Spring Boot With Embedded PostgreSQL for DAO Integration/Unit Testing and Local Development
In this article, we will go through how to use embedded PostgreSQL in your local development environment plus how to use it for DAO integration/unit testing.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIn this article, we will go through how to use embedded PostgreSQL in your local development environment plus how to use it for DAO integration/unit testing. If you have and are using PostgreSQL as your production database, your DAO testing should use the same database as your production one in order to have behavior consistency and the same environment precondition.
We will go through a sample Spring Boot application:
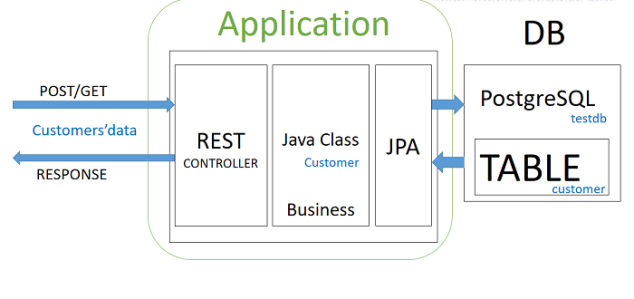
- The Spring Boot application dependencies
- DB configuration with embedded PostgreSQL for development
- Customer CRUD different layers with spring data, mapstruct, and lombok
- DAO unit testing with embedded PostgreSQL with custom data population on start
Spring Boot Dependencies
The main maven application dependencies will the typical Spring Boot dependencies (spring data..ect) plus the embedded PostgreSQL and other needed libraries, I will just highlight the embedded PostgreSQL for DB, mapstruct, and lombok for DTO and Entity mapping and boilerplate code
<dependency>
<groupId>ru.yandex.qatools.embed</groupId>
<artifactId>postgresql-embedded</artifactId>
<version>2.9</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.postgresql</groupId>
<artifactId>postgresql</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mapstruct</groupId>
<artifactId>mapstruct-jdk8</artifactId>
<version>1.2.0.Final</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>DB Configuration With Embedded PostgreSQL for Development
Now, to configure the data source to point to the embedded PostgreSQL run-time instance locally, the spring configuration will be:
/**
* the db spring configuration to use in production , to be replaced with actual production configuration , that is for local run only
*/
@Configuration
@EnableTransactionManagement
public class DbConfig {
private static final List<String> DEFAULT_ADDITIONAL_INIT_DB_PARAMS = Arrays
.asList("--nosync", "--locale=en_US.UTF-8");
/**
* @param config the PostgresConfig configuration which will be used to get the needed host, port..
* @return the created DB datasource
*/
@Bean
@DependsOn("postgresProcess")
public DataSource dataSource(PostgresConfig config) {
DriverManagerDataSource ds = new DriverManagerDataSource();
ds.setDriverClassName("org.postgresql.Driver");
ds.setUrl(format("jdbc:postgresql://%s:%s/%s", config.net().host(), config.net().port(), config.storage().dbName()));
ds.setUsername(config.credentials().username());
ds.setPassword(config.credentials().password());
return ds;
}
/**
* @return PostgresConfig that contains embedded db configuration like user name , password
* @throws IOException
*/
@Bean
public PostgresConfig postgresConfig() throws IOException {
// make it readable from configuration source file or system , it is hard coded here for explanation purpose only
final PostgresConfig postgresConfig = new PostgresConfig(Version.V9_6_8,
new AbstractPostgresConfig.Net("localhost", Network.getFreeServerPort()),
new AbstractPostgresConfig.Storage("test"),
new AbstractPostgresConfig.Timeout(),
new AbstractPostgresConfig.Credentials("user", "pass")
);
postgresConfig.getAdditionalInitDbParams().addAll(DEFAULT_ADDITIONAL_INIT_DB_PARAMS);
return postgresConfig;
}
/**
* @param config the PostgresConfig configuration to use to start Postgres db process
* @return PostgresProcess , the started db process
* @throws IOException
*/
@Bean(destroyMethod = "stop")
public PostgresProcess postgresProcess(PostgresConfig config) throws IOException {
PostgresStarter<PostgresExecutable, PostgresProcess> runtime = PostgresStarter.getDefaultInstance();
PostgresExecutable exec = runtime.prepare(config);
PostgresProcess process = exec.start();
return process;
}
}Customer CRUD different layers with spring data, mapstruct, and lombok.
For CUSTOMER CRUD sample, we will have:
- Customer entity
@Entity(name = "customer")
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Builder
public class Customer {
@Id
private long id;
private String name;
private String address;
private boolean isActive;
}- Customer Spring data repository
/**
* main customer repository
*/
@Repository
@Transactional
public interface CustomerRepository extends CrudRepository<Customer, Long> {
Optional<Customer> findCustomerByName(String name);
}- Customer DTO -> Just DTO :)
- Customer Map Struct mapper
@Mapper(componentModel = "spring", unmappedTargetPolicy = ReportingPolicy.IGNORE)
public interface CustomerMapper {
CustomerDto mapCustomerToDto(Customer customer);
Customer mapeDtoToCustomer(CustomerDto customerDto);
}Again, the full project code is on Github
DAO unit testing with embedded PostgreSQL with custom data population on start:
- For the unit test DB config, I intended to make it a little bit detailed as I need to show how you can load only specific entities, DAOs, and Data Repository as unit testing should be scoped and limited to the target DAO layer only and not to load whole application entities and DAOs. From comments and annotations, you will understand how to load specific repositories with their entities only.
@Configuration
@EnableTransactionManagement
@EnableJpaRepositories(basePackageClasses = {CustomerRepository.class})
@Profile("DaoTest")
public class DbConfig {
private static final List<String> DEFAULT_ADDITIONAL_INIT_DB_PARAMS = Arrays
.asList("--nosync", "--locale=en_US.UTF-8");
/**
* @param config the PostgresConfig configuration to use to start Postgres db process
* @return PostgresProcess , the started db process
* @throws IOException
*/
@Bean
@DependsOn("postgresProcess")
public DataSource dataSource(PostgresConfig config) {
DriverManagerDataSource ds = new DriverManagerDataSource();
ds.setDriverClassName("org.postgresql.Driver");
ds.setUrl(format("jdbc:postgresql://%s:%s/%s", config.net().host(), config.net().port(), config.storage().dbName()));
ds.setUsername(config.credentials().username());
ds.setPassword(config.credentials().password());
return ds;
}
/**
* @param dataSource the db data source
* @return the local entity manager factory bean
*/
@Bean
public LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean entityManagerFactory(DataSource dataSource) {
LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean lcemfb = new LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean();
lcemfb.setDataSource(dataSource);
// set the packages to scan , it can be useful if you have big project and you just need to local partial entities for testing
lcemfb.setPackagesToScan("io.romeh.postgresembeddeddaotesting.domain", "io.romeh.postgresembeddeddaotesting.dao");
HibernateJpaVendorAdapter va = new HibernateJpaVendorAdapter();
lcemfb.setJpaVendorAdapter(va);
lcemfb.setJpaProperties(getHibernateProperties());
lcemfb.afterPropertiesSet();
return lcemfb;
}
/**
* @param localContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean
* @return the JPA transaction manager
*/
@Bean
public JpaTransactionManager transactionManager(LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean localContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean) {
JpaTransactionManager transactionManager = new JpaTransactionManager();
transactionManager.setEntityManagerFactory(localContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean.getObject());
return transactionManager;
}
@Bean
public PersistenceExceptionTranslationPostProcessor exceptionTranslation() {
return new PersistenceExceptionTranslationPostProcessor();
}
/**
* @return the hibernate properties
*/
private Properties getHibernateProperties() {
Properties ps = new Properties();
ps.put("hibernate.temp.use_jdbc_metadata_defaults", "false");
ps.put("hibernate.dialect", "org.hibernate.dialect.PostgreSQL95Dialect");
ps.put("hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto", "update");
ps.put("hibernate.connection.characterEncoding", "UTF-8");
ps.put("hibernate.connection.charSet", "UTF-8");
ps.put(AvailableSettings.FORMAT_SQL, "true");
ps.put(AvailableSettings.SHOW_SQL, "true");
return ps;
}
@Bean
public PostgresConfig postgresConfig() throws IOException {
final PostgresConfig postgresConfig = new PostgresConfig(Version.V9_6_8,
new AbstractPostgresConfig.Net("localhost", Network.getFreeServerPort()),
new AbstractPostgresConfig.Storage("test"),
new AbstractPostgresConfig.Timeout(),
new AbstractPostgresConfig.Credentials("user", "pass")
);
postgresConfig.getAdditionalInitDbParams().addAll(DEFAULT_ADDITIONAL_INIT_DB_PARAMS);
return postgresConfig;
}
@Bean(destroyMethod = "stop")
public PostgresProcess postgresProcess(PostgresConfig config) throws IOException {
PostgresStarter<PostgresExecutable, PostgresProcess> runtime = PostgresStarter.getDefaultInstance();
PostgresExecutable exec = runtime.prepare(config);
PostgresProcess process = exec.start();
return process;
}
}- Then finally the Unit test class:
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = {DbConfig.class})
@ActiveProfiles("DaoTest")
@Sql(executionPhase = Sql.ExecutionPhase.BEFORE_TEST_METHOD, scripts = "classpath:dao/TestData.sql")
public class PostgresEmbeddedDaoTestingApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private CustomerRepository customerRepository;
@Test
public void testCustomerSave() {
customerRepository.save(Customer.builder()
.id(new Random().nextLong())
.address("brussels")
.name("TestName")
.build());
Assert.assertTrue(customerRepository.findCustomerByName("TestName") != null);
}
}It shows how to load your test configuration and how to insert some test data before starting the test case using @sql spring JDBC test annotation.
Hopefully this helps you understand how to do DAO unit testing with a custom test-data load and using embedded PostgreSQL. Let me know your thoughts in the comments!
Published at DZone with permission of Mahmoud Romeh, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments