Spring Hibernate With EhCache
Learn how to implement EhCache, an open-source caching solution, to boost performance in Spring applications by offloading the database.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For Freeehcache is an open-source, standards-based cache for boosting performance, simplifying scalability, and offloading your database. ehcache is used to improve performance by reducing the load on underlying resources. it can also be used for restful server caching, application persistence, and distributed caching.
in simple words, cache means a store of things that will be required in the future and can be retrieved rapidly.
how much will an application speed up with caching?
it depends on a multitude of factors:
- at what level data present in the cache can and is reused by the application.
- the proportion of response time eased by caching.
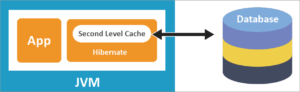
spring contains the cache manager interface org.springframework.cache.cachemanager, so we need to provide a concrete implementation for cache storage.
one of the implementations for caching is ehcache. this project involves ehcache in spring with the hibernate configuration. it follows the modelview controller (mvc) architecture.
first, have a maven project in eclipse using the web app archetype.
project structure

maven dependency
add this maven dependency into your application’s classpath to implement ehcache in your project:
<dependency>
<groupid>org.hibernate</groupid>
<artifactid>hibernate-ehcache</artifactid>
<version>4.3.5.final</version>
</dependency>configuring the cache storage
package com.spring.ehcache.config;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.enablecaching;
import org.springframework.cache.ehcache.ehcachecachemanager;
import org.springframework.cache.ehcache.ehcachemanagerfactorybean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.configuration;
import org.springframework.core.io.classpathresource;
@configuration
@enablecaching /*this annotation registers cacheinterceptor or annotationcacheaspect,
which will detect cache annotations like @cacheable, @cacheput, and @cacheevict.*/
public class ehcacheconfig {
/* it shows cache enabling with ehcache-related beans in a separate configuration class.
* overriding these two beans is not needed if you want to stay with the default definition,
* but we wanted to make cache transactions aware to synchronize put/evict operations with
* ongoing spring-managed transactions.*/
@bean
public ehcachemanagerfactorybean ehcachemanagerfactory() {
ehcachemanagerfactorybean cachemanagerfactorybean = new ehcachemanagerfactorybean();
cachemanagerfactorybean.setconfiglocation(new classpathresource("ehcache.xml"));
cachemanagerfactorybean.setshared(true);
return cachemanagerfactorybean;
}
@bean
public ehcachecachemanager ehcachecachemanager() {
ehcachecachemanager cachemanager = new ehcachecachemanager();
cachemanager.setcachemanager(ehcachemanagerfactory().getobject());
cachemanager.settransactionaware(true);
return cachemanager;
}
}
controller class
package com.spring.ehcache.controller;
import java.util.arraylist;
import java.util.list;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.requestmapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.requestmethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.restcontroller;
import com.spring.ehcache.entity.ehcacheentity;
import com.spring.ehcache.model.ehcachemodel;
import com.spring.ehcache.repository.ehcacherepositoryimpl;
@restcontroller
public class ehcachecontroller {
@autowired
ehcacherepositoryimpl myrepo;
@requestmapping(value = "test", method = {
requestmethod.options,
requestmethod.get
})
public list < ehcachemodel > mymethod() {
list < ehcachemodel > demo = new arraylist < > ();
list < ehcacheentity > mydemoentitylist = myrepo.getentity();
for (ehcacheentity mydemoentity: mydemoentitylist) {
ehcachemodel d = new ehcachemodel();
d.setid(mydemoentity.getuserid());
d.setname(mydemoentity.getname());
demo.add(d);
}
return demo;
}
}dao implementation
package com.spring.ehcache.repository;
import java.util.list;
import org.hibernate.criteria;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.cacheable;
import com.spring.ehcache.entity.ehcacheentity;
public class ehcacherepositoryimpl extends ehcacherepository {
/* @cacheable indicates that the result of invoking a method (or all methods in a class) can be cached.
* each time an advised method is invoked, the caching behavior will be applied,
* checking whether the method was already invoked for the given arguments.*/
@cacheable(value = "ehcache")
public list < ehcacheentity > getentity() {
list < ehcacheentity > mydemoentitylist = null;
criteria cr = currentsession().createcriteria(ehcacheentity.class);
mydemoentitylist = cr.list();
return mydemoentitylist;
}
}
create a
ehcache.xml
file to tell ehcache how and where to cache the data.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!doctype ehcache>
<ehcache>
<diskstore path="java.io.tmpdir"/>
<cache name="ehcache"
maxelementsinmemory="10000" eternal="false" timetoidleseconds="600"
timetoliveseconds="3600" overflowtodisk="true"/>
</ehcache>to get all data, execute these queries in the mysql database:
create schema `ehcaching` ;
create table `ehcaching`.`ehcache` (
`id` int(11) not null,
`name_column` varchar(255) not null,
primary key (`id`));
insert into `ehcaching`.`ehcache` (`id`, `name_column`) values ('1', 'dev');
insert into `ehcaching`.`ehcache` (`id`, `name_column`) values ('2', 'ankit');
insert into `ehcaching`.`ehcache` (`id`, `name_column`) values ('3', 'akshay');
insert into `ehcaching`.`ehcache` (`id`, `name_column`) values ('4', 'rahul');output

you can download the code here .
Published at DZone with permission of Dev Bhatia. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments