Cypress Test Cases Execution With CI/CD GitHub Action
GitHub Actions is a continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) platform that allows you to automate your build, test, and deployment pipeline.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeWhat Are GitHub Actions?
GitHub Actions is a continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) platform that allows you to automate your build, test, and deployment pipeline. You can create workflows that build and test every pull request to your repository or deploy merged pull requests to production.
GitHub Actions goes beyond just DevOps and lets you run workflows when other events happen in your repository. For example, you can run a workflow to automatically add the appropriate labels whenever someone creates a new issue in your repository. GitHub provides Linux, Windows, and macOS virtual machines to run your workflows, or you can host your own self-hosted runners in your own data center or cloud infrastructure.
Set Up CI/CD GitHub Action
Pre-Condition :
The user should have a GitHub account and be already logged in.
Step 1
Create a repository. In my case, let’s say “cypress_github_Action.”Initially, there is no code in the created repo.
Step 2
Push the code to the newly created repo. Below is a simple test case where we searched some data and verified it.
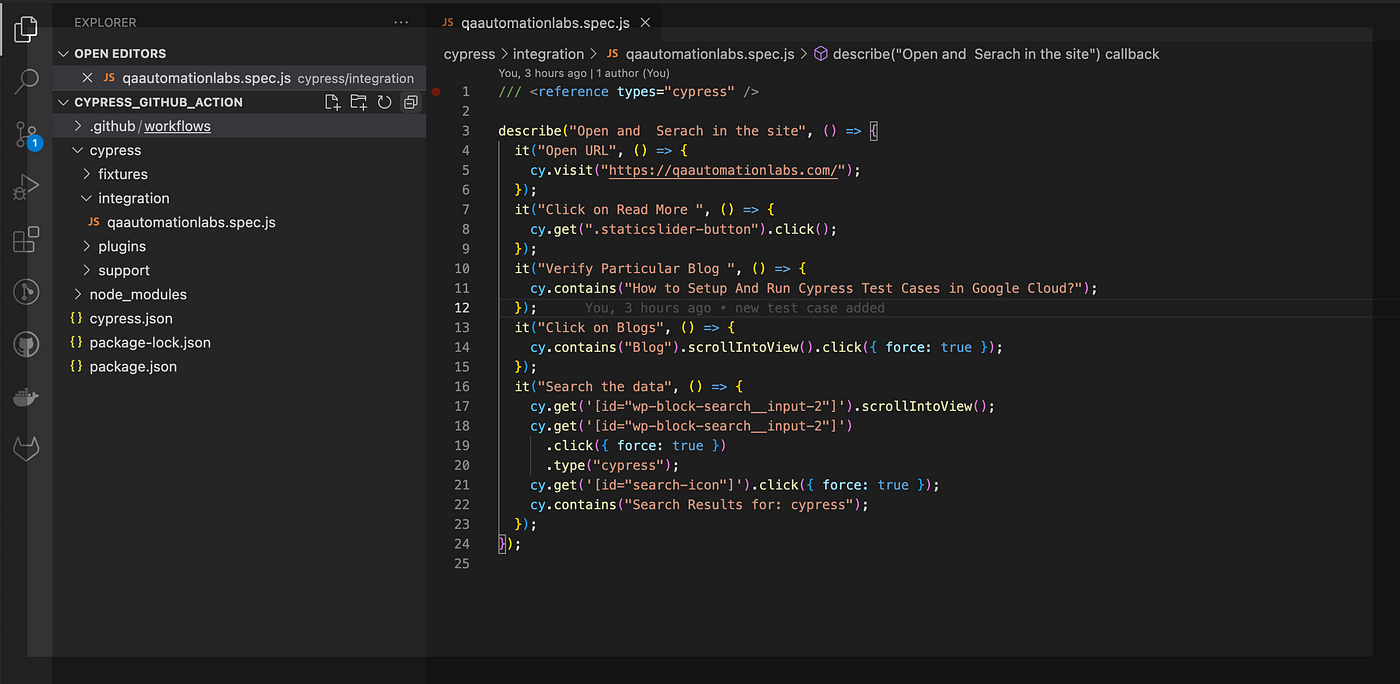
The code snippet is below:
/// <reference types=”cypress” />
describe(“Open and Search in the site”, () => {
it(“Open URL”, () => {
cy.visit(“https://qaautomationlabs.com/”);
});
it(“Click on Read More “, () => {
cy.get(“.staticslider-button”).click();
});
it(“Verify Particular Blog “, () => {
cy.contains(“How to Setup And Run Cypress Test Cases in Google Cloud?”);
});
it(“Click on Blogs”, () => {
cy.contains(“Blog”).scrollIntoView().click({ force: true });
});
it(“Search the data”, () => {
cy.get(‘[id=”wp-block-search__input-2″]’).scrollIntoView();
cy.get(‘[id=”wp-block-search__input-2″]’).click({ force: true }) .type(“cypress”);
cy.get(‘[id=”search-icon”]’).click({ force: true });
cy.contains(“Search Results for: cypress”);
});});Step 3
After pushing the code, click on the “Actions” Tab.
Step 4
After clicking on the Actions Tab, go to the bottom and click on Configure under Automation -> Manual workflow Section (Highlighted below).

Workflow
A workflow is a configurable automated process that will run one or more jobs. Workflows are defined by a YAML file checked into your repository and will run when triggered by an event in your repository, or they can be triggered manually or at a defined schedule. Workflows are defined in the .github/workflows directory in a repository,
Under project/.github/workflow/manual.yml created.

Step 5
Update the manual.yml with the below code. We can update the .yml name at your convenience.
# This is a basic workflow that is manually triggered:
name: Cypress test in GitHub Action
on: [push]
jobs:
my_job:
name: deploy to staging
runs-on: ubuntu-18.04
steps:
— name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v1
– name: cyress test cases
uses: cypress-io/github-action@v2.9.7
with:
start: npm start
Explanation of lines used above:
Line#3 name: Name of the workflow.
Line#4 on: The on keyword lets you define the events that trigger when the workflow is run. For more information, see “Triggering a workflow.” We can use on keywords with the appropriate event as per our project requirement.
Line#6 Jobs: Groups together all the jobs that run in the workflow file.
Line#7,#8 #9: Name of the Job and system on which job will run in this case Job will run in ubuntu
Line#10 steps: Groups together all the steps that you will run as part of the job. Each job in a workflow has its own steps section.
Line #11,#12: The uses keyword tells the job to retrieve the action named actions/checkout. This is an action that checks out your repository and downloads it to the runner.
Finally, Line #16 and #17, our Cypress GitHub Action will:
- Install npm dependencies
- Start the project web server (
npm start) - Run the Cypress tests within our GitHub repository within Electron.
Run Cypress Test cases on GitHub-hosted virtual machines.
As we push the code, the workflow starts to run automatically.

Click on deploy to staging.
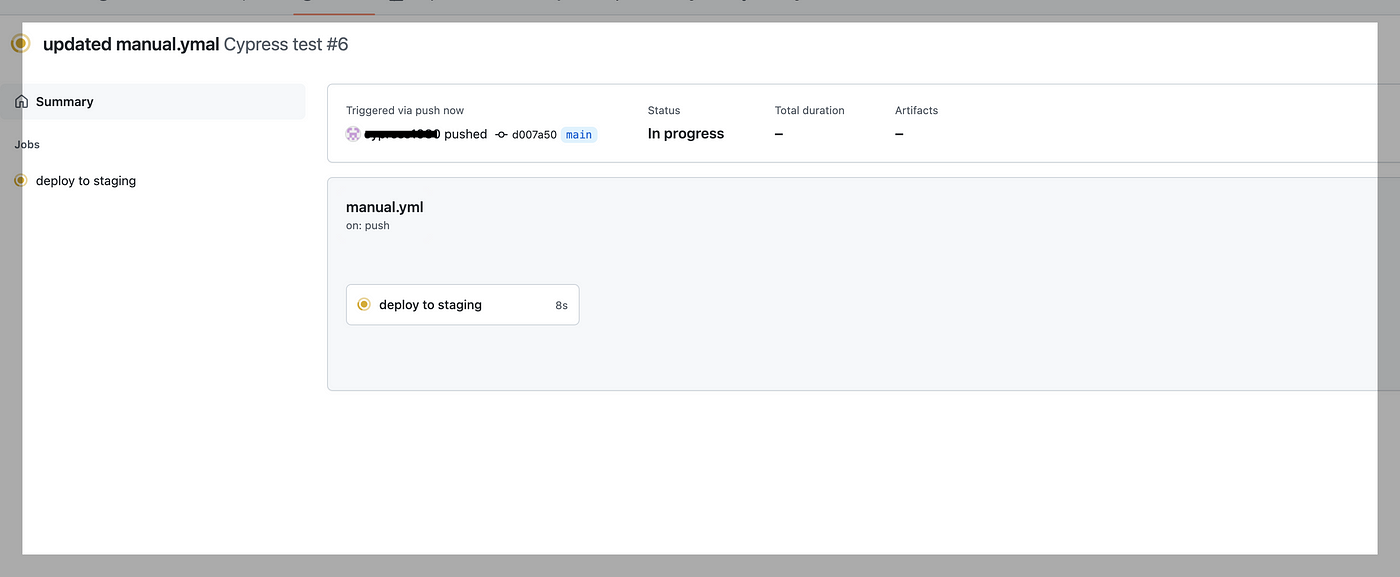
In the below screenshot, we can see Cypress test cases start running in GitHub-hosted virtual machines:

We have one test case to run. Once all test cases are executed check icon becomes GREEN:

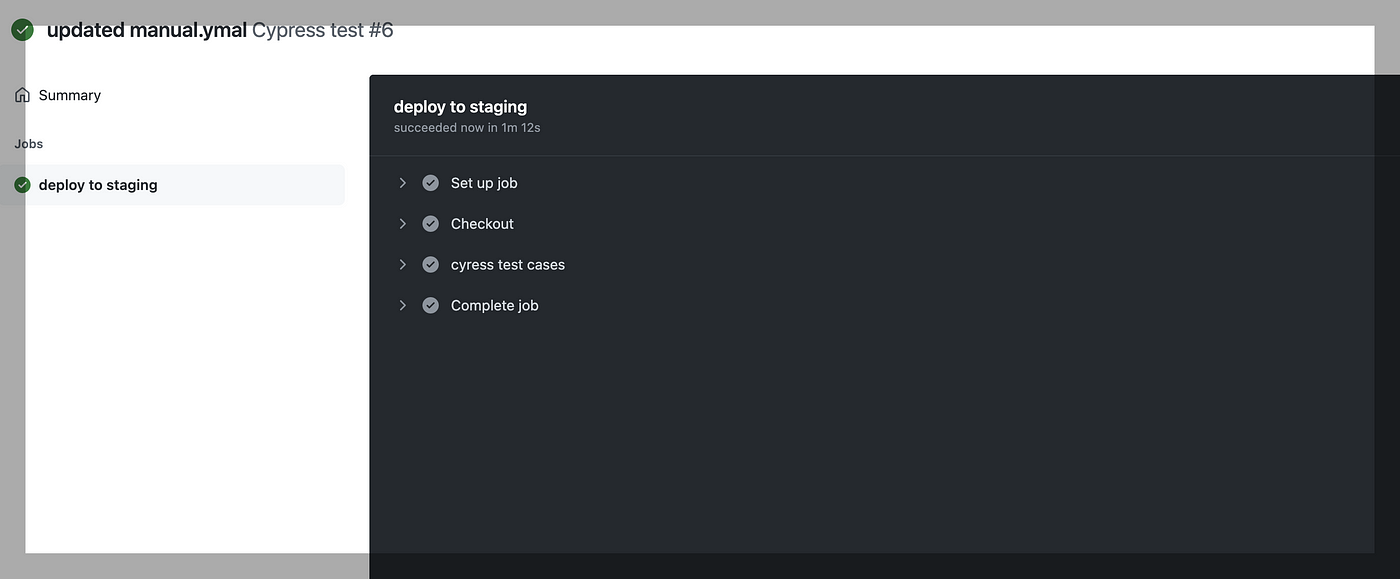
Click “cypress test cases.” In the below screenshot, we can see we have one test case that is executed successfully:
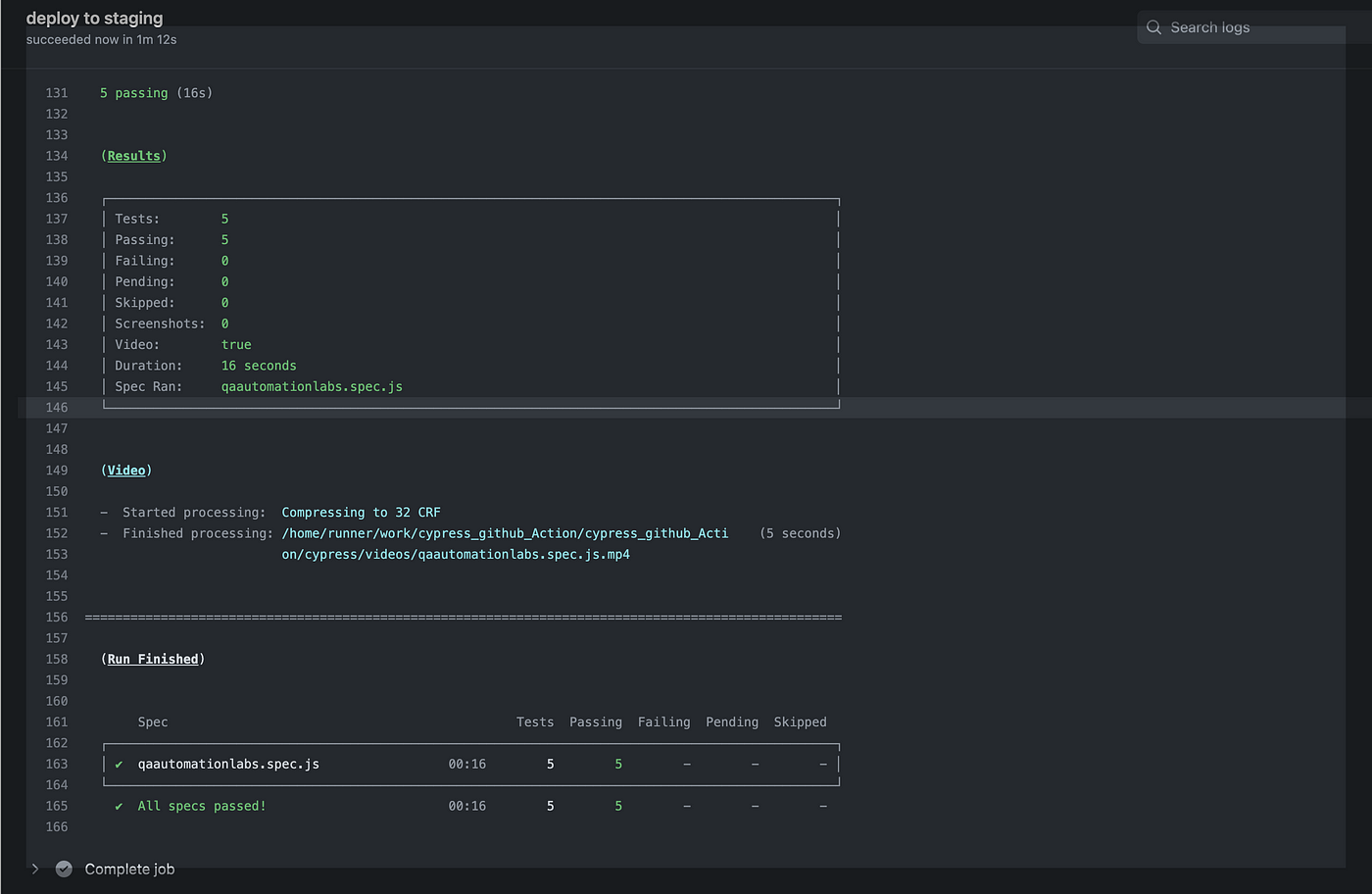
Run Cypress Test Cases in GitHub Actions With Docker Images
GitHub Actions provides the option to specify a container image for the job. Cypress offers various Docker Images for running Cypress test cases in CI.
Below we add the container using a Cypress Docker Image built with Google Chrome.
Step 1
Update the existing manual.yml file with containers.
name: Run Cypress Tests using Cypress Docker Image
on: [push]
jobs:
cypress-run:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
# specify the cypress contained with node
container: cypress/browsers:node12.18.3-chrome87-ff82
steps:
— name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v2
# Install NPM dependencies,
# and run all Cypress tests
— name: Cypress run
uses: cypress-io/github-action@v4
with:
# Specify Browser since container image is compiled with chrome
browser: Chrome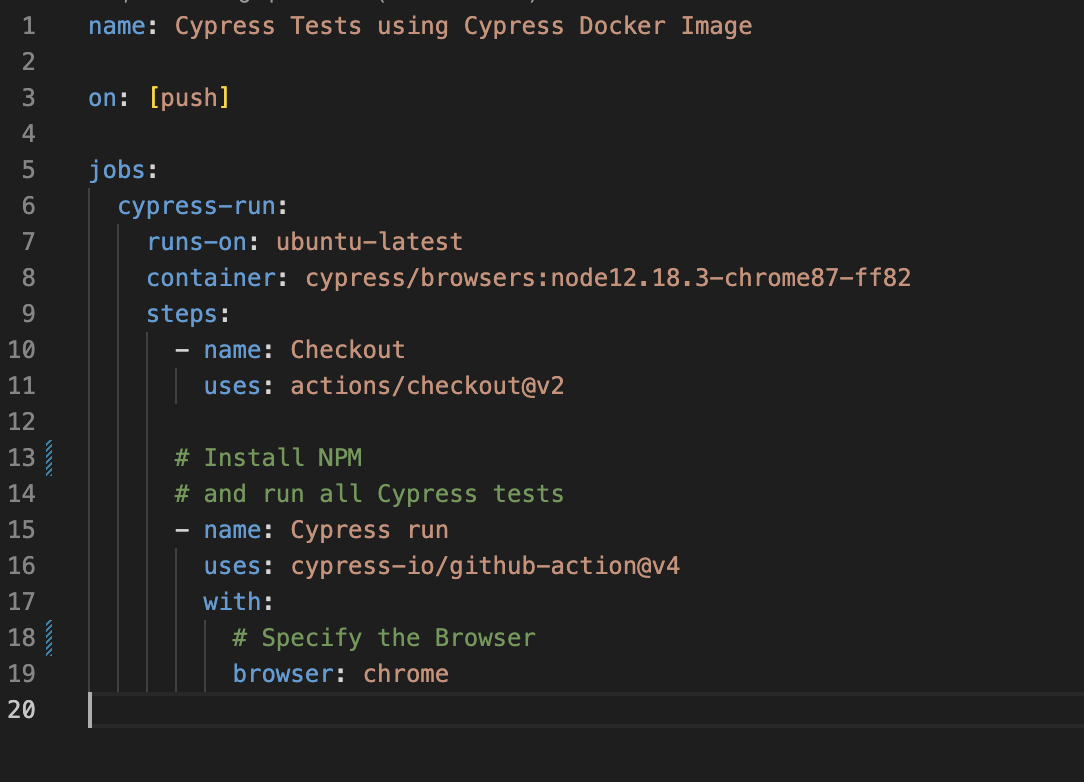
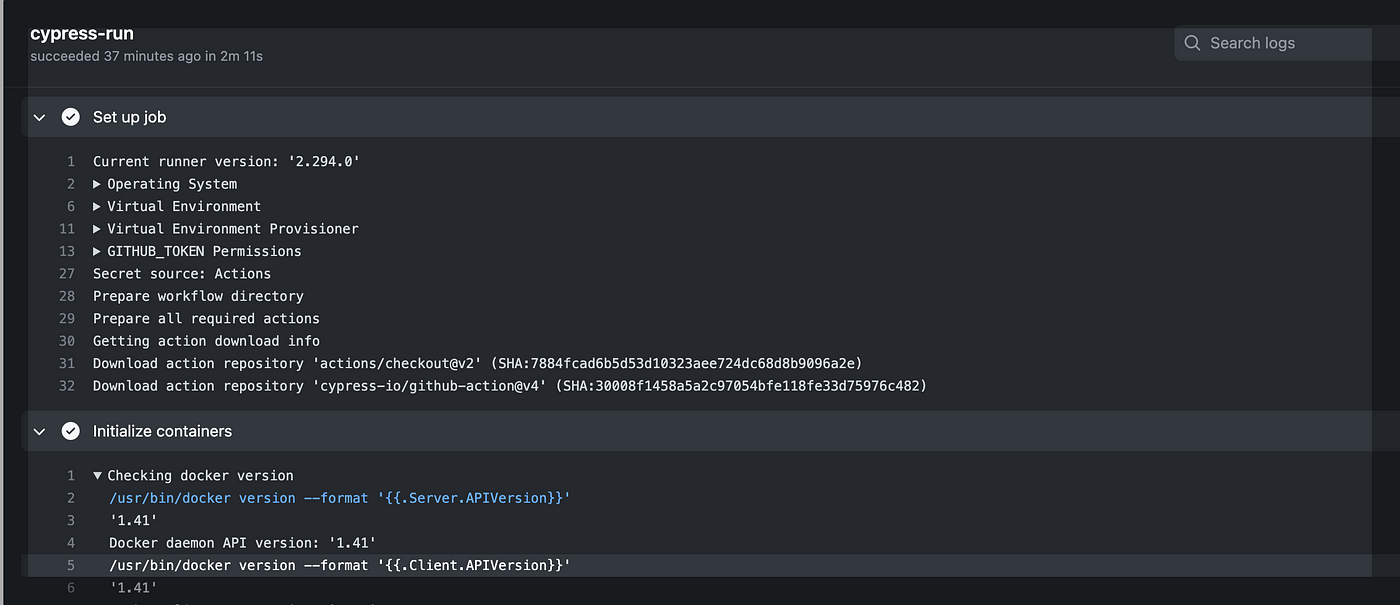
Step 2
Push the code as we push the code build to start triggering. In the below screenshot, we can see docker is initialized.
In the next step, the code is checkout from the .git.
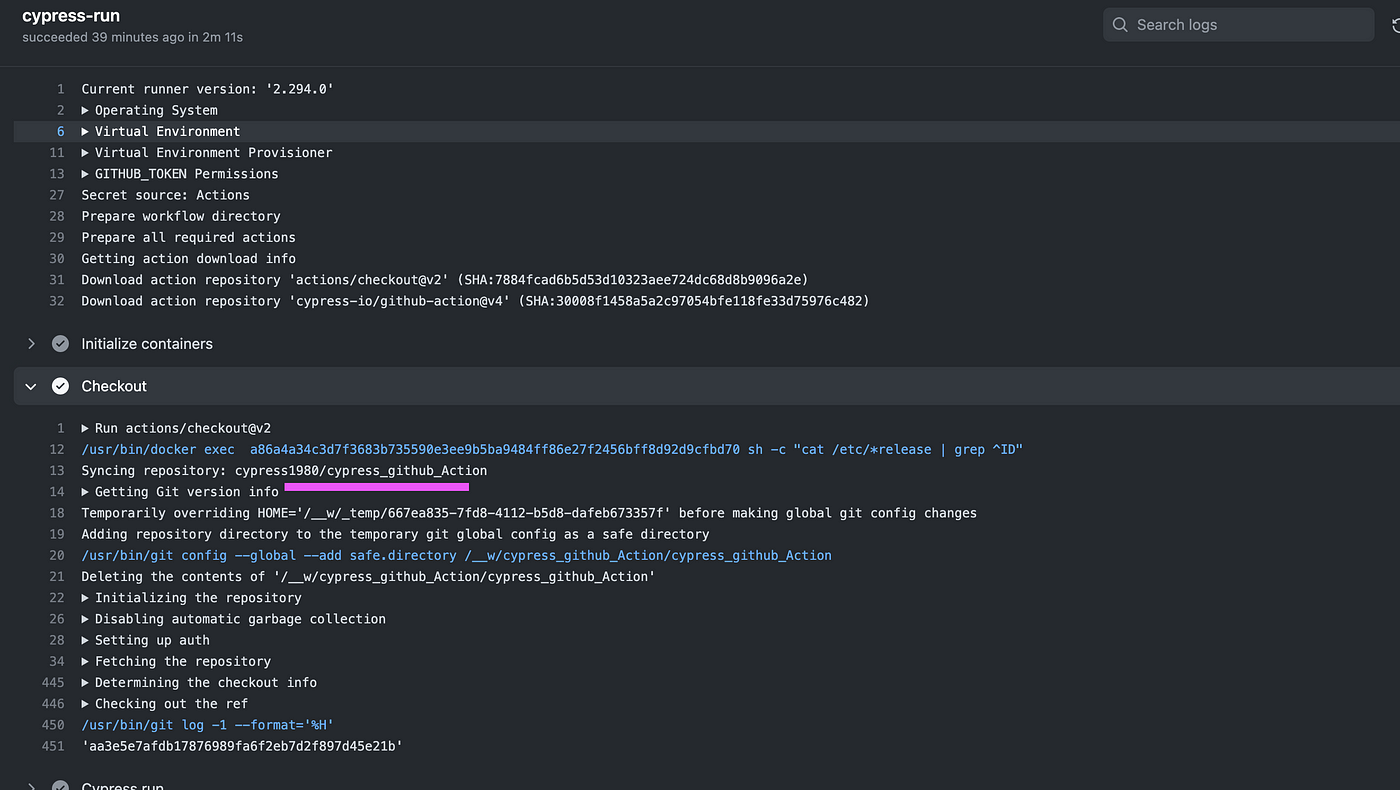
Once code checkout, Cypress test cases start executing in the Docker image.
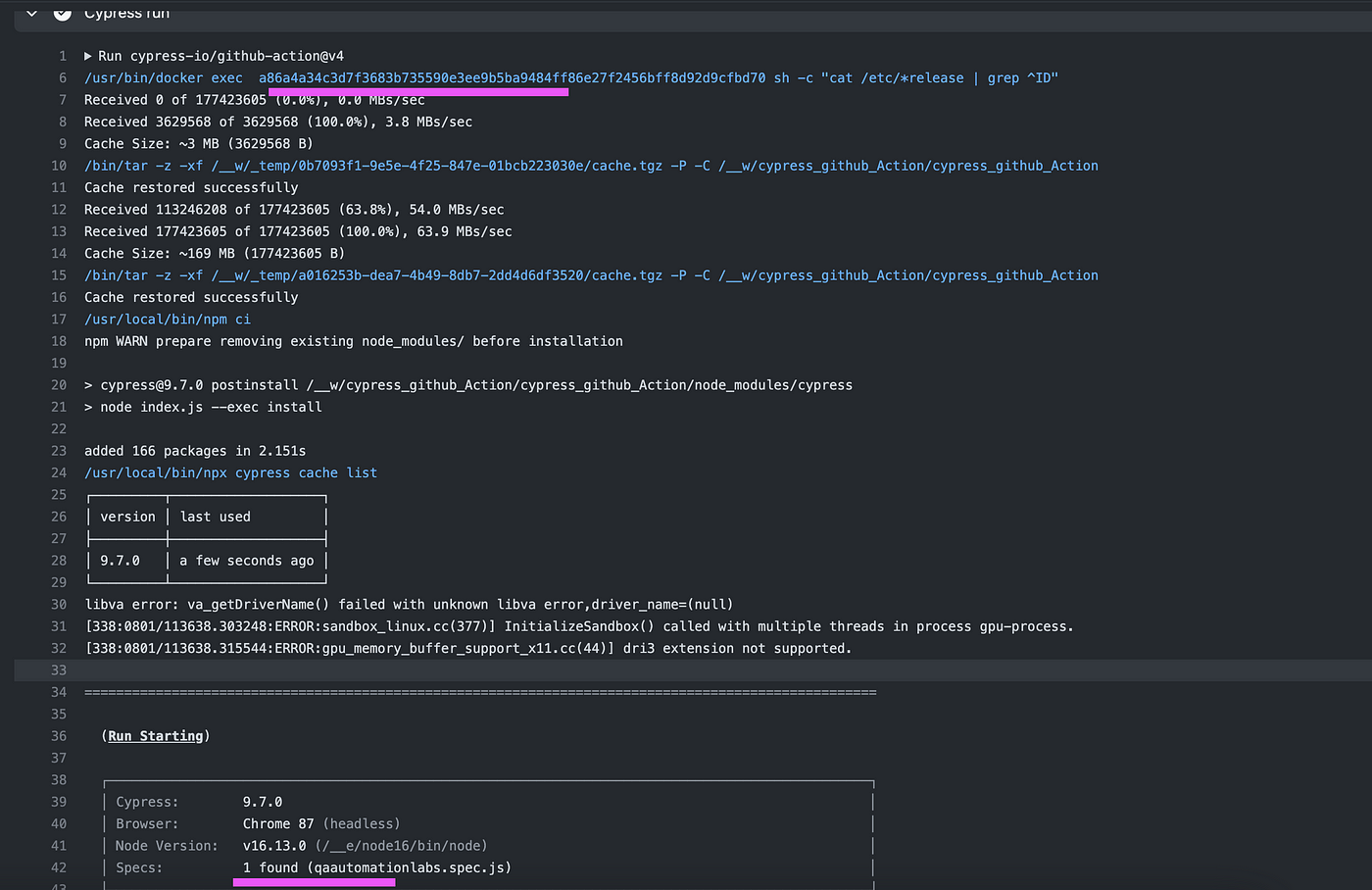
Finally, test cases are executed successfully in the docker image.
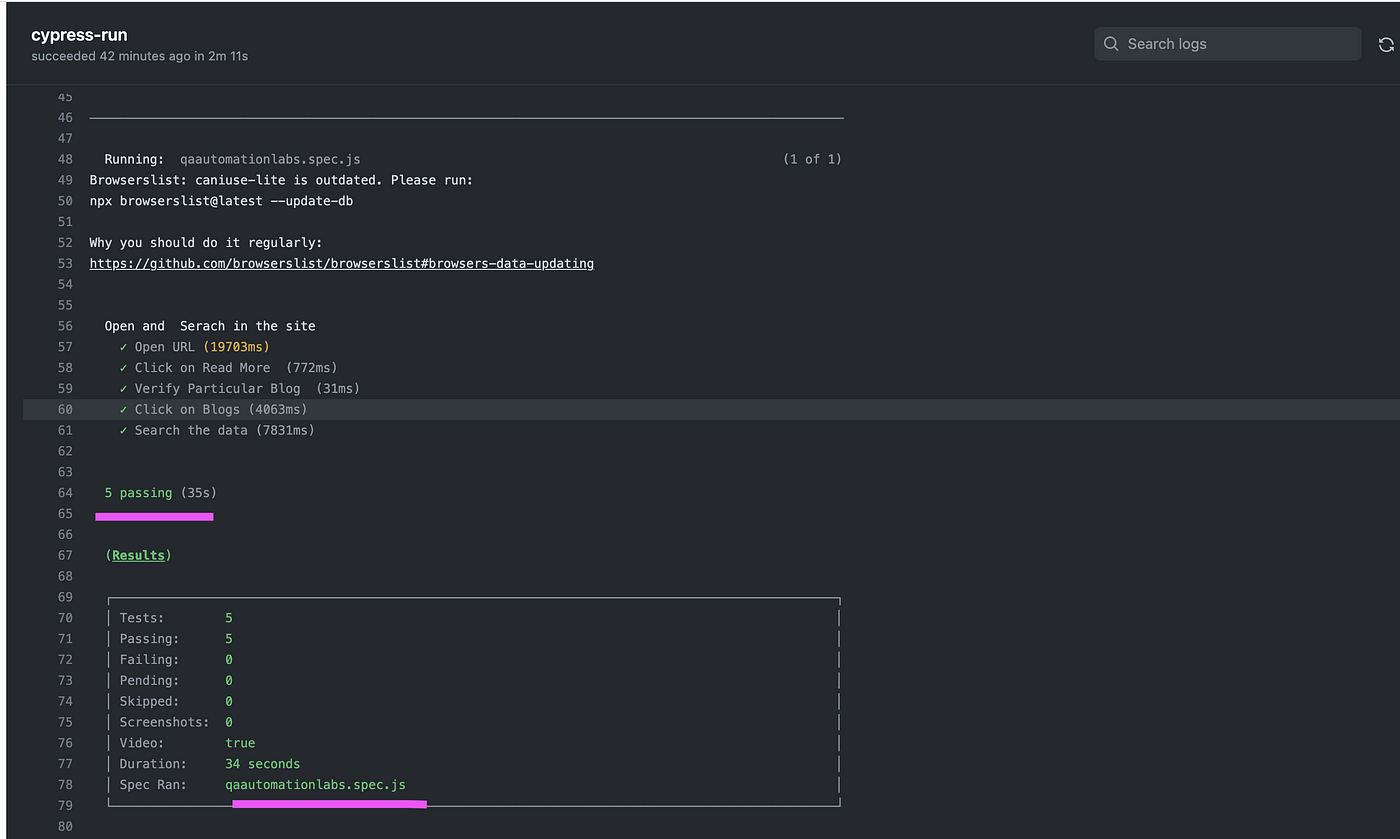
Once all test cases are executed container is stopped.
Published at DZone with permission of Kailash Pathak. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments