Step-by-Step Guide on How to Apply Client ID Enforcement Policy in Mule 4
This article demonstrates step by step guide on how to implement Client ID Enforcement Policy in Mule 4.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIn this step-by-step guide, we are demonstrating exact steps of how Client ID Enforcement Policy can be applied in Mule4 using Autodiscovery and API Manager.
Prerequisites
- Must know how to write RAML and publishing it to Exchange
- Must be familiar with Anypoint Studio
- Must be familiar with Anypoint Platform
There are five parts in this tutorial. After completing all of these parts, we will end up having a Client ID Enforcement Policy implemented on the API.
- Designing API Specifications using Design Center
- Application implementation using Anypoint Studio
- Creating an API using API Manager
- Requesting Access to the API using Exchange
- Applying a Policy using API Manager
Details of each part are given below.
Designing API Specifications Using Design Center
Create RAML in Design Center with a single Get resource and a client-id-enforcement trait
Client-id-enforcement trait includes client_id and client_secret to be filled in headers of request.
xxxxxxxxxx
#%RAML 1.0
titleclient-id-enforcement-project
descriptionclient-id-enforcement-project
versionv1
baseUrihttps//localhost/version
protocols HTTP HTTPS
mediaTypeapplication/json
documentation
titleclient-id-enforcement-project documentation
contentsome documentation
traits
client-id-required
headers
client_id
typestring
descriptionClient ID provided by API Manager
requiredtrue
client_secret
typestring
descriptionClient Secret provided by API Manager
requiredtrue
/getCustomer
get
isclient-id-required
description
Get Customer by passing customer_id
queryParameters
customer_id
displayNamecustomer_id
typeinteger
descriptionCustomer ID
example12345
requiredtrue
responses
200
body
application/json
400
body
application/json
500
body
application/json
Publish that RAML in Exchange.
Application Implementation Using Anypoint Studio
Create a project/implementation in Studio by importing the RAML from Exchange.
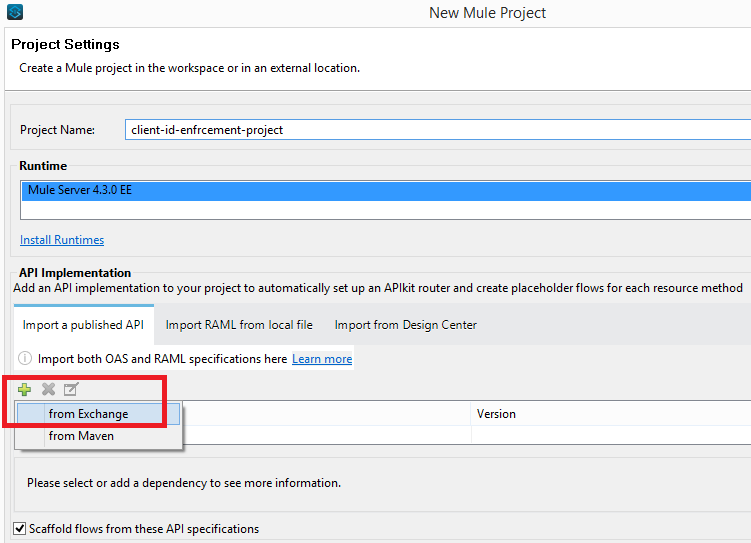
As you have imported the RAML from Exchange, you will see that after creating the project, the API specifications will be added as a zip file in project libraries rather than the API folder in project resources.
If you have imported the RAML from Design Center, you will see that after creating the project, the API specifications will be added inside the api folder in project resources.
Its a best design practice to import the RAML from Exchange rather than Design Center. In this manner, we are enforcing the user to only edit the RAML through Design Center.... it will not make any discrepancy in RAML versions on Studio and Design Center.
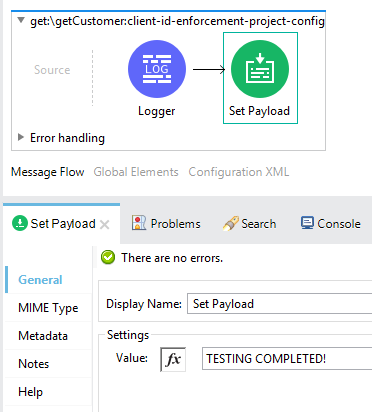
Now we need to implement the flow so that it returns something on Postman.
Execute it on localhost to confirm that we are getting expected outcome on postman if we pass dummy client_id, client_secret in request headers otherwise we get Bad Request.
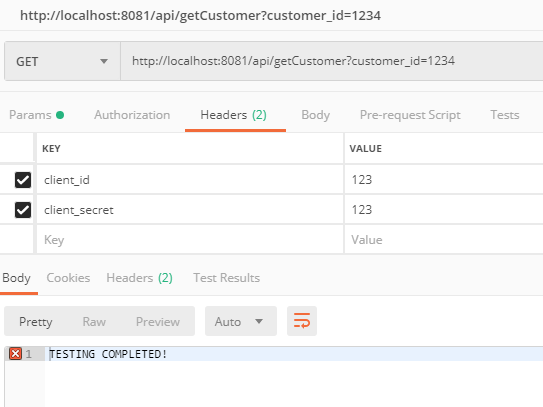
We are getting expected payload when we pass dummy client_id and client_secret.
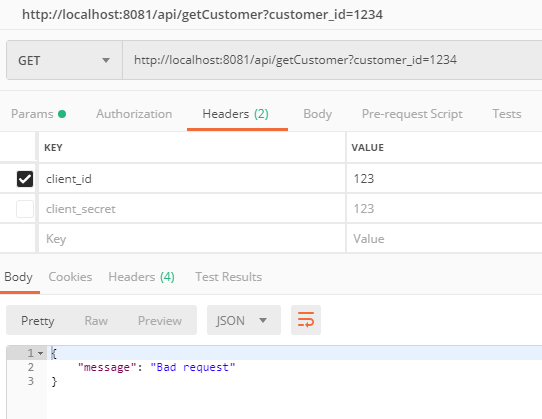 We are getting expected 400 bad request when we don't pass dummy client_id or client_secret
We are getting expected 400 bad request when we don't pass dummy client_id or client_secret
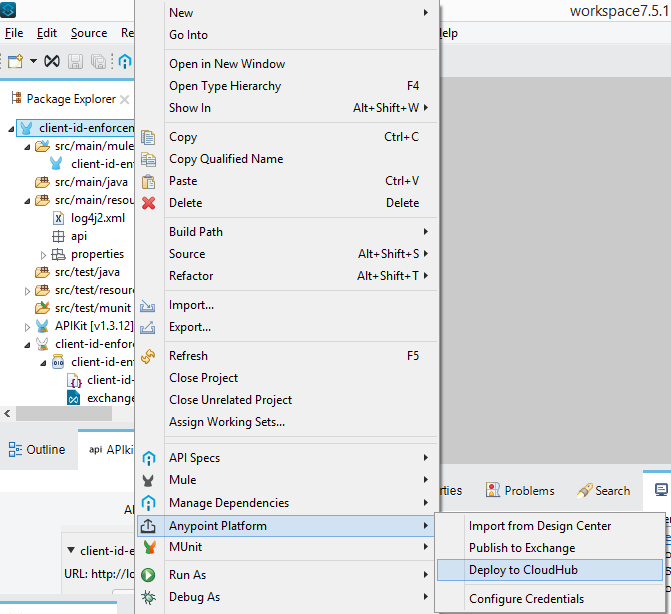
Deploy the project/implementation in Cloudhub by either uploading the exported jar file, or by deploying the project directly from Anypoint Studio.
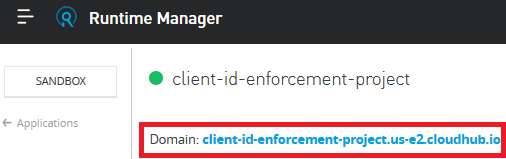
Confirm that the application is now listed under Runtime Manager. Click on it and copy the Domain link as highlighted below.
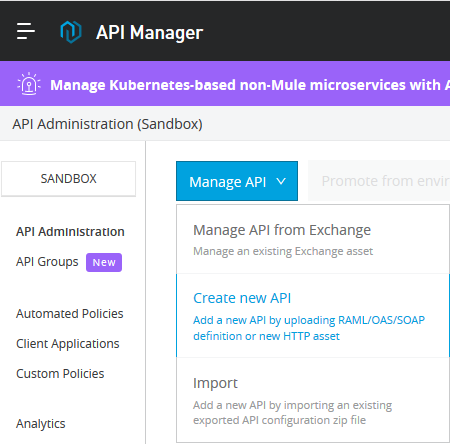
Creating an API Using API Manager
In API Manager, click on Manage API and then click on Create new API.
Provide some name of your choice and select HTTP API in Asset types as follow. Leave the advance settings as it is and click Continue.
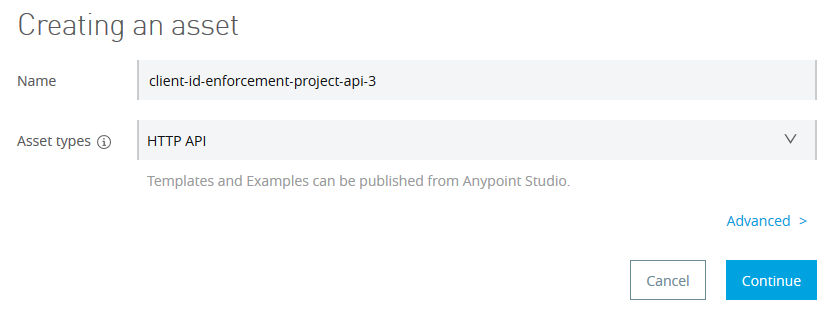
On the next page, select the options as follows and then click Save.
Note: Select Endpoint with Proxy in case you would like to implement the new API as Proxy API.
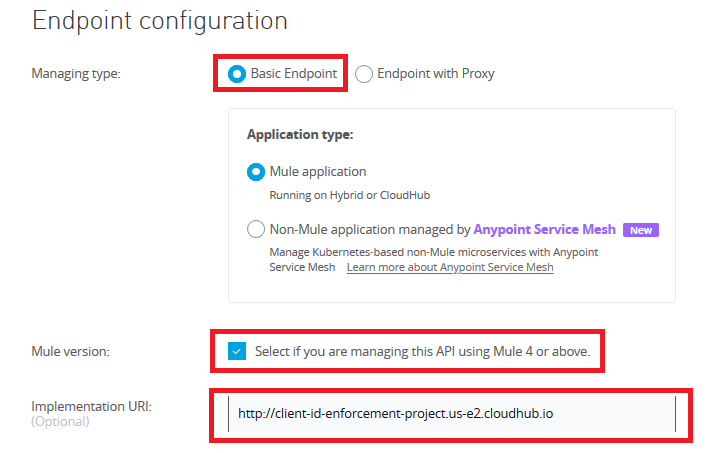
Implementation URL would be the Domain link we have just copied from the above step.
Confirm that the status of the new API that we just have created is 'unregistered' now.
Inside API Manager, click on the API version underneath the API name to open its details and then copy the Autodiscovery API ID.
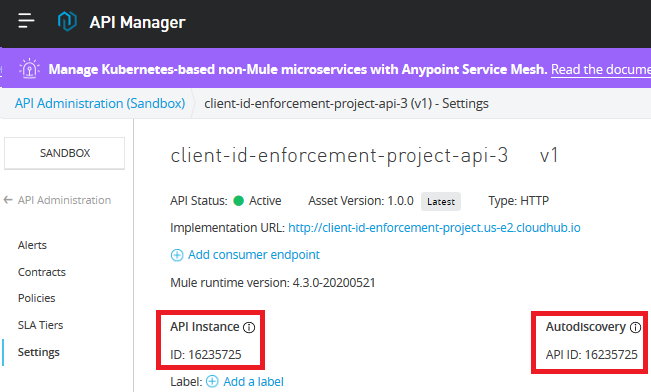
Paste it in the Studio project's properties files with the name api.id.
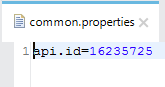
Now refer it in the Autodiscovery config. Also select the main flow in Autodiscovery config.
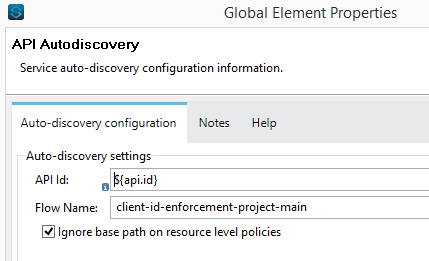
Once again deploy the project/implementation to cloudhub. But this time, we also need to make it sure that either at the time of deployment (i.e. if we are deploying via Anypoint Studio) or after the deployment in application settings (i.e. if we are uploading the jar file to Runtime Manager), we include below-mentioned properties in the properties tab.
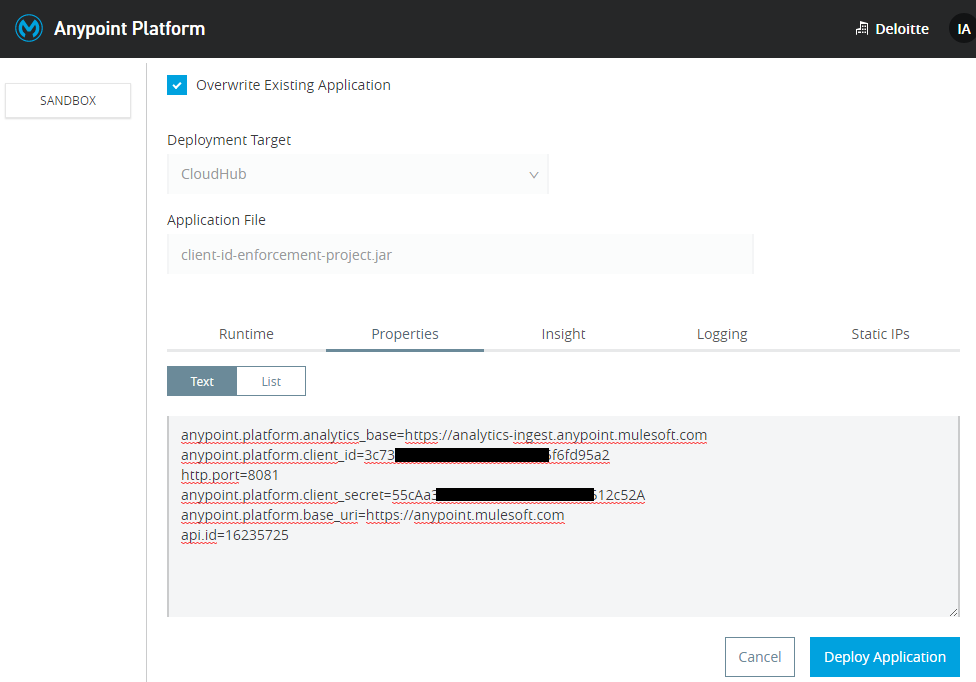
xxxxxxxxxx
anypoint.platform.analytics_base=https://analytics-ingest.anypoint.mulesoft.com
anypoint.platform.client_id=3c73d789c3*************fd95a2
http.port=8081
anypoint.platform.client_secret=55cAa33927************91512c52A
anypoint.platform.base_uri=https://anypoint.mulesoft.com
api.id=16235725
- anypoint.platform.analytics_base is having a hard coded value for analytics
- anypoint.platform.client_id is the client_id of your chosen environment e.g Design, Sandbox, Production where you have deployed the application
- anypoint.platform.client_secret is the client_secret of your chosen environment e.g Design, Sandbox, Production where you have deployed the application
- anypoint.platform.base_uri is having a hard coded value
- api.id is the Autodiscovery ID
- http.port is the port your application is running
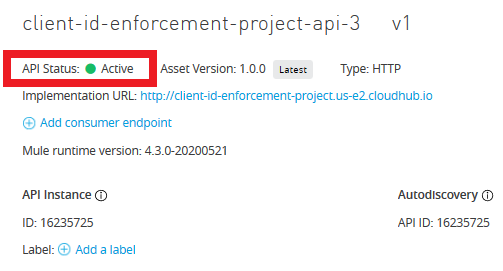
After successful deployment, confirm that the status of the new API is 'Active' now.
Requesting Access to the API Using Exchange
Now it’s time to get the 'client side' client_id and client_secret. For this, we need to create an application that request the access for the API we just have created in API Manager in the above step.
Note: I am saying it application because later on you will see it in the Contracts inside API Manager under the heading 'Applications'.
Click on API Manager, go to the details of the API, and click on 'View API in Exchange'.
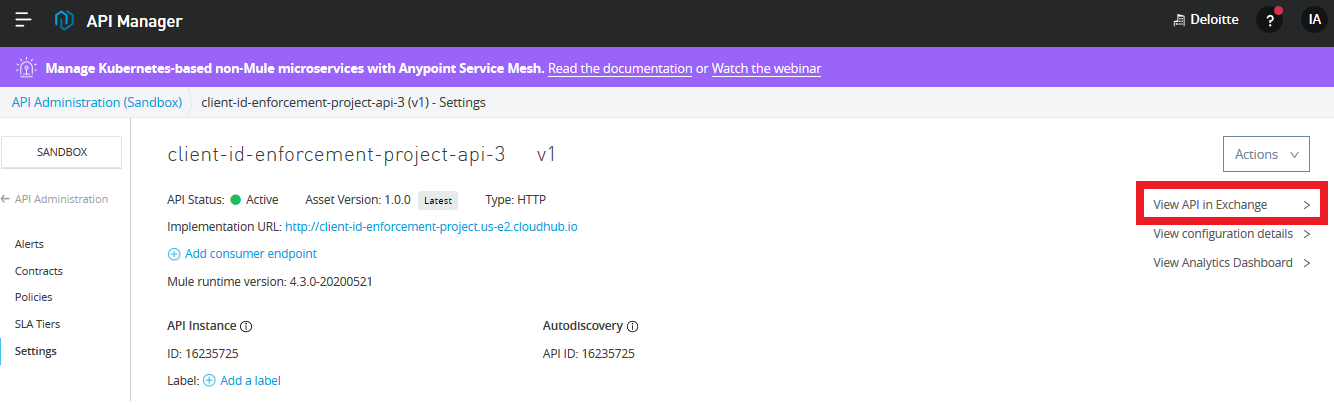
On the top right hand corner, we are having a button 'Request Access'. Click it.
Fill the API Instance name whatever you like
Application drop down should be showing the Autodiscovery API ID for the API we have created above.
Click Request Access to get the access and the next page will show the client_id and client_secret
Now you should see the Client ID and Client Secret on the next page. (This is the client id and client secret you need to pass from client side e.g. postman in request headers as client_id and client_secret)
Confirm that now in Contract under API Manager, we are having a contract application listed. This contract application is the contract with API.
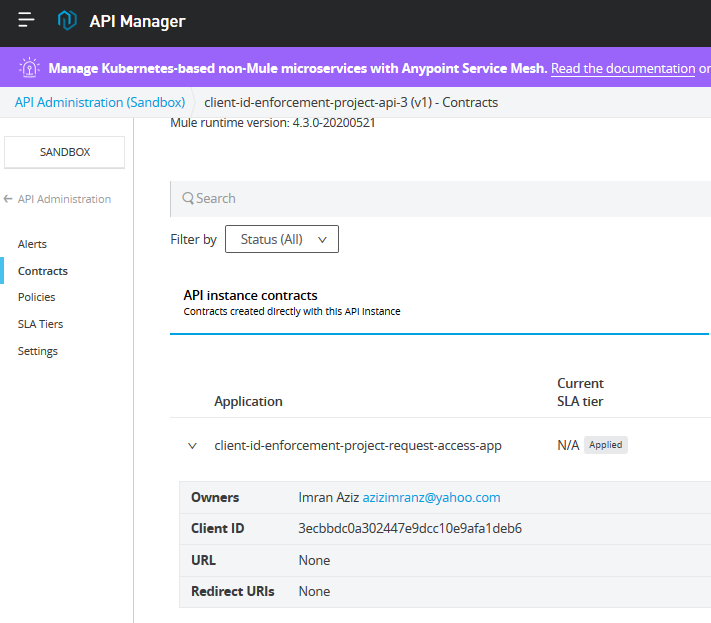
Now we have an Implementation (created in part 2), we have an API (created in part 3), we have the Request Access Application (created in part 4).
Applying a Policy using API Manager
Enforce the policy by clicking the Policies under API Manager.
Click on Client ID Enforcement.
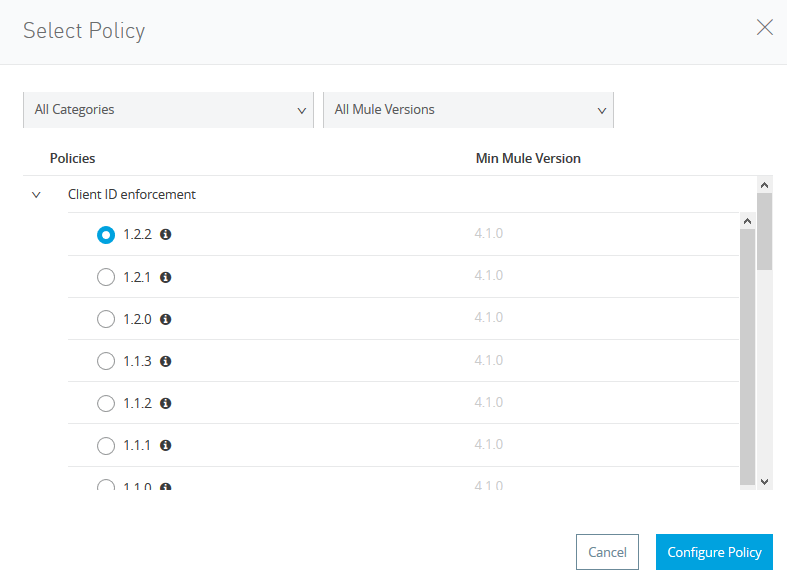
Click on Custom Expression.
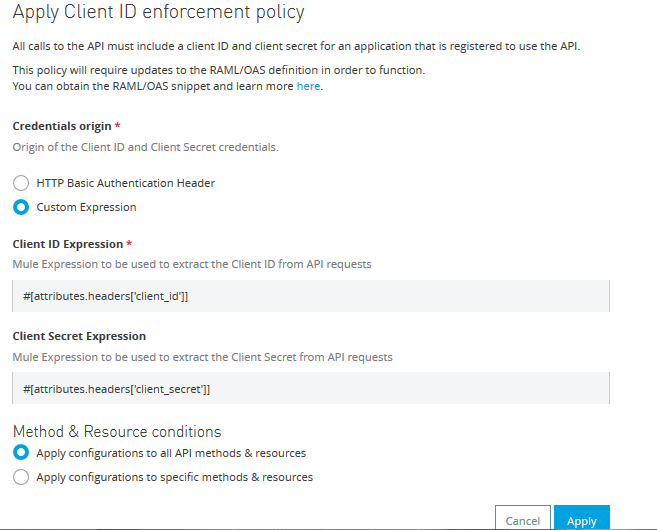
Inside Client ID Expression, fill #[attributes.headers['client_id']] and inside Client Secret Expression, fill #[attributes.headers['client_secret']]
It can be changed depending upon where you want to get the client_id and client_secret from. In this tutorial, we have mentioned to get it from request headers.
Test the client ID enforcement from Postman or SOAPUI after few minutes.
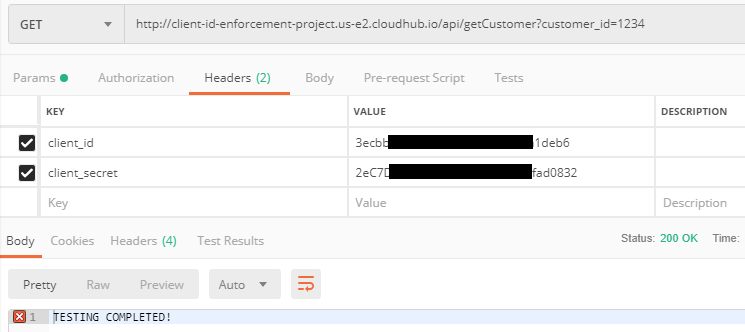
Getting the correct result after passing the correct client_id and client_secret.
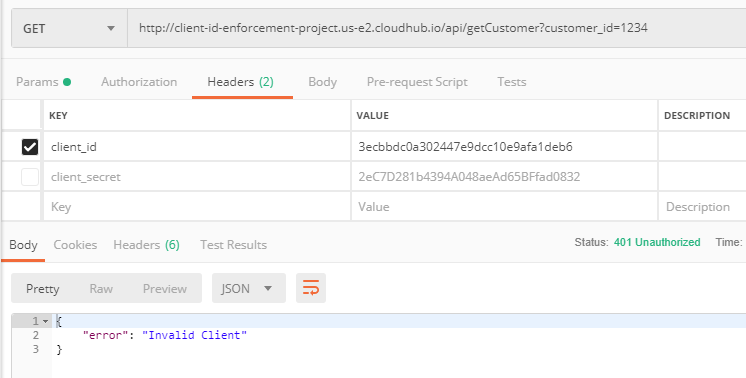
We are getting expected 401 Unauthorized when we don't pass either client_id or client_secret.
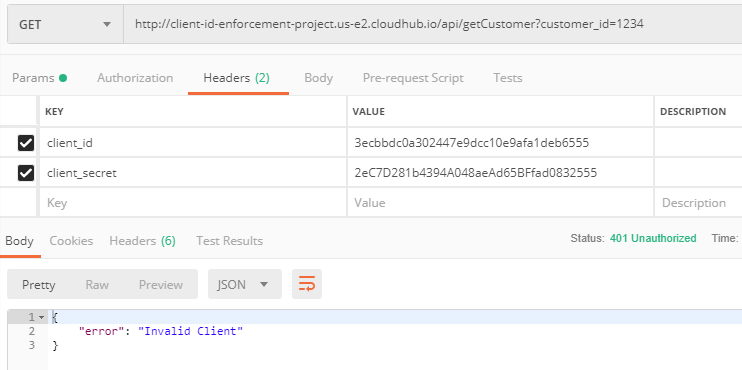
We are again getting expected 401 Unauthorized when we change either client_id or client_secret.
Conclusion
This article demonstrated step by step guide on how to implement Client ID Enforcement Policy in Mule4.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments