4 Use Cases of Serverless Architecture
Serverless computing has vastly improved the capacity of virtual computing. Check out some ways you can use serverlss tech here.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeServerless architectures have rapidly emerged as a new technology concept in recent years. Using this architecture, developers can create a variety of applications for various industries. Many enterprises have already started adopting serverless products into their solutions. Serverless solutions help you build light, highly-flexible, and stateless applications easily. In this article, we will explore four common applications of serverless with Alibaba Cloud Function Compute.
Before we begin, let's familiarize ourselves with the history and features of serverless architecture.
Evolution of Serverless Technology
Developers are constantly on the lookout for more effective ways to maintain the software development lifecycle. Every introduction of a new technology concept is accompanied with an increase in productivity. Similarly, serverless architecture was introduced to help businesses focus on application development. With serverless, businesses no longer have to worry about server infrastructure, reducing development costs and shortening the development cycle.
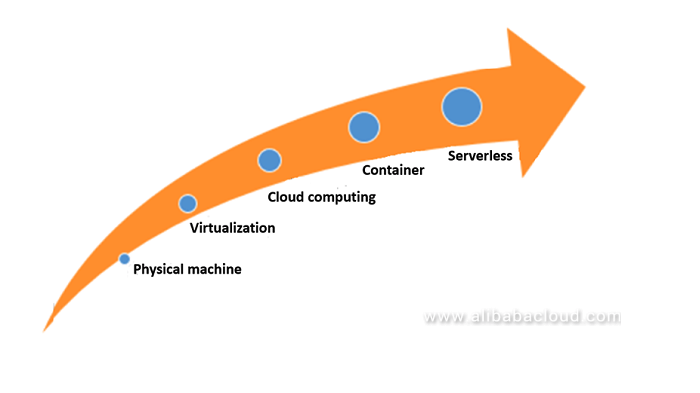
The development process for serverless architecture is built upon previous achievements starting from virtualization (cloud computing). Although the process is rather continuous, it is marked by several notable milestones:
- Virtualization technology is introduced to virtualize large physical servers into individual VM resources.
- Virtualization clusters are moved to cloud computing platforms for simple O&M.
- Each VM is subdivided into Docker containers based on the principle of minimizing the operating space.
- Applications built on Docker containers do not require any runtime environment management, only a serverless architecture for the core code.
- Serverless is introduced to help developers focus on application logic rather than server infrastructure.
Features of Serverless Architecture
Serverless architectures has the following features:
- Granular computing resources
- Resources do not need to be pre-allocated
- Highly-scalable and flexible architecture
- Users only need to pay for the resources they use
Specifically, Alibaba Cloud Function Compute provides you with the following advantages:
- No infrastructure management. Function Compute allows you to focus on developing main business logic with low operation and maintenance cost.
- Seamless integration with Alibaba Cloud services. Function Compute helps you build applications quickly. For instance, you can hook up a function with OSS for image and video data processing. When new data is uploaded to OSS, a function is triggered automatically to process the uploaded data.
- Elastic scaling in milliseconds. Function Compute absorbs all of your traffic instantly in any scale.
- Pay-As-You-Go. You are only charged for the computing resources you actually use, which significantly reduces your costs. It is suitable for business scenarios with unpredictable traffic patterns.
| Function Compute | Self-built Computing Environment | |
| Maintainability |
|
|
| Reliability | Code and configurations are stored in OSS with automatic, multi-level redundant backup |
|
| Cost |
|
|
| Security |
|
|
Typical Applications of Serverless Architecture
Scenario 1: Event-Triggered Computing
Serverless can be applied to scenarios that involve multiple devices accessing various file types, such as mobile phones and PCs uploading images, videos, and text files.
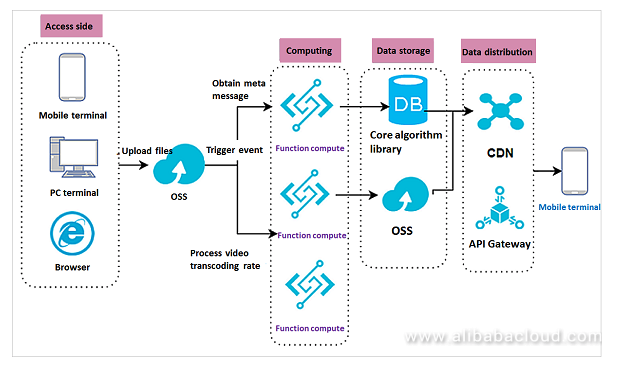
You can apply a serverless architecture for similar use cases on Alibaba Cloud by using Function Compute with Object Storage Service (OSS). After a user uploads video files to OSS, Function Compute is triggered to obtain and transmit the object metadata to the core algorithm library. Based on the algorithm, the core algorithm library pushes the relevant video files to the CDN origin site, hot-loading the specified video. In another scenario, after video files are uploaded to OSS, Function Compute is triggered to synchronize multiple transcoding rates and store the processed video files in OSS. This provides a lightweight data processing solution.
In multimedia processing scenarios, massive volumes of files are often uploaded to OSS for processing, such as watermarking, transcoding, fetching file attribute data. Function Compute can help users easily address technical difficulties in event-triggered computing scenarios through these features:
- Function Compute can set OSS triggers to receive event notifications. In Function Compute, you can write codes to process files and transmit files to OSS over the intranet. The entire process is simple and scalable.
- You can build your core code into Function Compute and use the code to concurrently process event notifications.
- Function Compute currently supports internal interaction with other products.
Scenario 2: Elastic Resizing for Live Video Broadcasting
Serverless architecture is ideal for live video broadcasting scenarios. In the diagram below, the broadcasting room client collects audio and video streams from hosts and audiences and sends them to Function Compute for multiplexing. Function Compute sends the collected data to the multiplexing service for synthesis and pushes the synthesized video stream to CDN. Viewers can pull the live stream in real time to view the multiplexed and synthesized video.
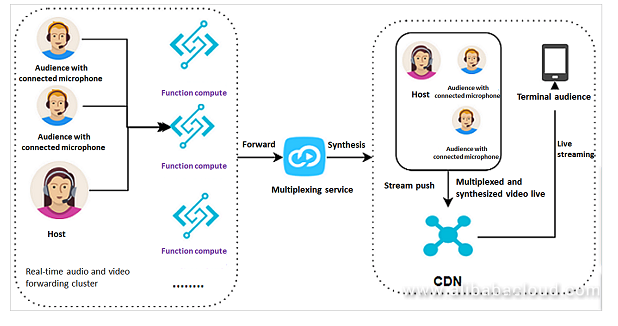
In certain live video scenarios, multiple audience members may interact, so the host is simultaneously connected to multiple microphones. The host can connect multiple audience members or friends to the screen and synthesize the picture into a single scenario, which is then provided to the livestream viewers.
Serverless architecture addresses the difficulties that may arise in such scenarios. As a real-time audio and video forwarding cluster for the host and connected microphones, Function Compute automatically resizes multiple execution environments used to process real-time data streams based on the concurrent volume. After traffic peaks, Function Compute can reduce the resource volume appropriately. Code management capabilities are deployed on the cloud, allowing you to modify and maintain code iterations at any time. You no longer have to manage multiple software runtime environments.
Scenario 3: IoT Data Processing
Serverless architecture can be applied to Internet of Things (IoT) scenarios such as the one shown below.
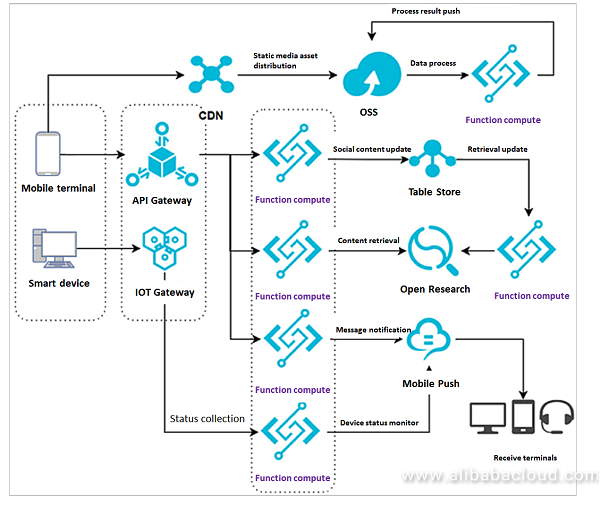
The architecture is divided into two parts:
- Web application: Simulates a social media content update and data processing flow. Requests from web users are forwarded from API Gateway to Function Compute for processing. Function Compute then updates the processed content in the database and updates the index. Another Function Compute instance pushes the index update to the search engine, where the new content is retrieved by external customers. This is a closed loop data process.
- Smart devices: The IoT gateway pushes smart device statuses to Function Compute for processing. Function Compute uses an API to send messages to Mobile Push, which pushes the messages to mobile terminals for status confirmation and management.
Smart device status processing also generates several key technical difficulties. You must design an efficient non-polling technical framework to process the status data from a large number of devices to the IoT platform. Then, you need a way to efficiently and transparently transmit the processed data to other products, such as writing to a database or pushing data to mobile terminals.
Scenario 4: Shared Delivery Dispatch System
Customers can use a dispatch platform to choose from the services provided by various sellers, such as ordering food or buying products. The dispatch platform then notifies the nearest delivery staff to pick up the relevant product from the nearest seller and deliver the product to the customer. A simple process is shown in the following figure:
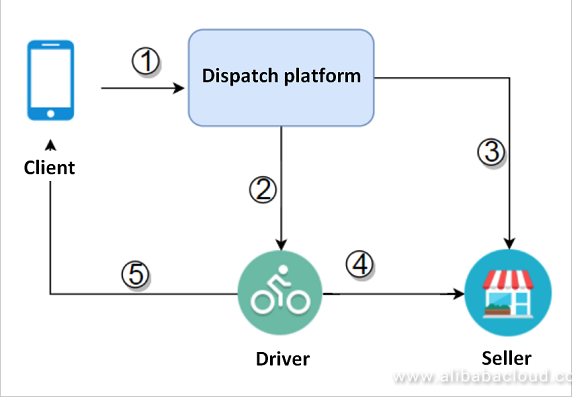
Process details:
- The customer notifies the dispatch platform to order a product.
- The dispatch platform notifies the nearest delivery staff.
- The dispatch platform simultaneously notifies the seller to sell the product.
- The delivery staff goes to the specified seller to pick up the product.
- The delivery staff delivers the product to the customer's location.
Such a process can be easily implemented with a serverless architecture. In the diagram below, Alibaba Cloud Function Compute is used with other products to develop a delivery dispatch system.
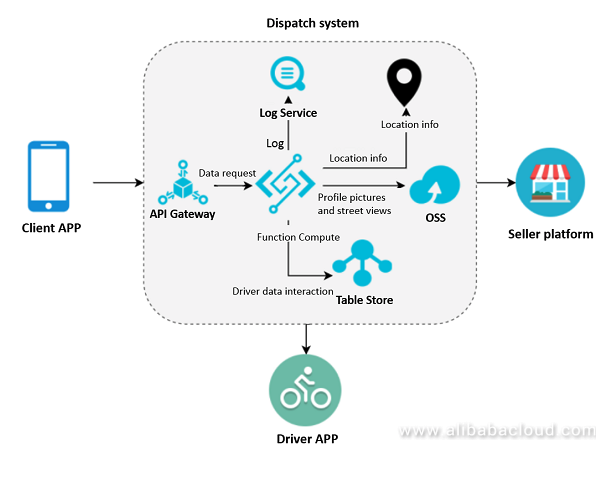
Process details:
- The customer app transparently transmits an order request through API Gateway to Function Compute.
- Function Compute transmits the processed data to Table Store.
- Table Store stores route data, seller information, and location information.
In this solution, Function Compute can provide dynamic resizing capabilities, while API Gateway performs authentication and ensures secure access. Function Compute can communicate with multiple products to seamlessly use other resources and content. All processed data is stored in Table Store databases, and all logs are directly loaded to Log Service for subsequent data reporting.
Summary
Through the preceding scenarios, we can conclude that serverless architecture brings a multitude of benefits not only to developers but also to businesses. Alibaba Cloud Function Compute helps you develop a serverless architecture while addressing cost, efficiency, and connectivity considerations.
Although Function Compute is applicable to many scenarios, it is not a one-size-fits-all solution. For example, it may not be the most cost effective solution for businesses that do not have significant request fluctuations. In addition, Function Compute's execution environment does not record states, so serverless frameworks are not well suited to tightly coupled applications. However, as an emerging technology, serverless frameworks have yet to show its full potential for developers and businesses.
Published at DZone with permission of Leona Zhang. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments