Portfolio Architecture Examples: Application Development Collection
In this latest post about the Red Hat Portfolio Architectures, learn more about the featured collection of application development architectures.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeThis article is a continuation of a series of posts about our project named Portfolio Architectures. An earlier post, Portfolio Architecture Examples: Healthcare Collection, begins with a project overview, introduction, and examples of tooling and workshops available for the project. You may want to refer back to that post to gain insight into the background of Portfolio architecture before reading further.
Application Development Collection
The collection featured today is centered around architectures supporting application development and cloud development. There are currently fifteen architectures in this collection and we'll provide a short overview of each, leaving the in-depth exploration as an exercise for the reader.

In each of these architecture overviews, you'll find a table of contents outlining the technologies used, several example schematic diagrams with descriptions, and a link in the last section to open the diagrams directly into the online tooling in your browser.
Business Optimization
According to Google Arts & Culture, "Retail is the process of selling consumer goods or services to customers through multiple channels of distribution to earn a profit. Retailers satisfy demand identified through a supply chain. The term retailer is typically applied where a service provider fills the small orders of many individuals, who are end-users, rather than large orders of a small number of wholesale, corporate or government clientele."
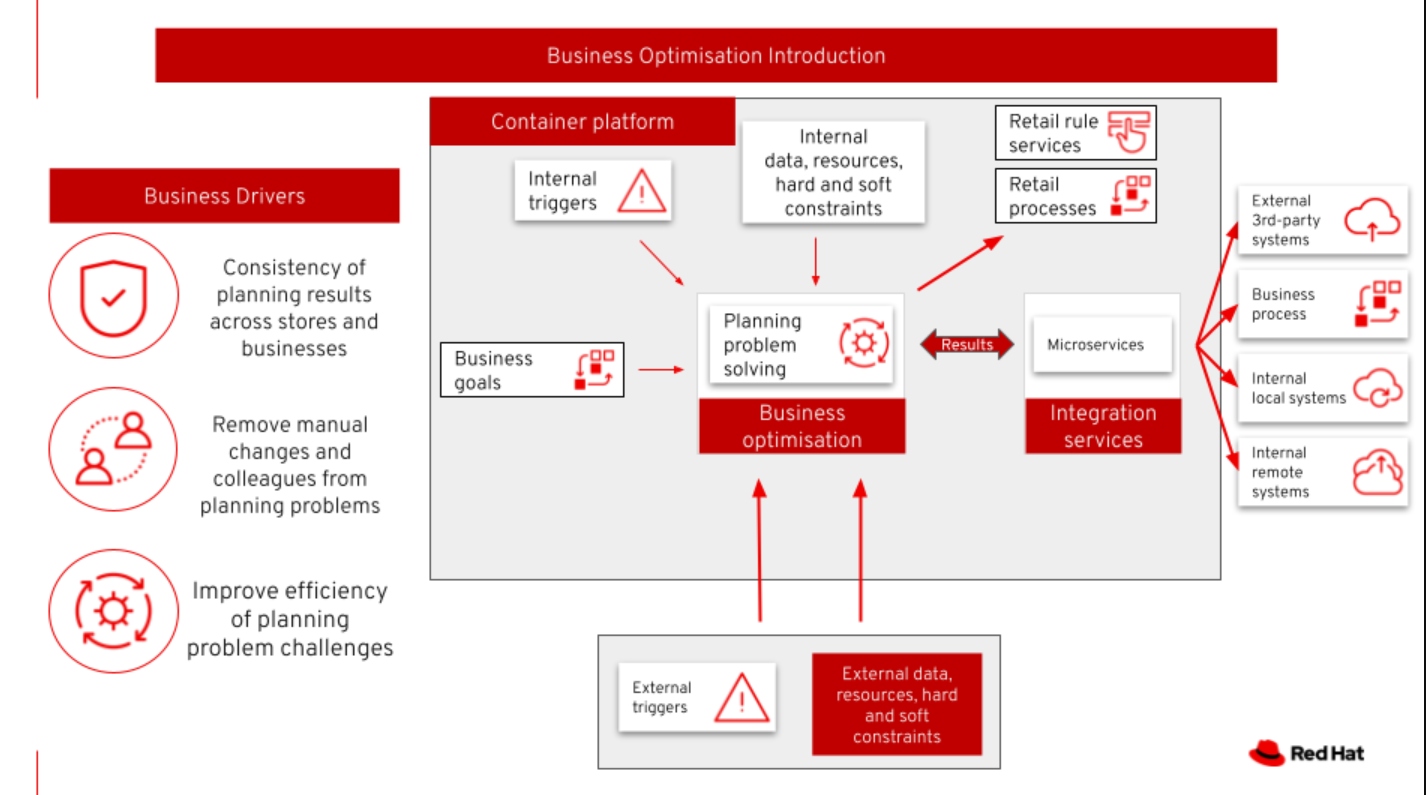
The use case is optimizing delivery routing, automating rostering of staff, and improving the efficiency of tasks across multiple stores.
Cloud-Native Development
Cloud-native development is an approach to building and running applications to fully use the advantages of the cloud computing model (i.e., responsive, elastic, and resilient applications). Red Hat empowers organizations to build and run scalable applications in modern, dynamic environments such as public, private, and hybrid clouds.
Containers and orchestration, DevOps and continuous delivery, microservices and service meshes, and declarative application programming interfaces (APIs) are key building blocks of cloud-native application development. These technologies and techniques deliver loosely coupled systems that are resilient, manageable, and observable. Combined with robust automation, they allow businesses to make high-impact application improvements frequently and predictably with minimal effort and risk. Additionally, cloud-native architecture and technologies provide the foundation for newer development models such as serverless computing and Functions-as-a-Service.

The use case is an approach to building and running applications to fully exploit the advantages of the cloud computing model (i.e. responsive, elastic, and resilient applications).
Designing an Omnichannel Customer Experience
An omnichannel approach provides a unified customer experience across platforms, creating a single view for customers to interact with their own information.
Red Hat provides a foundation for IT teams to develop and deliver omnichannel services through a combination of integration and process automation technologies. Agile integration defines how organizations are transforming and delivering on their digital promise to customers by integrating applications and services across on-premise infrastructure and cloud environments. Business automation, in the form of process integrations, is captured to enable access to complex process services.

The use case for omnichannel implies integration and orchestration of channels such that the experience of engagement across all the channels someone chooses to use.
Edge Medical Diagnosis
This architecture covers edge medical diagnosis in the healthcare industry. It accelerates medical diagnoses using condition detection in medical imagery with AI/ML at medical facilities.
The use case is accelerating medical diagnosis using condition detection in medical imagery with AI/ML at medical facilities.
Headless E-commerce
As stated earlier, retail is the process of selling consumer goods or services to customers through multiple channels of distribution to earn a profit. The term electronic commerce (e-commerce) refers to a business model that allows companies and individuals to buy and sell goods and services over the internet.

The use case is deploying a container-based e-commerce website while moving away from a tightly coupled existing e-commerce platform.
Integrating With SaaS Applications
Integrating with Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) applications is the process of operationally connecting SaaS solutions to other separate computer systems or applications into a single larger system, allowing each solution to functionally work together.
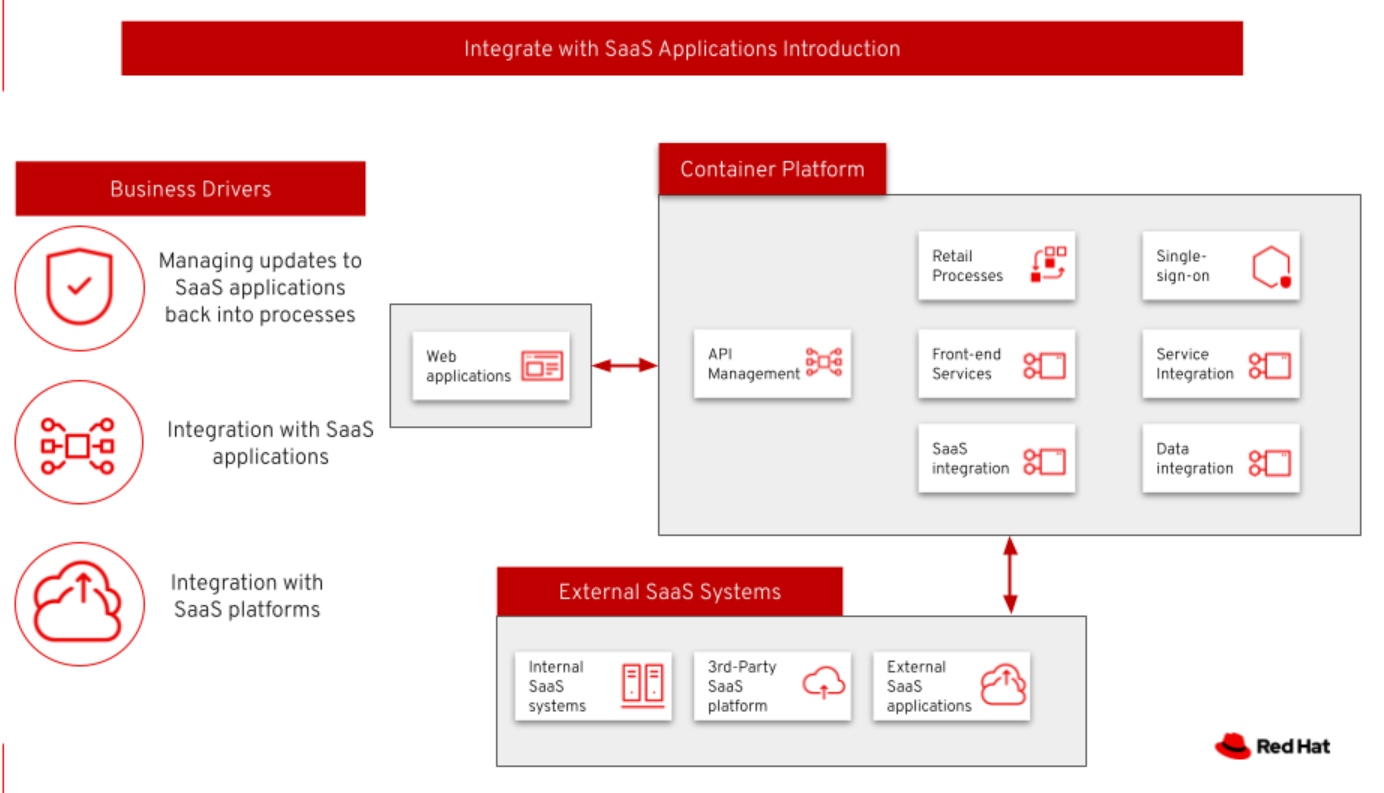
The use case is providing integration with SaaS applications, platforms, and services, and empowers organizations to build and run scalable applications in modern, dynamic environments such as public, private, and hybrid clouds.
Intelligent Data as a Service (iDaaS)
Intelligent DaaS (Data as a Service) is about building and delivery of systems and platforms in a secure and scalable manner while driving data needs for moving towards consumerization in healthcare. Feel free to explore this portfolio architecture here.

The use case is Intelligent Data as a Service (iDaaS) is about building and delivery of systems and platforms in a secure and scalable manner while driving data needs for moving towards consumerization in healthcare.
Modernizing Testing With Data Synthesis
Data synthesis is about enabling innovation with a focus on enabling massive amounts of data to be available for business users' and developers' needs in a secure and scalable manner.

The use case is modernizing testing with data synthesis, a testing innovation with a focus on enabling massive amounts of data to be available for both business users and developers in a secure and scalable manner.
Open Banking
Financial services institutions understand that today’s banking customers expect fast, easy-to-use services they can tap into anytime, anywhere, and are therefore accelerating the adoption of digital technologies to enable a variety of new offerings.
(Note: This project is a new architecture and currently in progress, so sharing one of the schematic architecture diagrams and you can monitor this project for updates as it progresses to completion.)
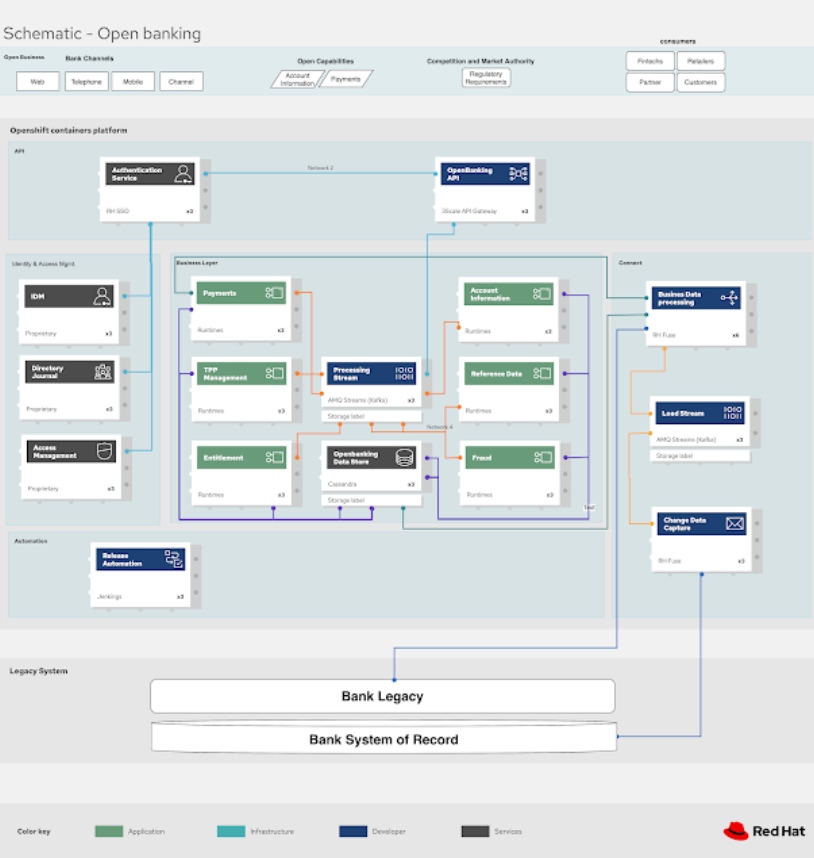
The use case is a cloud-ready, modular open-source approach, offering a wide range of technology options and allowing low-effort integration covering all aspects of an Open Banking implementation.
Payments
An offering of (near) real-time payments lets businesses, consumers, and even governments send and accept funds that provide both availability to the recipient and instant confirmation to the sender. Enabling real-time or at least faster payments that improve the speed of online payment experiences to customers has the potential to give banks a greater opportunity to win, serve, and retain their customers. By building solutions that capture real-time payment business, banks also can drive higher payment volumes, ideally at lower costs as well as engage new customer segments.

The use case examines financial institutions enabling customers with fast, easy to use, and safe payment services available anytime, anywhere.
Point of Sale
A point of sale, or point of purchase, is where you ring up customers. When customers check out online, walk up to your counter, or pick out an item from your stand or booth, they're at the point of sale. Your point of sale system is the hardware and software that enables your business to make those sales.

The use case is simplifying and modernizing central management of distributed point of sale devices with built-in support for container-based applications.
Real-Time Stock Control
Real-time inventory management is an automated process of recording sales and purchases through the use of software. It gives you a complete picture of what's happening with inventory, allowing your business to react quickly to supply chain needs.

The use case is providing (near) real-time stock positions and dynamic pricing promotions information to retailer omnichannels.
Retail Data Framework
A data framework refers to the process of managing enterprise retail data. The framework or system sets the guidelines and rules of engagement for business and management activities, especially those that deal with or result in the creation and manipulation of data.

The use case is creating a framework for access to retail data from customers, stock, stores, and staff across multiple internal teams.
Store Health and Safety
Store health and safety are all about managing risks to protect workers and stores. In a global context, health and safety is also an essential part of the movement toward sustainable operational growth.

The use case is managing effective in-store compliance, health and safety, and employee checks and procedures.
Supply Chain Integration
Supply chain integration is a large-scale business strategy that brings as many links of the chain as possible into a closer working relationship with each other. The goal is to improve response time, production time, and reduce costs and waste.

The use case is streamlining integration between different elements of a retail supply chain for on-premise, cloud, and other third-party interactions.
Additional Portfolio Architecture Solutions
If you are interested in more architecture solutions like these, feel free to export the Portfolio Architecture Examples repository. More architecture collections include:
Published at DZone with permission of Eric D. Schabell, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.


Comments