Mobile Test Automation Using the Robot Framework
Learn about the components of the Robot framework and how it makes mobile test automation easy, including continuous integration and more.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIn the current technological era, it is normal to find 4-5 new Android-based apps uploaded to the Play Store every week. Seeing competitors deliver apps so frequently creates pressure to deliver quality apps in a short span of time. During this limited time, mobile application development and testing of the business' purpose should be achieved. With this pressure, there is a need to automate certain processes which can save time while providing a trusted output.
That being said, mobile test automation can save a lot of time and is always preferred over the entire manual test execution process. With much less effort, the verification of frequent test cases that manual execution requires can be automated, and more effort can be diverted to new features of the application, which are vulnerable and tend to have more defects.
Mobile Automation Strategy
Smartphone applications on Android or iOS are built as either hybrid, native, or as a web app. Regardless of the type of the application under test, the selection strategy for automation framework does not vary to a large extent.
Selecting the Automation Framework
Here, the challenge is to figure out the framework, which is either paid or has the capability to operate and reach every UI part of the application. Also, it should have different libraries that can communicate with the backend blocks of the application under testing, such as databases or web services.
Considering all the available types of applications in the market, the following frameworks are very promising for giving robust outputs:
Test Beds for Test Runs
The other challenge is to decide if the automation should be run on real devices or emulators. There are different third-party software for emulators (Genymotion is a renowned example), which is promising for about 90% of capabilities of the application, excluding some hardware and network-dependent test cases. Choosing a real device depends on the Android version and hardware capabilities the AUT works on.
Robot Framework: Appium Library
Robot framework is an open-source framework which understands text and HTML formatted test case scripts and has a keyword-driven methodology. It is a wrapper that is written over many frameworks with the help of test libraries. These test libraries are selected according to the framework we choose to automate different types of applications.
To drive applications using the Appium framework, the Robot framework's Appium library is preferred. Here most of the capabilities of Appium are framed in form of keywords, which are easily understood by a tester who would want to read the scripts and understand what is exactly being performed in the particular test.
One of the renowned frameworks used for UI based automation for all three types of applications is Appium. To write a robust automation framework using Appium, the Robot framework library for Appium is recommended.
Case Study
I will walk you through a small case study done on a simple native application with at least two test cases automated with a hybrid framework and using the Robot framework with an Appium library and utilities written in Python.
Note: The following ways can also be used with hybrid apps as well as web apps.
Application Under Test (AUT)
Now I am going to take a simple hybrid app, the default email app for the Android platform, involving the following cases:
- Launch Default Email Application and check if launched correctly.
- Switch to correct Inbox correctly
- Verify the Mail is sent properly
Software/Hardware Involved
- Real device or emulator (Genymotion ) (preferably Android 4.2.2 or higher)
- Robot Framework
- Appium library of the Robot framework
- Python 2.7.5 or higher
- Appium 1.2.4.1 or higher
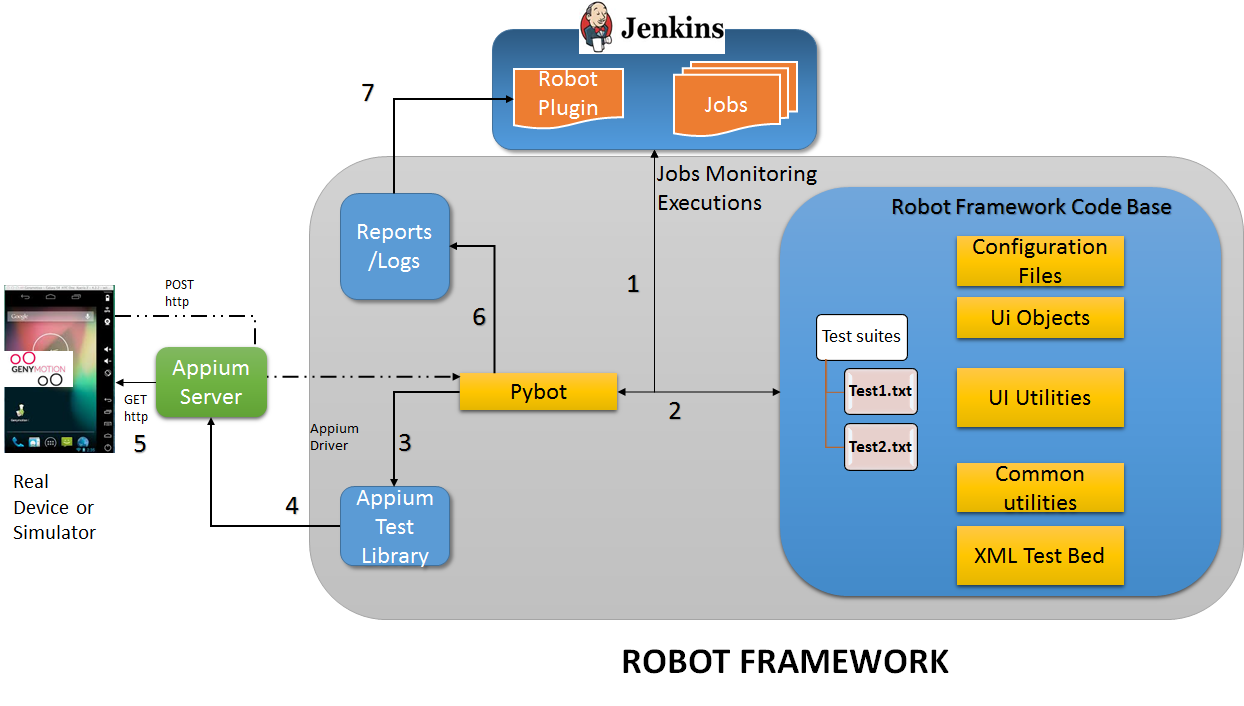
Key Components of the Robot Framework
Jenkins: Continuous Integration
Jenkins is a continuous monitoring tool that takes care of all the activities required to run as part of an end-to-end automation run. In the figure above, the role of Jenkins is to monitor the jobs that have been triggered to run the pybot tests.
Note: The Source Control Repository can also be used as Source for Jenkins Job to fetch the automation code repository.
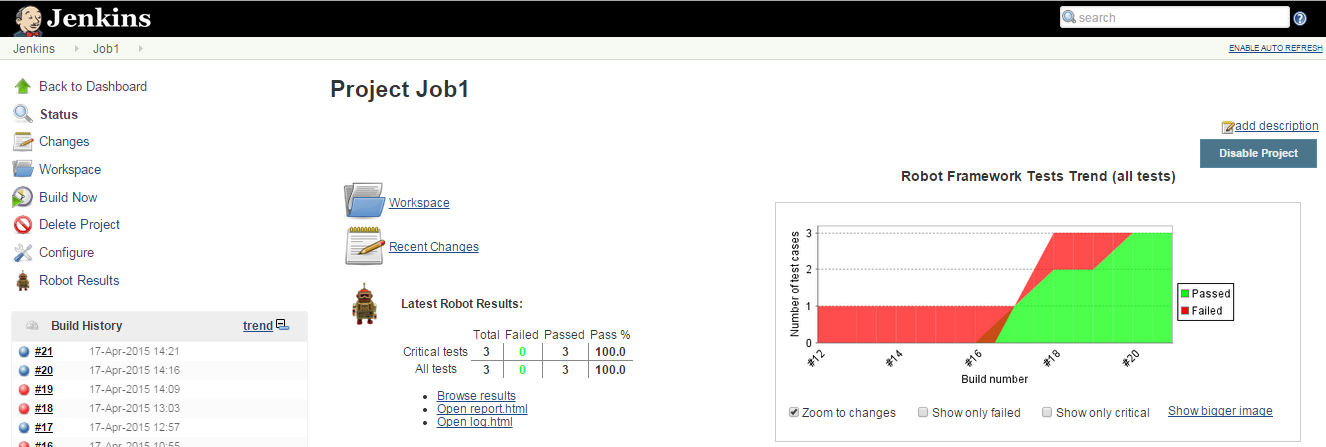
The following image shows one of the Jenkins jobs, which triggers a test script file named Launch_email_app.txt.
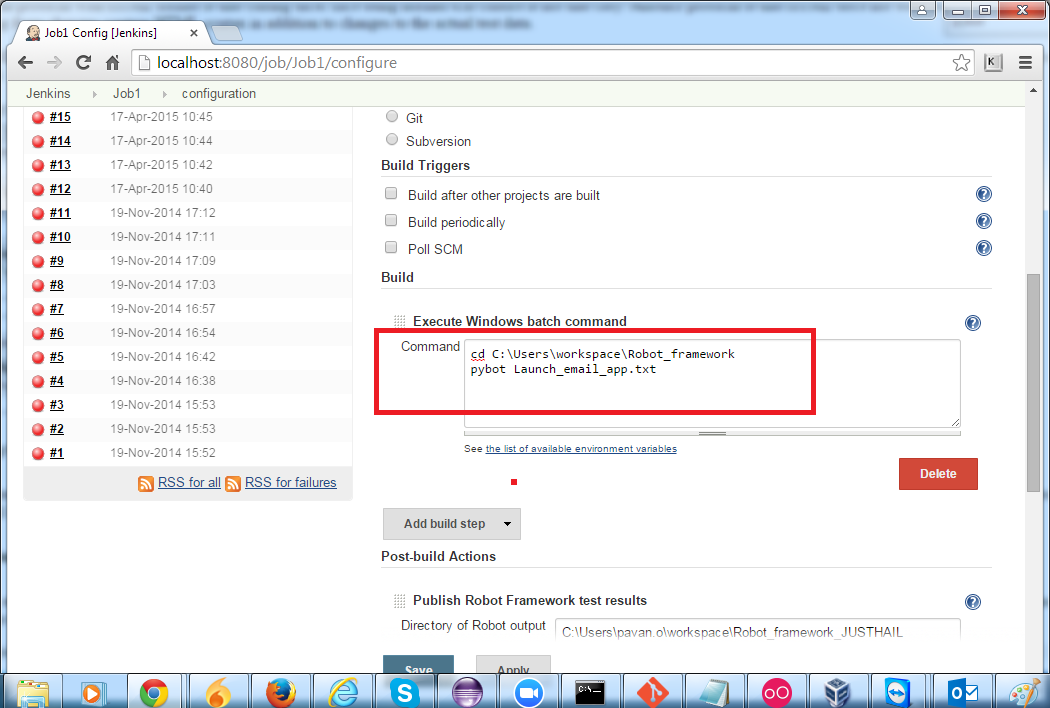
Test Suite: Launch_email_app.txt
This is a test script file which has three test cases under the "Testcase" tag. The labels under this tag are considered test methods by the Robot framework. They are executed in a sequential manner with a top-to-bottom approach.
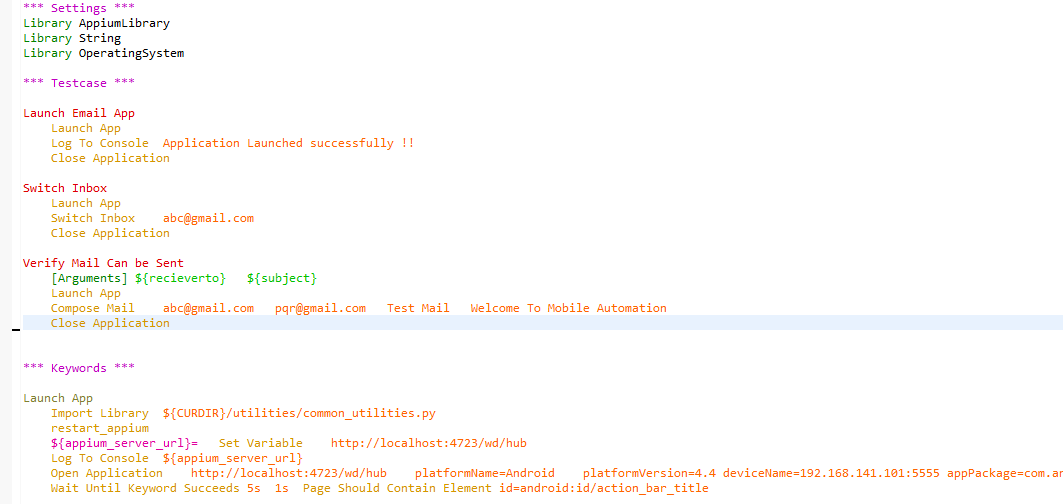
Pybot
This is a Robot framework module used to trigger the test scripts written in the Robot framework format. Here the pybot reads the different framework files and executes the tests by performing different actions on the UI of apps.
Robot Framework Code Base
The folder structure which comprises of all scripts that use Appium libraries to communicate and operate on the UI of the application. It comprises the different external libraries according to the need.
Appium Server
Appium is the open-source engine that runs on Node.js and is an interpreter used to drive Appium library commands to perform actions on the UI of applications. It needs to be up and running during an interaction with the UI of the application. To access the shell capabilities of the virtual device, the <adb> command with different parameters can be useful.
Real Device or Emulators
The automation test scripts that need to be run are mostly executed on virtual devices. The software Genymotion hosts different Android versions devices and runs in a virtual way. If the tests are specific to real devices, then without any changes in a single line of the framework, they can be executed, provided the UI has all the same elements as what is expected in the code.
Reports/Logs
The good part of using the Robot framework is its superior logging and reporting of features in test case executions. The reports are generated in a standard manner, or they can be customized. Please find some stills of these reports below.
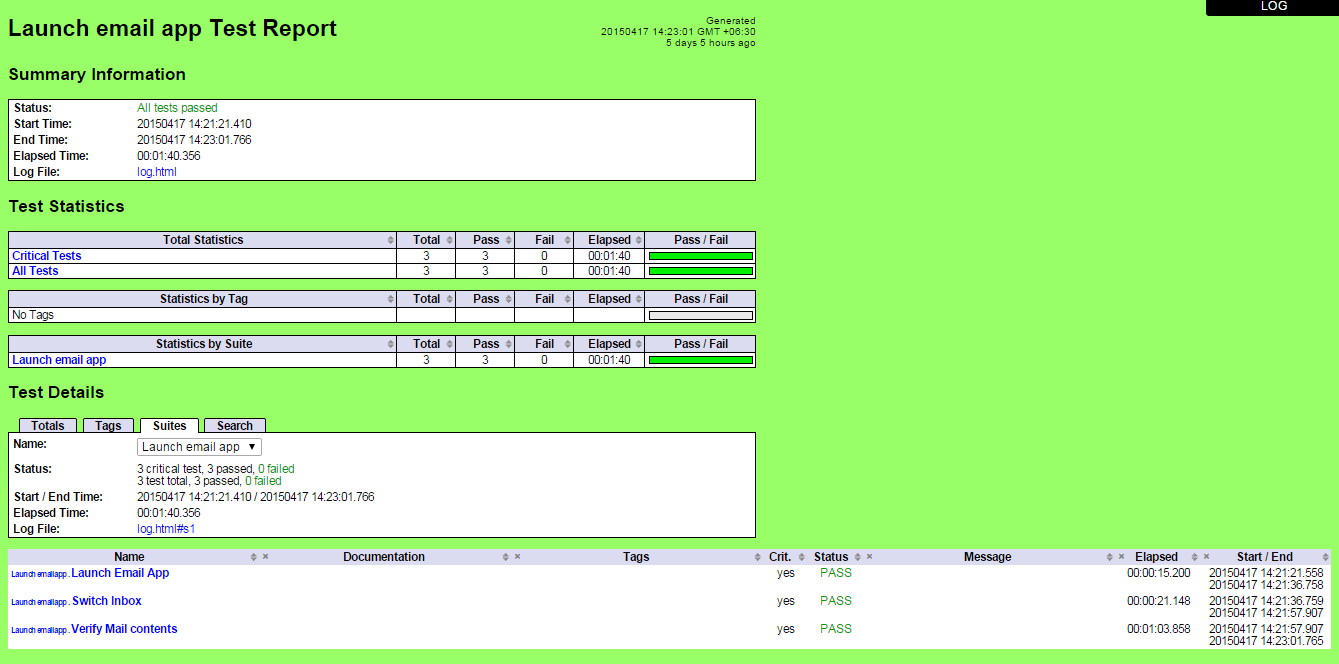
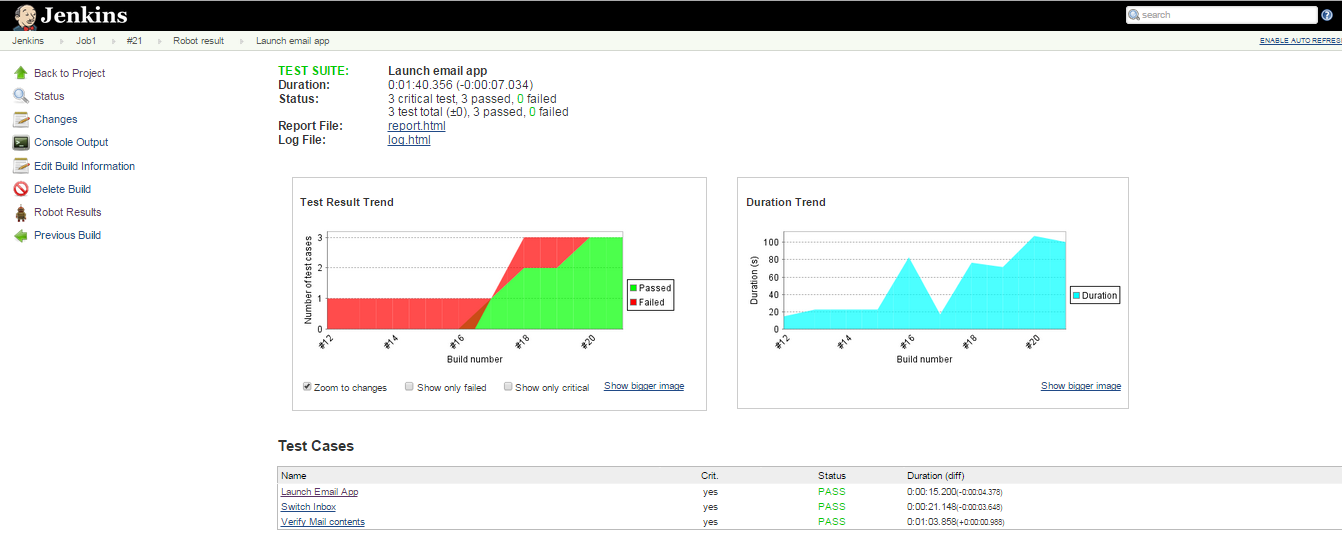
Test Reports
This is a Report.html page which is automatically created after test runs. This page summarizes different test suites and their runs with the pybot command that was triggered. These reports are interactive and can be drilled down to have a detailed analysis of how the steps in test scripts went.
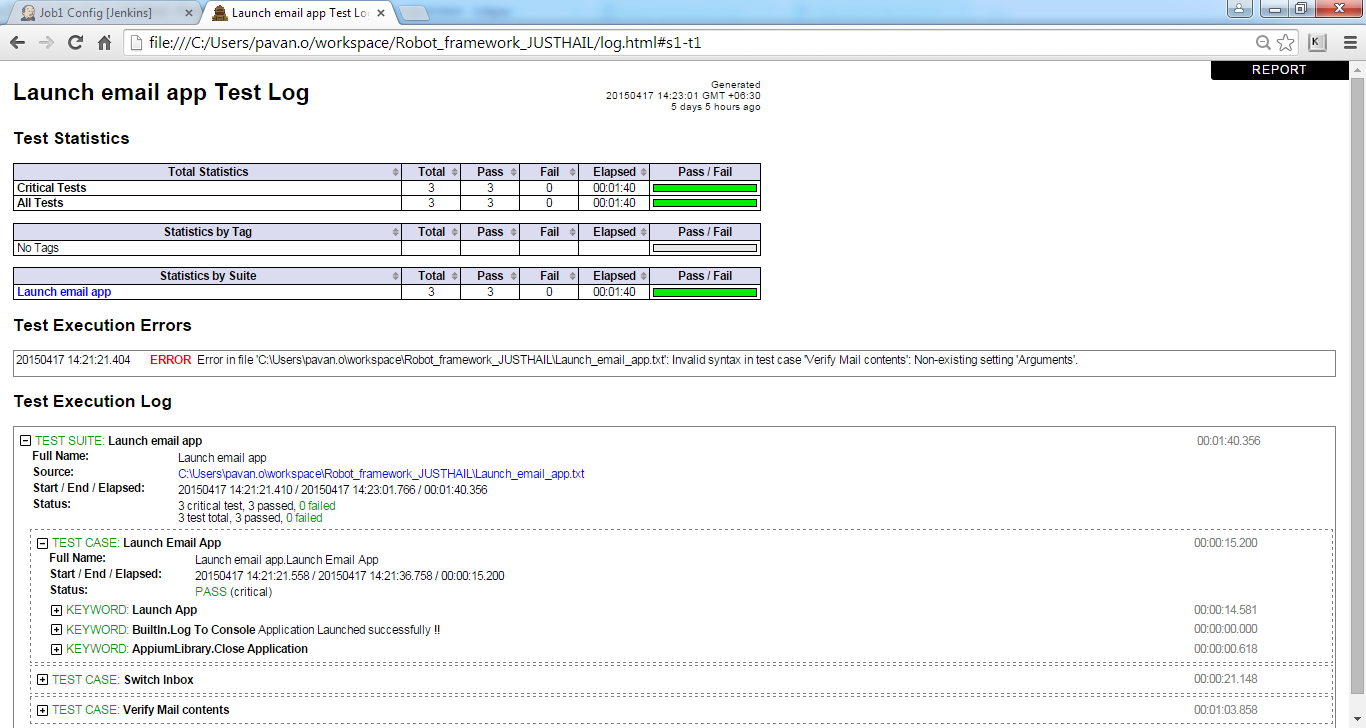
Test Logs
The following image shows the logs of the test case runs. Here are the detailed view and runtime values flowing in the variables. This approach saves time, avoiding the need to debug the code and then fix it.
Jenkins: Robot Plug-in Report
Jenkins has a plug-in for the Robot framework which shows interactive reports. We can drill down the reports to see details to analyze the health of the test cases running in consecutive job runs. The trend of every test case in every job run can also be analyzed with this plug-in.
Zymr's Mobile Automation Framework
There is no doubt that test automation is a useful way to save time and effort. Using the Robot framework is a great way to help improve your mobile application development process.
Published at DZone with permission of . See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments