The Try Block in Rust
I wrote previously about libs for error management in Rust. This week, I want to write about the try block, an experimental feature.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeI wrote previously about libs for error management in Rust. This week, I want to write about the try block, an experimental feature.
The Limit of The ? Operator
Please check the above article for a complete refresher on error management in general and the ? operator in particular. In short, ? allows to hook into a function call that returns a Result:
- If the
Resultcontains a value, it continues normally - If it contains an error, it short-circuits and returns the
Resultto the calling function.
fn add(str1: &str, str2: &str) -> Result<i8, ParseIntError> {
Ok(str1.parse::<i8>()? + str2.parse::<i8>()?)
}
fn main() {
print!("{:?}", add("1", "2"));
print!("{:?}", add("1", "a"));
}The output is the following:
Ok(3)
Err(ParseIntError { kind: InvalidDigit })Note that the defining function's signature must return a Result or an Option. The following block doesn't compile:
fn add(str1: &str, str2: &str) -> i8 {
str1.parse::<i8>()? + str2.parse::<i8>()?
}the `?` operator can only be used in a function that returns `Result` or `Option`The Verbose Alternative
We must manually unwrap to return a non-wrapper type, e.g., i8 instead of Option.
fn add(str1: &str, str2: &str) -> i8 {
let int1 = str1.parse::<i8>(); //1
let int2 = str2.parse::<i8>(); //1
if int1.is_err() || int2.is_err() { -1 } //2-3
else { int1.unwrap() + int2.unwrap() } //4
}- Define
Resultvariables - Manually checks if any of the variables contains an error, i.e., the parsing failed
- Return a default value since we cannot get a
Result. In this case, it's not a great idea, but it's for explanation's sake - Unwrap with confidence
The try Block to the Rescue
The sample above works but is quite lengthy. The try block is an experimental approach to make it more elegant. It allows "compacting" all the checks for errors in a single block:
#![feature(try_blocks)] //1
fn add(str1: &str, str2: &str) -> i8 {
let result = try {
let int1 = str1.parse::<i8>();
let int2 = str2.parse::<i8>();
int1.unwrap()? + int2.unwrap()? //2
};
if result.is_err() { -1 } //3
else { result.unwrap() } //4
}- Enable the experimental feature
- Use the
?operator though the defining function doesn't returnResult - Check for errors only once
- Unwrap confidently
Alas, the code doesn't compile:
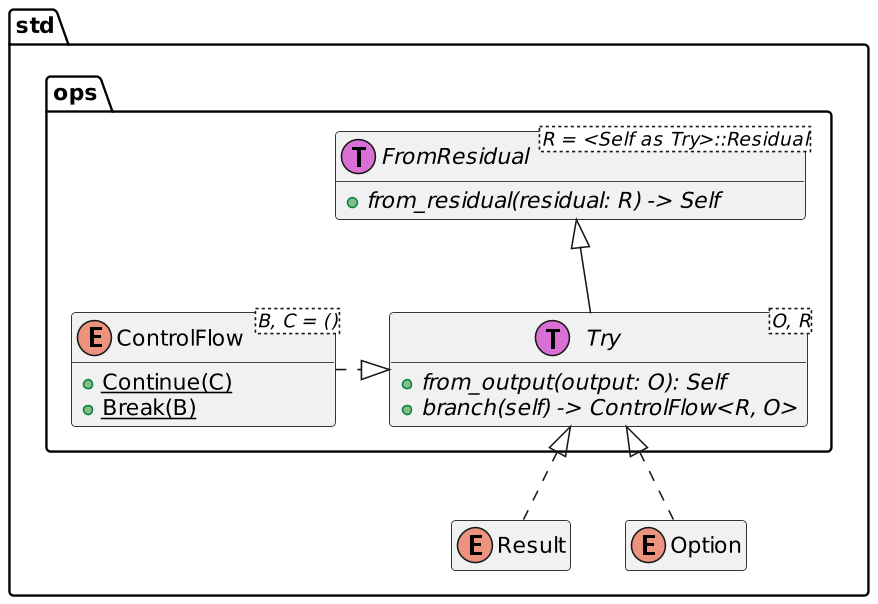
the `?` operator can only be applied to values that implement `Try`i8 doesn't implement Try. Neither i8 nor Try belong to our crate; a custom implementation would require the use of the wrapper-type pattern. Fortunately, a couple of types already implement Try: Result, Option, Poll, and ControlFlow.
fn add(str1: &str, str2: &str) -> i8 {
let result: Result<i8, ParseIntError> = try { //1
str1.parse::<i8>()? + str2.parse::<i8>()? //2
};
if result.is_err() { -1 }
else { result.unwrap() }
}- The compiler cannot infer the type
- Using
?onResultinside thetryblock is now allowed
Conclusion
I learned about the try block in Java over twenty years ago. Java needs it because exceptions are at the root of its error-handling system; Rust doesn't because it uses Functional Programming for its error handling — mainly Result.
The ? operator builds upon the Result type to allow short-circuiting in functions that return Result themselves. If the function doesn't, you need a lot of boilerplate code. The experimental try block relieves some of it.
To Go Further
Published at DZone with permission of Nicolas Fränkel, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments