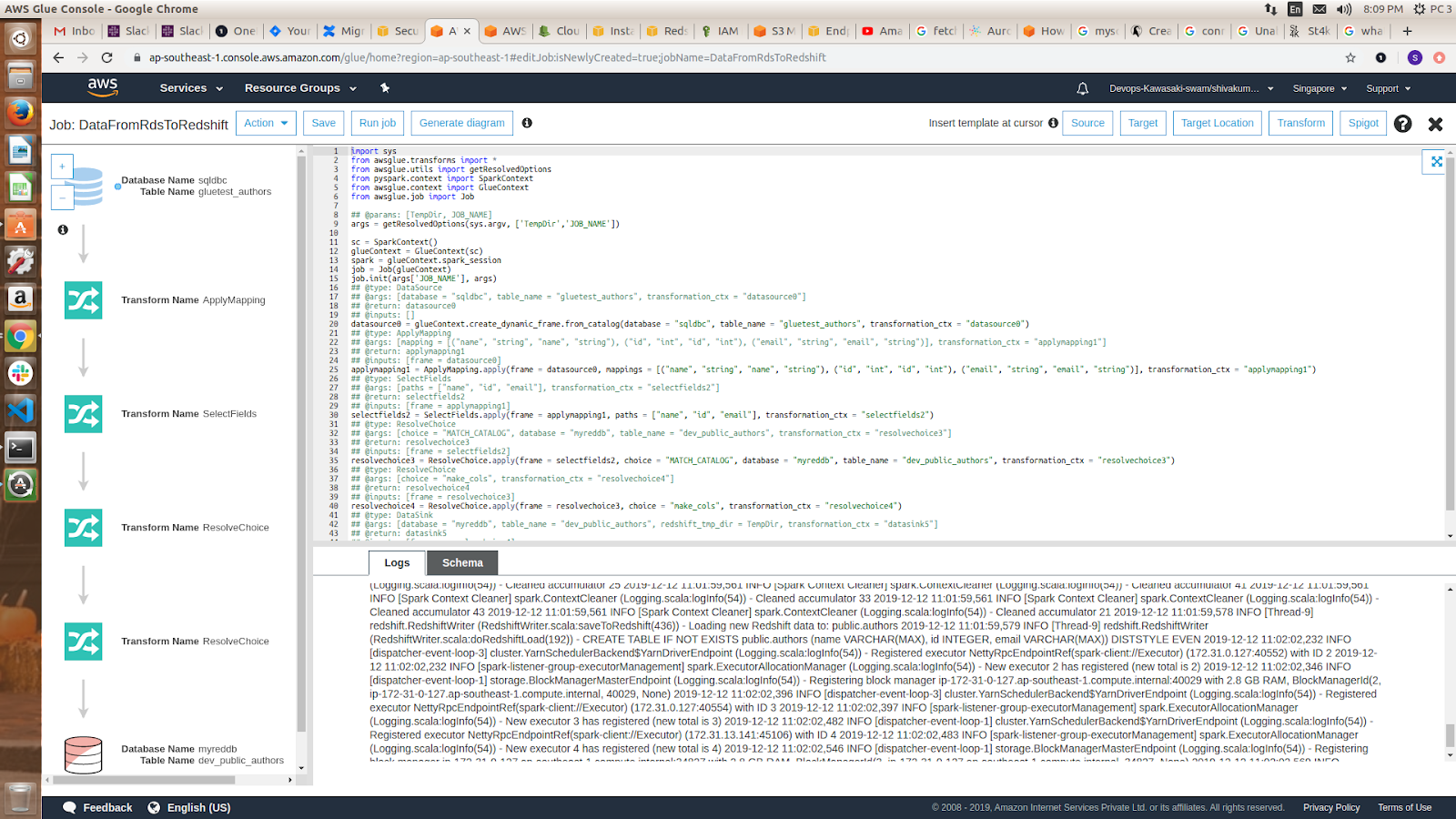
Once the mapping is completed, it generates the following code and diagram. Once the execution is completed, you can view the output log. Now, check the data in Redshift.
Benefits Of Using Glue For The Migration
There are a lot of benefits to be gained from using Redshift. The scalable nature of the data warehouse platform is a clear advantage if you want to start collecting large sums of data for business purposes. In this part, however, we need to acknowledge the benefits of using AWS Glue for the migration.
AWS Glue allows large data migrations to be treated as a simple task. There is no need to spend a fortune on data transfers or worry about the long migration process. Everything happens almost immediately, and you have complete control over the process.
If you need the prowess of Redshift to manage petabytes of data, now is the perfect time to start using the service. Migrate your data by following the steps we discussed in this article and you can run fast, detailed queries on Redshift immediately.
This post was originally published here.
Published at DZone with permission of Shivakumar Anugandula. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments