Seamless CI/CD Integration: Playwright and GitHub Actions
Integrate Playwright with GitHub Actions to automate testing and deployment workflows, ensuring seamless CI/CD, rapid feedback, and reliable web apps.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeGitHub Action integration with Playwright enables seamless automated testing and deployment workflows for web applications. GitHub Actions, the platform’s automation tool, allows these tests to be triggered automatically upon code changes, ensuring rapid feedback and efficient bug detection.
This integration empowers teams to build, test, and deploy with confidence, automating repetitive tasks and enhancing overall development productivity. By combining the versatility of Playwright with the automation capabilities of GitHub Actions, developers can streamline their workflows, delivering high-quality web applications with speed and precision.
What Is Playwright?
Microsoft Playwright is an open-source automation framework for end-to-end testing, browser automation, and web scraping. Developed by Microsoft, Playwright provides a unified API to automate interactions with web browsers like Microsoft Edge, Google Chrome, and Mozilla Firefox. It allows developers to write scripts in various programming languages, including Java, Python, JavaScript, and C#.
Here are some key features of Playwright:
- Multi-Browser Support: Playwright supports multiple web browsers, including Firefox, Chrome, Safari, and Microsoft Edge. This allows developers and testers to run their tests on different browsers with a consistent API.
- Headless and Headful Modes: Playwright can run browsers in both headless mode (without a graphical interface) and headful mode (with a graphical interface), providing flexibility for different use cases.
- Cross-Browser Testing: Playwright allows you to write tests that run on multiple browsers and platforms, ensuring your web application works correctly across different platforms.
- Emulation of Mobile Devices and Touch Events: Playwright can emulate various mobile devices and simulate touch events, enabling you to test how your web application behaves on different mobile devices.
- Parallel Test Execution: Playwright supports parallel test execution, allowing you to run tests concurrently, reducing the overall test suite execution time.
- Capture Screenshots and Videos: Playwright can capture screenshots and record videos during test execution, helping you visualize the behavior of your application during tests.
- Intercept Network Requests: You can intercept and modify network requests and responses, which is useful for testing scenarios involving AJAX requests and APIs.
- Auto-Waiting for Elements: Playwright automatically waits for elements to be ready before performing actions, reducing the need for manual waits and making tests more reliable.
- Page and Browser Contexts: Playwright allows you to create multiple browser contexts and pages, enabling efficient management of browser instances and isolated environments for testing.
What Is GitHub Actions?
GitHub Actions is an automation platform offered by GitHub that streamlines software development workflows. It empowers users to automate a wide array of tasks within their development processes. By leveraging GitHub Actions, developers/qa engineers can craft customized workflows that are initiated by specific events such as code pushes, pull requests, or issue creation. These workflows can automate essential tasks like building applications, running tests, and deploying code.
Essentially, GitHub Actions provides a seamless way to automate various aspects of the software development lifecycle directly from your GitHub repository.
How GitHub Actions Effective in Automation Testing
GitHub Actions is a powerful tool for automating various workflows, including QA automation testing. It allows you to automate your software development processes directly within your GitHub repository. Here are some ways GitHub Actions can be effective in QA automation testing:
1. Continuous Integration (CI)
GitHub Actions can be used for continuous integration, where automated tests are triggered every time there is a new code commit or a pull request. This ensures that new code changes do not break existing functionality. Automated tests can include unit tests, integration tests, and end-to-end tests.
2. Diverse Test Environments
GitHub Actions supports running workflows on different operating systems and environments. This is especially useful for QA testing, as it allows you to test your application on various platforms and configurations to ensure compatibility and identify platform-specific issues.
3. Parallel Test Execution
GitHub Actions allows you to run tests in parallel, significantly reducing the time required for test execution. Parallel testing is essential for large test suites, as it helps in obtaining faster feedback on the code changes.
4. Custom Workflows
You can create custom workflows tailored to your QA automation needs. For example, you can create workflows that run specific tests based on the files modified in a pull request. This targeted testing approach helps in validating specific changes and reduces the overall testing time.
5. Integration With Testing Frameworks
GitHub Actions can seamlessly integrate with popular testing frameworks and tools. Whether you are using Selenium, Cypress, Playwright for web automation, Appium for mobile automation, or any other testing framework, you can configure GitHub Actions to run your tests using these tools
In the next section, you will see how we can integrate GitHub Actions with Playwright to execute the test cases.
Set Up CI/CD GitHub Actions to Run Playwright Tests
Pre-Condition
The user should have a GitHub account and already be logged in.
Use Cases
For automation purposes, we are taking two examples, one of UI and the other of API.
Example 1
Below is an example of a UI test case where we log in to the site https://talent500.co/auth/signin. After a successful login, we log out from the application.
// @ts-check
const { test, expect } = require("@playwright/test");
test.describe("UI Test Case with Playwright", () => {
test("UI Test Case", async ({ page }) => {
await page.goto("https://talent500.co/auth/signin");
await page.locator('[name="email"]').click();
await page.locator('[name="email"]').fill("applitoolsautomation@yopmail.com");
await page.locator('[name="password"]').fill("Test@123");
await page.locator('[type="submit"]').nth(1).click();
await page.locator('[alt="DropDown Button"]').click();
await page.locator('[data-id="nav-dropdown-logout"]').click();
});
});Example 2
Below is an example of API testing, where we automate using the endpoint https://reqres.in/api for a GET request.
Verify the following:
- GET request with Valid 200 Response
- GET request with InValid 404 Response
- Verification of user details
// @ts-check
const { test, expect } = require("@playwright/test");
test.describe("API Testing with Playwright", () => {
const baseurl = "https://reqres.in/api";
test("GET API Request with - Valid 200 Response", async ({ request }) => {
const response = await request.get(`${baseurl}/users/2`);
expect(response.status()).toBe(200);
});
test("GET API Request with - Invalid 404 Response", async ({ request }) => {
const response = await request.get(`${baseurl}/usres/invalid-data`);
expect(response.status()).toBe(404);
});
test("GET Request - Verify User Details", async ({ request }) => {
const response = await request.get(`${baseurl}/users/2`);
const responseBody = JSON.parse(await response.text());
expect(response.status()).toBe(200);
expect(responseBody.data.id).toBe(2);
expect(responseBody.data.first_name).toBe("Janet");
expect(responseBody.data.last_name).toBe("Weaver");
expect(responseBody.data.email).toBeTruthy();
});
});Steps For Configuring GitHub Actions
Step 1: Create a New Repository
Create a repository. In this case, let’s name it “Playwright_GitHubAction.”
Step 2: Install Playwright
Install Playwright using the following command:
npm init playwright@latestOr
yarn create playwrightStep 3: Create Workflow
Define your workflow in the YAML file. Here’s an example of a GitHub Actions workflow that is used to run Playwright test cases.
In this example, the workflow is triggered on every push and pull request. It sets up Node.js, installs project dependencies, and then runs npx playwright test to execute Playwright tests.
Add the following .yml file under the path .github/workflows/e2e-playwright.yml in your project.
name: GitHub Action Playwright Tests
on:
push:
branches: [main]
pull_request:
branches: [main]
jobs:
test:
timeout-minutes: 60
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
- uses: actions/setup-node@v3
with:
node-version: 18
- name: Install dependencies
run: npm ci
- name: Install Playwright Browsers
run: npx playwright install --with-deps
- name: Run Playwright tests
run: npx playwright test
- uses: actions/upload-artifact@v3
if: always()
with:
name: playwright-report
path: playwright-report/
retention-days: 10Here’s a breakdown of what this workflow does:
Trigger Conditions
The workflow is triggered on push events to the main branch.
Job Configuration
- Job name: e2e-test
- Timeout: 60 minutes (the job will terminate if it runs for more than 60 minutes)
- Operating system: ubuntu-latest
Steps
- Check out the repository code using
actions/checkout@v3. - Set up Node.js version 18 using
actions/setup-node@v3. - Install project dependencies using
npm ci. - Install Playwright browsers and their dependencies using
npx playwright install --with-deps. - Run Playwright tests using
npx playwright test. - Upload the test report directory (
playwright-report/) as an artifact usingactions/upload-artifact@v3. This step always executes (if: always()), and the artifact is retained for 10 days.
Test results will be stored in the playwright-report/ directory.
Below is the folder structure where you can see the .yml file and test cases under the tests folder to execute.
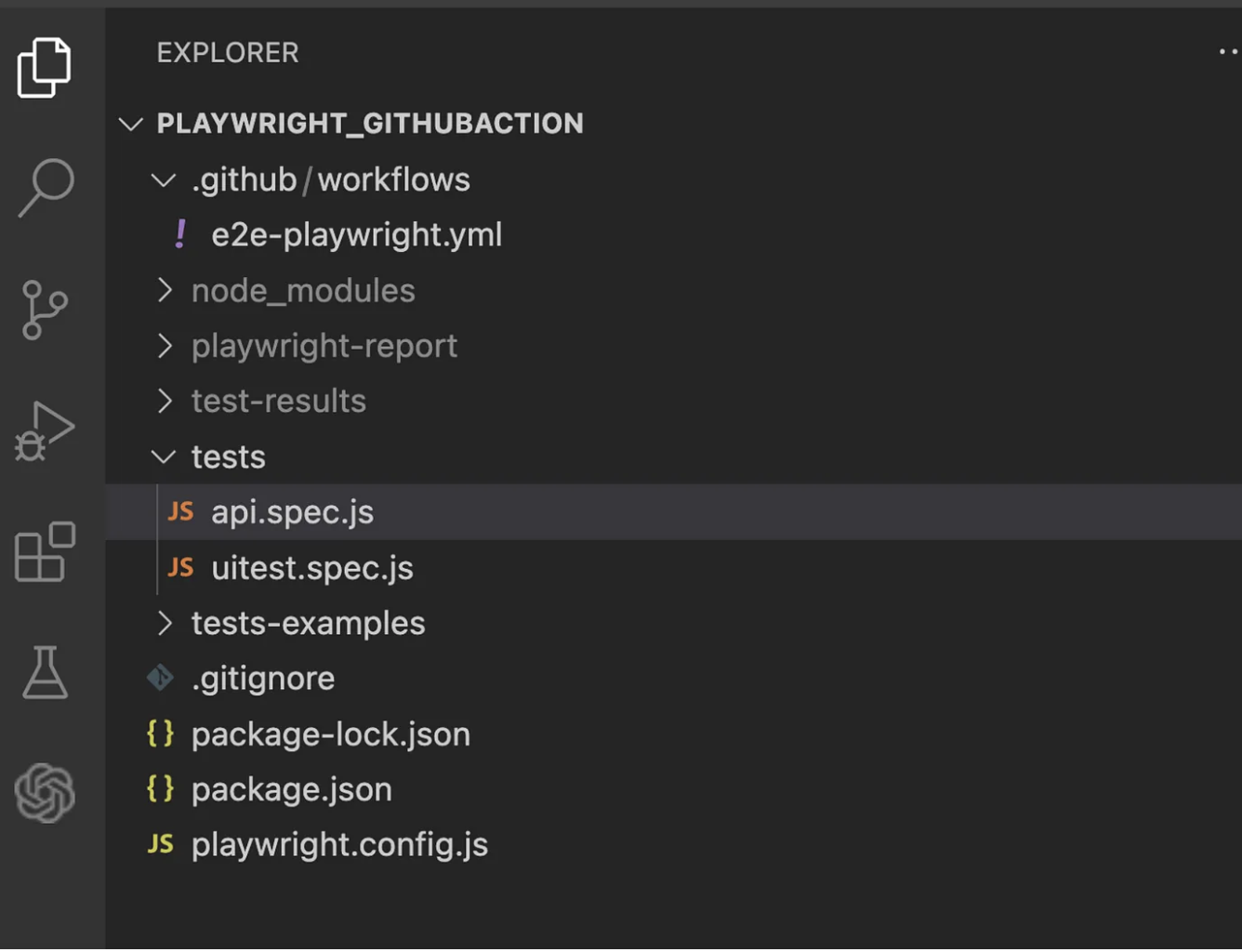
Execute the Test Cases
Commit your workflow file (e2e-playwright.yml) and your Playwright test files. Push the changes to your GitHub repository. GitHub Actions will automatically pick up the changes and run the defined workflow.
As we push the code, the workflow starts to run automatically.
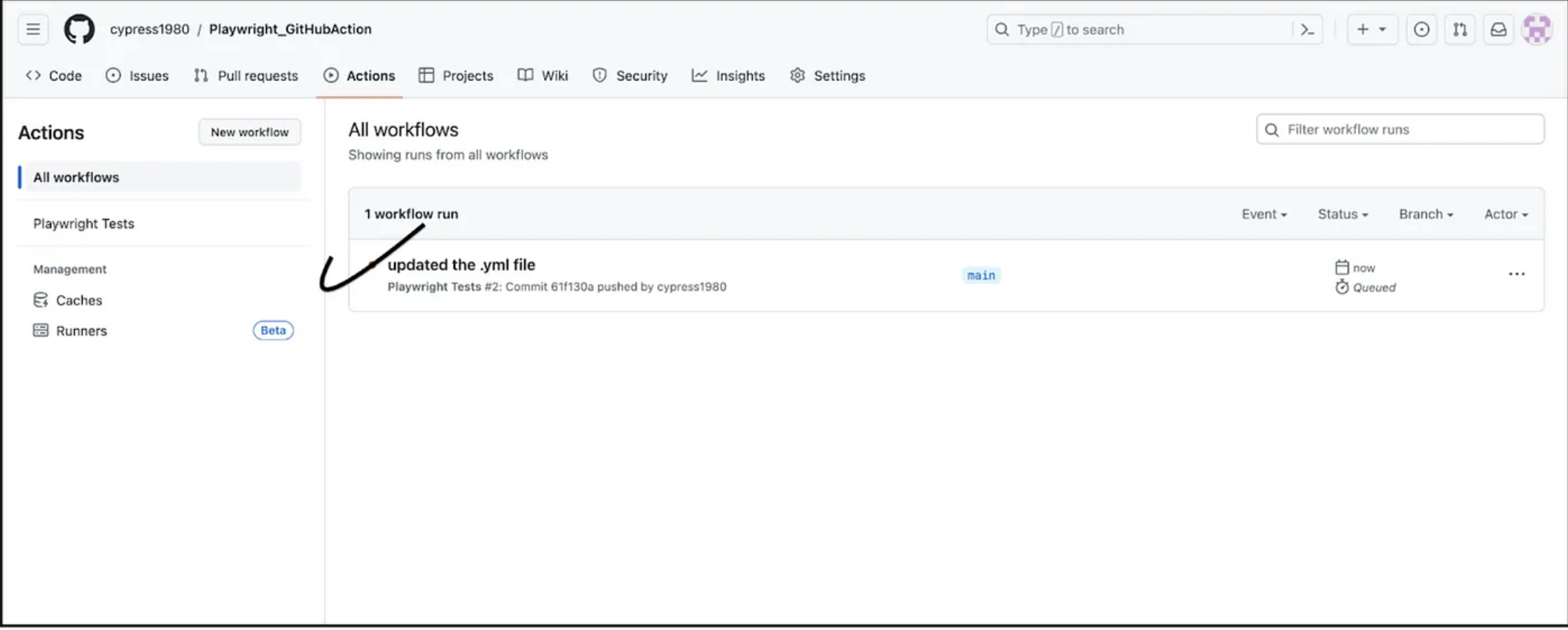
Click on the above link to open the e2e-test.
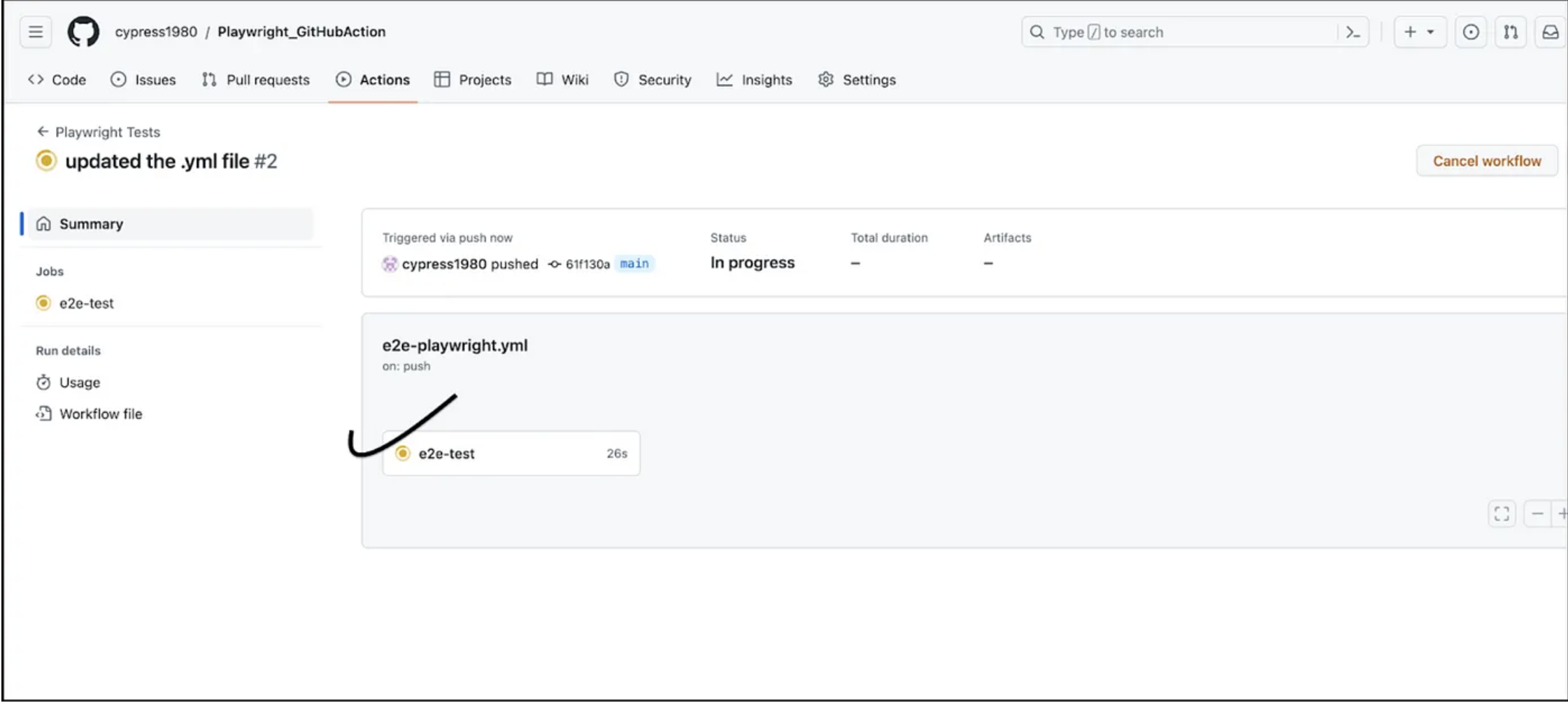
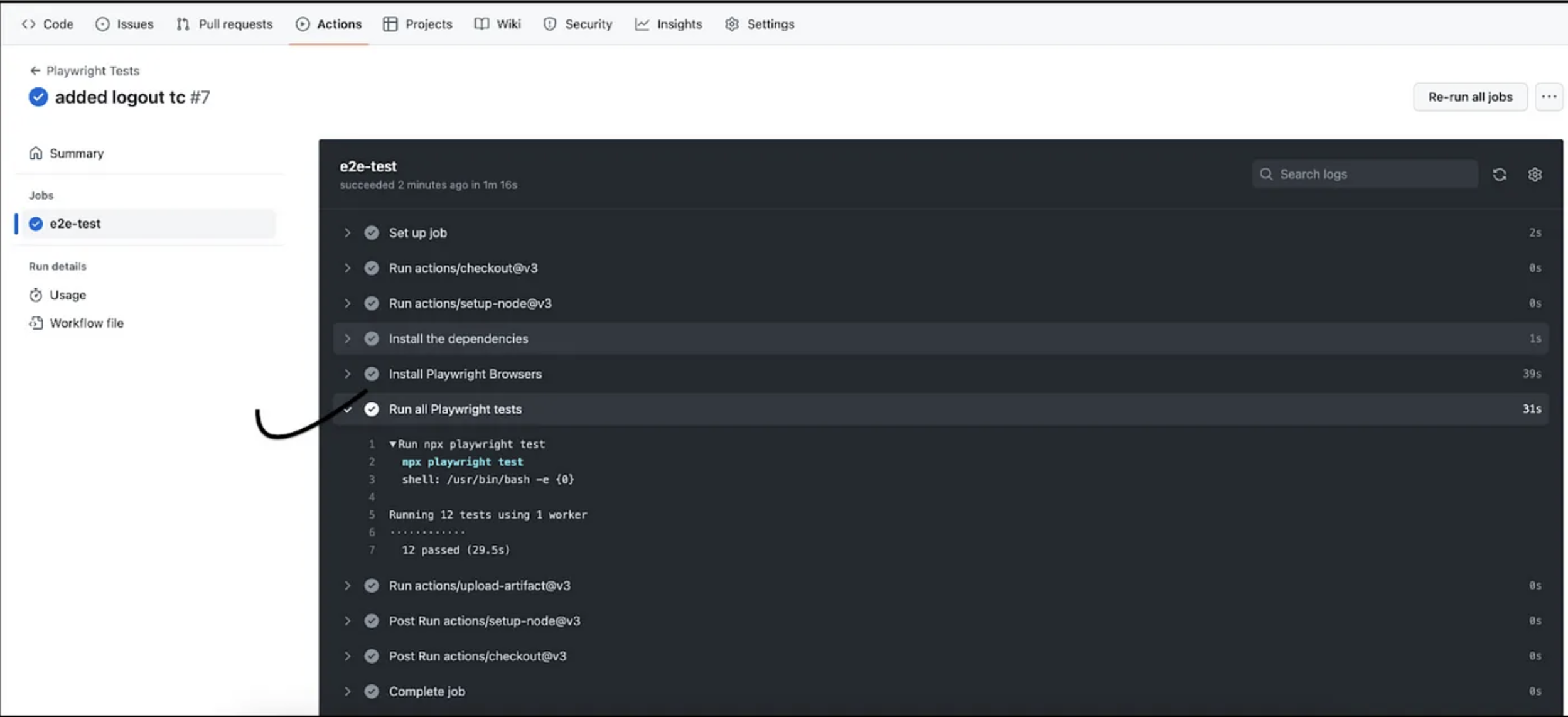
Click on e2e-test. In the screen below, you can see the code being checked out from GitHub, and the browsers start installing.
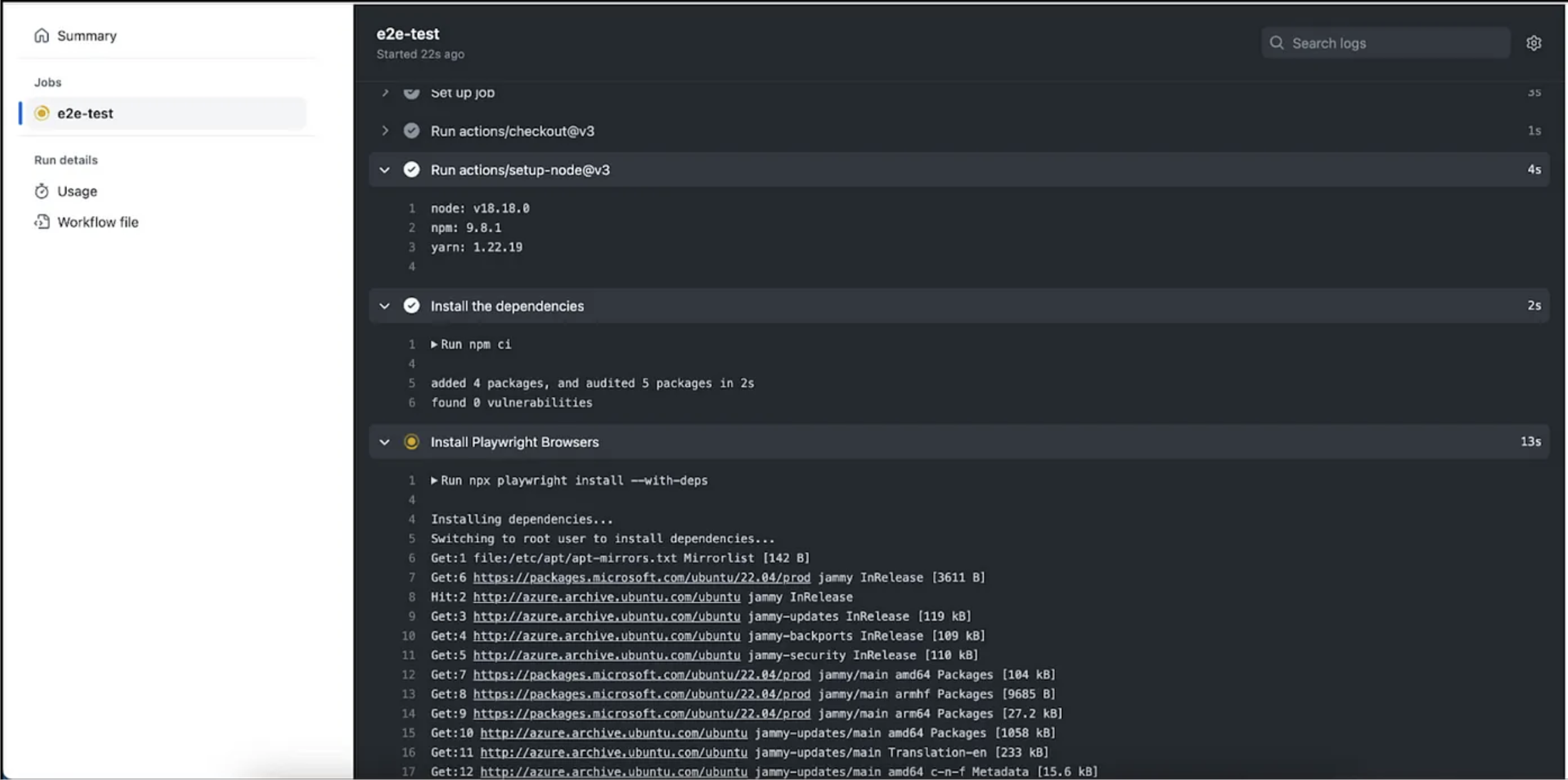
Once all dependencies and browsers are installed, the test cases start executing. In the screenshot below, you can see all 12 test cases passed in three browsers (Firefox, Chrome, and WebKit).
HTML Report
Click on the playwright-report link from the Artifacts section. An HTML report is generated locally
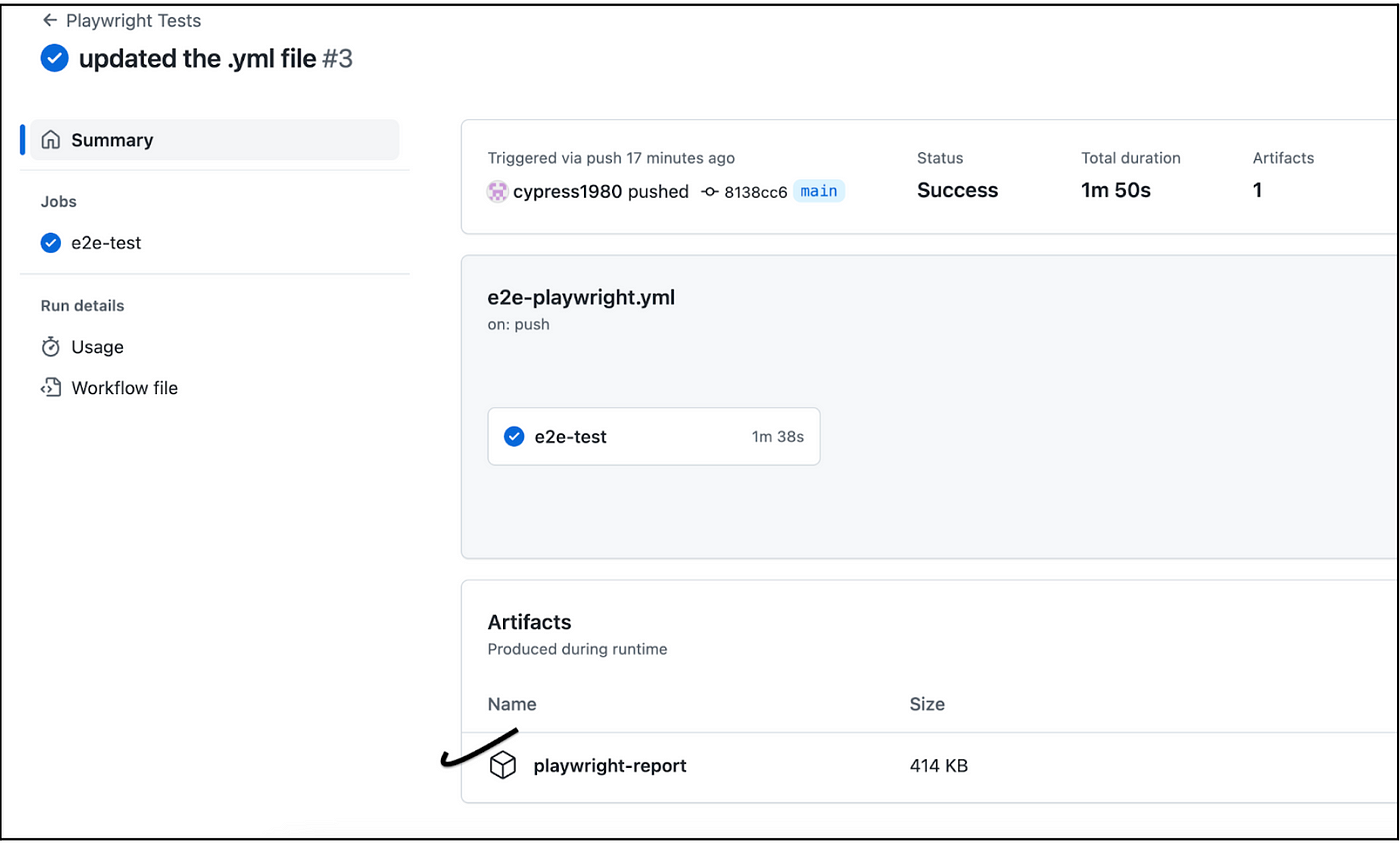
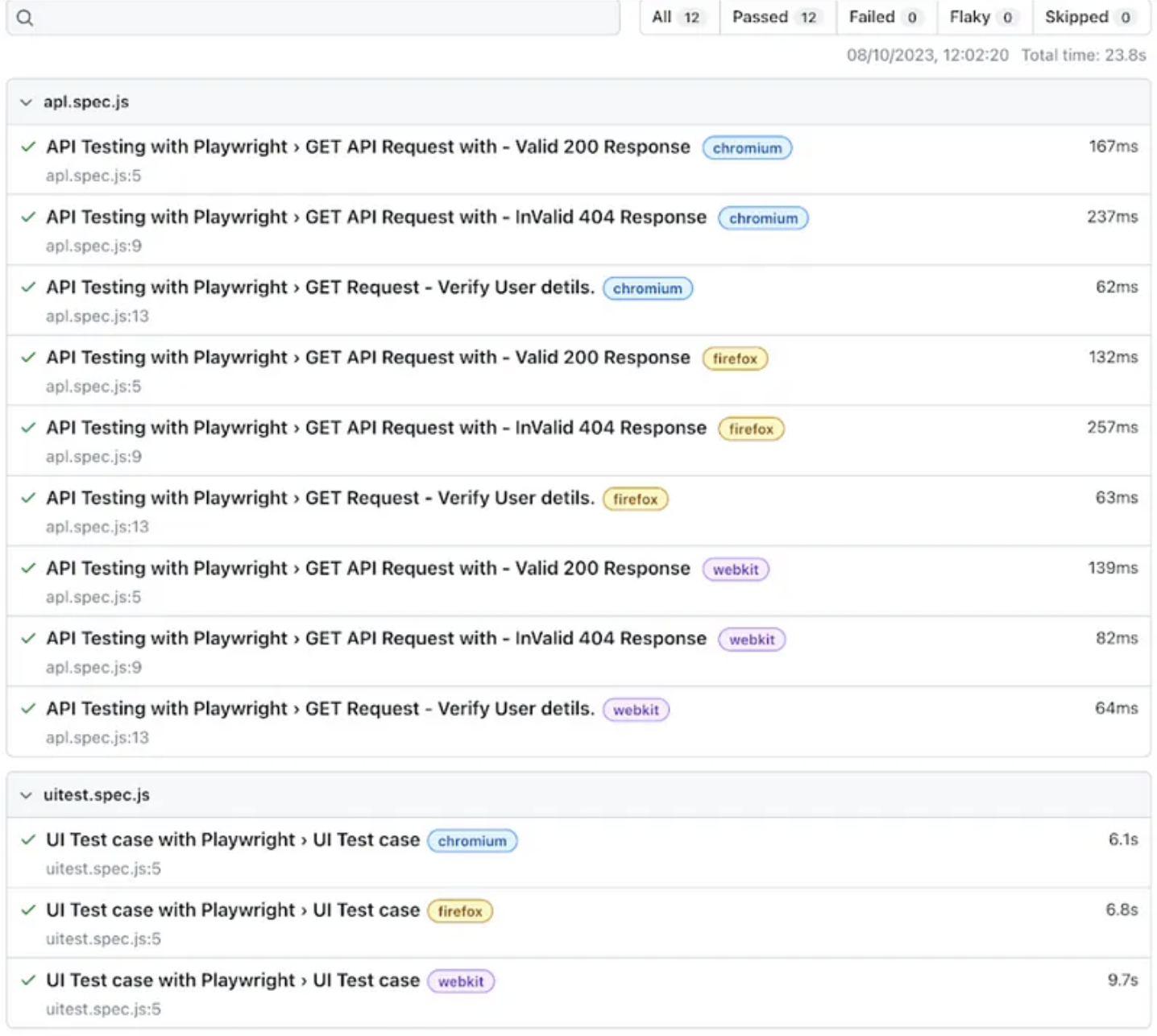
Click the link above to view the HTML report. Both API and UI test cases are passed.
Wrapping Up
GitHub Actions automate the testing process, ensuring every code change is thoroughly examined without manual intervention. Playwright’s ability to test across various browsers and platforms guarantees a comprehensive evaluation of your application’s functionality.
By combining GitHub Actions and Playwright, developers can streamline workflows, ensure code quality, and ultimately deliver better user experiences.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments