Top Microservices Frameworks
Choose right framework for microservices architecture.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeMicroservices architecture is a methodology wherein fragment monolithic single application into small applications and services which executes lightweight applications. Business capabilities and independently deployable models are the primary goals for Microservices development. Microservices architecture built using different programming languages and deployed them and connect.
Benefits of Microservices
- Adoption of New technology and process.
- Independent scaling of applications.
- Cloud-ready.
- Seamless integrations.
- Effective Hardware utilization.
- Service level Security.
- API-based functions for reuse effectively.
- Independently Develop and Deploy applications.
Selection Criteria for Framework Selection
The following are some of the critical aspects that can be considered while choosing the proper framework:
- Popularity — Measured by the industry acceptance of the framework based on the number of customers who have made the framework an enterprise standard. The other indicators that could help are the availability of documentation and the number of skilled resources available in the market.
- Maturity of the Community — Reputation of the supporting the framework such as Apache or Google, or Spring. Maturity of the framework in terms of community / commercial support and the frequency of releases to fix issues and add new features.
- Ease of Development — Frameworks selected application development easy and enhances developer productivity. IDEs and tools that support the frameworks also play an essential role in rapid application development.
- Learning Curve — Availability of documentation in the form of tutorials, best practices, and solutions for typical problems play an important role in reducing the learning curve and improving overall developer productivity.
- Architecture Support — Frameworks provide code modules and interfaces with built-in design patterns that remove the coding complexity from application developers.
- Support of Automation — Framework support for automating the tasks related to build and deploy of microservices
- Independent Deployments — Framework has to support dour aspects of independent deployment — upward compatibility, downward compatibility, reusability, and portability
- Continuous Integration — Developers integrate code into a shared repository frequently, preferably several times a day. Each integration can then verified by an automated build and automated tests framework to support.
Different frameworks are available to develop Microservices according to the project requirement. Java, Python, C++, Node JS, and .Net are a few languages for developing microservices. Let us explore the languages and their related frameworks that support microservices development in detail. The below diagram shows different frameworks related to each language popularly used in 2021 and beyond.
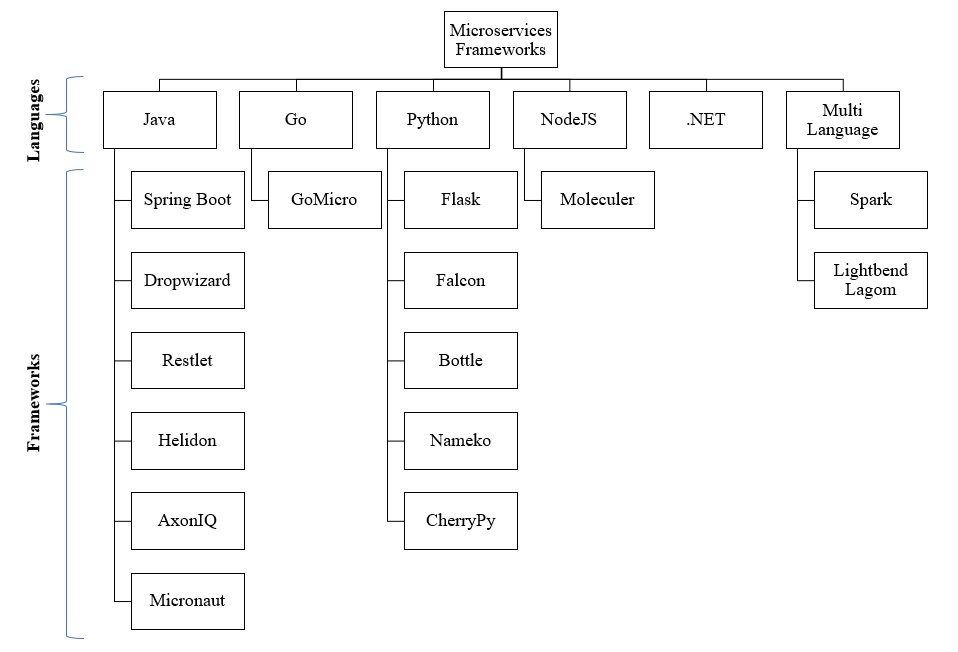
Microservices Frameworks
1. Java
Several Frameworks available for developing Microservices architecture using Java programming language:
- Spring Boot — Spring Boot is a popular Microservice framework in the Java framework. Build small as well as large-scale applications. Spring boot is easy to integrate with another popular framework as well by using Inversion of Control.
- Dropwizard — Dropwizard framework used to develop ops-friendly, high-performance, and Restful web services. Out-of-box support of configuration, application metrics, logging, and operation tools.
- Restlet — Restlet Framework follows the RST architecture style that helps Java developers to build microservices. Adopted and supported by Apache Software License.
- Helidon — Collection of Java libraries for writing microservices. Simple to use with tooling capabilities, micro profile support, reactive web server, and observable and resilient.
- AxonIQ — Event-driven open source microservices framework focuses on Command Query Responsibility Segregation (CQRS), Domain-Driven Design (DDD), and event scoring.
- Micronaut — JVM Based full-stack framework to build modular, easily testable microservice and serverless applications. Build full feature microservices including Dependency Injection, auto-configuration, service discovery, HTTP routing, and HTTP client. Micronaut aims to avoid downsides of frameworks Spring, Spring Boot by providing Faster start time, reduce memory footprint, minimal use of reflection, and calm unit testing.
- Lagom — Open source reactive microservices framework for Java or Scala. Lagom builds on Akka and Play.
2. GoLang
Several Frameworks available for developing Microservices architecture using the Go programming language
- GoMicro — RPC pluggable library provides the fundamental building blocks for writing microservices in Go language. Features support API gateway, Interactive CLI, Service Proxy, Templates, and Web Dashboards.
3. Python
Several Frameworks available for developing Microservices architecture using the Phyton programming language:
- Flask — Web Server Gateway Interface (WSGI) Web-based lightweight microservices framework in Phyton. Flask-RESTPlus is an extension for Flask that adds support for quickly building REST APIs.
- Falcon — Web-based API framework for building robust Phyton app backends and microservices. The framework works excellent with both Asynchronous Server Gateway Interface (ASGI), and WSGI
- Bottle - Fast, lightweight, and straightforward WSGI microservice Phyton-based web framework. Distributed single file module and has no dependencies except Python Standard Library.
- Nameko — Nameko framework for building microservices in Phyton with build-in support of RPC over AMQP, Asynchronous events, HTTP GET and POST, and WebSocket RPC.
- CherryPy — CherryPy allows developers to build web applications using object-oriented Python programming.
4. NodeJS
Several Frameworks available for developing Microservices architecture using the NodeJS programming languages
- Molecular — Event-driven microservices architecture built using NodeJS. Built-in service registry and dynamic service discovery, Load-balancing request and events, fault tolerance feature, and built-in caching.
5. .NET
ASP.Net, the framework used for web development and makes it API. Microservices supports built-in features like building and deploying microservices using Docker containers.
6. MultiLanguage
Several Frameworks available for developing Microservices architecture using the multi-languages
- Spark — Creating web-based microservices applications using Kotlin and Java. Expressive and straightforward Java/Kotlin web framework DSL built for rapid development.
Conclusion
Choosing the right microservices frameworks for application development is challenging for enterprises and developer communities for building robust applications quickly and in a cost-efficient manner. The framework choice should be based on industry acceptance, skill availability, community support, learning curve, ease of development, and support for architecture best practices. IT organizations have to understand the pros and cons of their framework selection and ensure that their choice will not impact their future business and operational needs.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments