Traceroute Command in Python and How to Read a Traceroute
Traceroute or tracert command traces the hops between the origin and destination. In this post, we'll learn traceroute and how it helps in network troubleshooting.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeOn operating systems like Windows or Linux, there is an invaluable tool called the traceroute command (on Windows, the equivalent command is called tracert). This command-line tool enables system administrators or network engineers to troubleshoot common networking issues.
Administrators use a traceroute to probe for bottlenecks whenever a user complains that the connection to a website or server is slow. In addition, the traceroute command is used if a server is unreachable, as it will show which particular part of the network route is problematic.
How Does Traceroute Work?
The traceroute command works by sending out network packets to a destination host. Each host also will show their response times.
By analyzing the route, network engineers can determine if the routing is optimal. The response time provides vital clues to pinpoint which hops have latency issues.
To get the usual traceroute result along with geolocation results such as country, region, cities, and much more, the system administrator can use the Python IP2Trace tool. Below is a simple demo of the features that IP2Trace brings.
Installing Python IP2Trace
Let’s get started with the demo. Firstly, you’ll need to install some prerequisites. NOTE: The installation steps below are for the Debian 11 Linux operating system as that’s our demo machine.
Secondly, to install Python and the IP2Trace, run the below commands:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install python3 python3-pip
sudo pip install IP2TraceAfter that, download the IP2Location BIN database files. You can get the IP2Location LITE database and download it for free.
After downloading the zipped file containing the BIN, extract the BIN file out and store it in our recommended folder /usr/share/ip2location. Just create the folder if it doesn’t exist.
A Simple Demo of the IP2Trace Usage Using DB25
It is pretty straightforward to use the IP2Trace command. Below we will query the basic geolocation data from our DB25.BIN file (default folder is the recommended folder above) for the IP address 8.8.8.8.
sudo ip2tracepy 8.8.8.8 -d DB25.BIN See the result below:
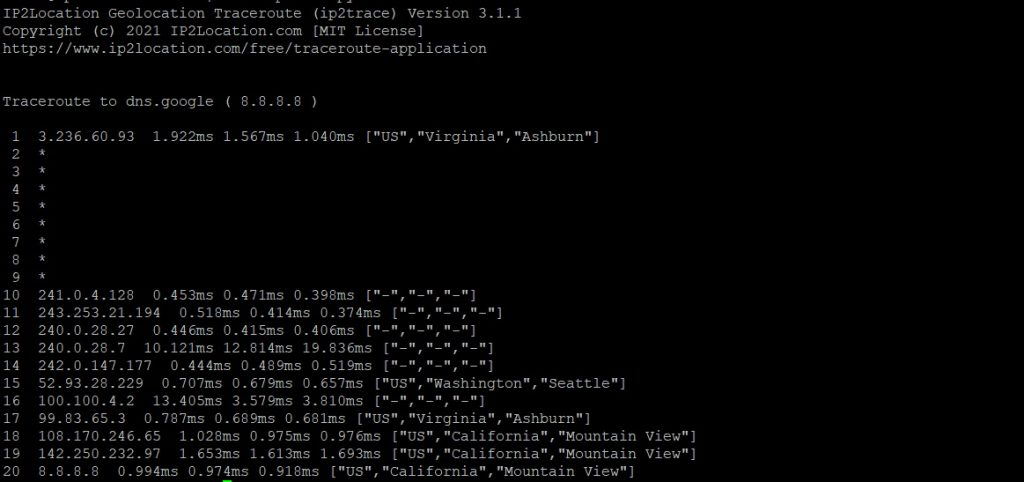
* By default, IP2Trace returns the country code, region, and city when data is available.
Each line is a host or hops along the route to the final destination server. Pay close attention to the 3 numbers after the IP address. These are the response time for each of the 3 packets that were sent out.
As we’re using the DB25 database, let’s modify the command above to output more fields from the BIN file. We want to display the country code, country name, region name, city name, ISP name, network speed, and usage type. Analyzing these data helps to provide further insights into the root cause of the issues.
sudo ip2tracepy 8.8.8.8 -d DB25.BIN -o country_code country_name region_name city_name isp net_speed usage_typeSee the result below:
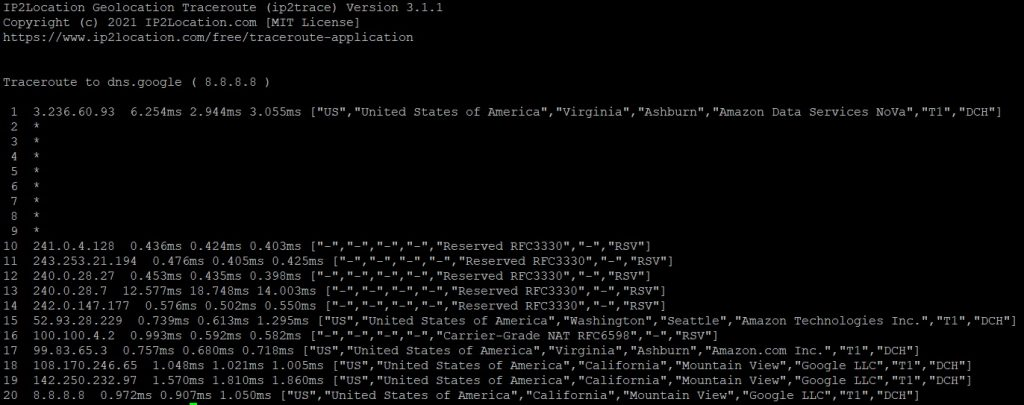
Discover what are the various options supported by the command in IP2Location Traceroute Application. You can use the command below too.
sudo ip2tracepy -h Pros
- IP2Trace improves on the existing traceroute command by adding the geolocation info.
- Geolocation data can make troubleshooting network issues easier.
- It is easier to install the Python IP2Trace compared to the C IP2Trace.
Cons
- Require installation of Python to function.
- Must have experience in running commands in the console.
- Needs regular updates of the BIN file to maintain the accuracy of geolocation.
Conclusion
Traceroute is a command-line tool commonly used by network and system administrators. For instance, system administrators use a traceroute to monitor internet connectivity. It helps to visualize the path traffic, including packet loss and high latency.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments