Learn More About AWS DevOps Architecture and Tools
In this post, we will concentrate on Amazon web Services (AWS) DevOps. We'll discuss design, best practices, and some of the AWS DevOps tools.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIt is a blend of "growth" and "operations,". DevOps is a collection of agile software design practices. It's a simplistic approach and there's a lot of different varieties to choose from.
In this post, we will concentrate on Amazon web Services (AWS) DevOps. We'll discuss design, best practices, and some of the AWS DevOps tools. You can revisit a few simple words and definitions before we scrutinize AWS DevOps.
What Is DevOps?
Building on the earlier brief description, Amazon defines DevOps as follows:
DevOps is a synthesis of ideologies, methods, and instruments of culture. This enhances the ability of an organization to deliver high-speed applications and services. It develops and improves products at a faster pace. This includes traditional software development and infrastructure management processes
What Is AWS?
Cloud computing has increased in popularity. This is because users have a choice of more than a dozen different cloud providers. This includes Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, and IBM Cloud Services. AWS is the acronym for the cloud service Amazon provides, Amazon web Services. AWS provides all the services and features you usually get in an in-house data center. It is the largest accessible cloud provider. Now that you've learned DevOps and AWS, let's look at what the AWS DevOps is exactly.
AWS DevOps
AWS DevOps is Amazon's answer to the DevOps methodology. It is using its cloud infrastructure and dedicated resources and services. AWS offers a collection of flexible services. This allows designers to develop and deliver products quickly. This is possible using AWS DevOps practices. This will simplify the provision and management of infrastructure.
Besides also helps in deploying application code, automating software release processes. You can track the performance of the application and infrastructure." This helps users to securely store and version source code for applications. While creating, checking, and deploying to either on-site environments or AWS you can store information.
Cloud computing has three main categories:
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
AWS falls under the IaaS category. It is a flexible instant-computing network that the user completely manages. This includes virtual servers and operating systems (OSes). I hope with the introduction you reach an understanding of AWS DevOps. Let us continue our understanding by analyzing AWS DevOps architecture.
AWS DevOps Architecture
You need to break down the underlying architecture of the system. It is possible by using AWS EC2 as our example, to get a better idea of what's involved in implementing DevOps on AWS. EC2 is an Elastic Computing Cloud. It allows users to configure virtual machines and their infrastructure from a central console. Automation helps the managers to make sure resource size suits the needs of their company. That makes the whole process more cost-effective and efficient.
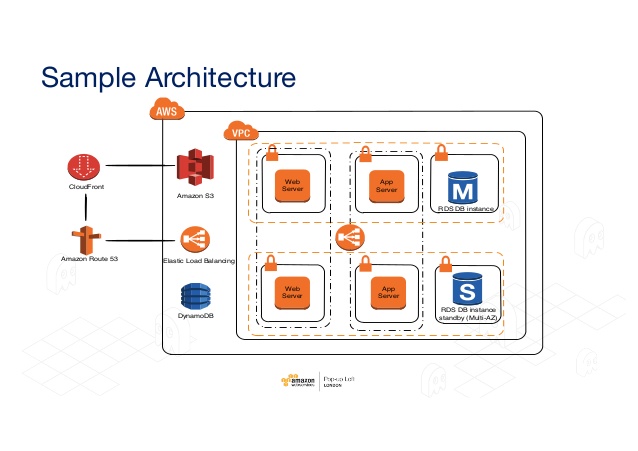
Balancing Pack
Many architectures of the web application support load balancing. This virtual network appliance distributes EC2 traffic through several available web server resources. It depends on traffic demands, you can increase or reduced traffic. To automate this AWS provides the Elastic Load Balancing operation.
CloudFront on Amazon
The service provides content like a website and may include forms of features, uploading, and statics. You can operate in combination with other AWS components. This is compatible with non-AWS clouds.
Protection Collective Amazon
Security is a major concern because of the rise in hacking incidents. This feature serves as a firewall for inbound networks. To gain access to EC2, customers need to specify the approved protocols, ports, and source IP ranges. Users that offer one or more security groups to each EC2 instance, each of which will send the approved traffic to the correct instance.
Elastic Cache
This web service handles the memory cache of the cloud. The elastic caches reduce the burden on the services. Therefore, increases efficiency and scalability.
Amazon Relational System Database (RDS)
The RDS service simplifies the setup, application, and scalability of a cloud-based relational base. This handles the functions and activities of day-to-day database management. This offers a scalable, cost-effective way to work with relational databases. RDS currently supports the following databases.
- Amazon Aurora
- MariaDB
- Microsoft SQL Server
- MySQL
- Oracle
- PostgreSQL databases
Simple Storage Service (S3) by Amazon
The AWS cloud provides two ways to access, back up, and store data from web apps and other properties. S3 provides users with a simple interface for accessing any amount of data. You can access from anywhere on the network, at any time. Within containers, users store data as objects. In turn, these objects you may access, add to, read, or delete as required.
Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS)
This is a high-performance storage block solution. This helps to manage data partitions and application logs. Users switch to EBS when they need easy access and stability over the long term. EBS volumes are suitable for handling primary storage for databases, file systems. Besides, it needs access to unformatted, raw, block-level storage, and granular updates.
Amazon Scaling Auto
This service generates server capacity groups. Therefore, you can extend or reduce as required and on-demand by users.
Create and Deploy AWS DevOps
To create and deploy AWS DevOps you need these following tools.
- AWS Code Pipeline
- AWS Code Commit
- AWS CodeBuild
- AWS CodeDeploy services from a Construct and Deploy point of view
AWS Code Pipeline
AWS Code Pipeline is similar to the Jenkins Pipeline.
It helps to see the end-to-end delivery process visually. Therefore, you usually install the following.
Source Code Repository in a Code Pipeline
The source code will need to be either in the repository of AWS CodeCommit or GitHub.
Construct Software:
You can configure the specifics of AWS CodeBuild as part of the pipeline.
Deploy Software
It is to configure AWS CodeDeploy into the system.
When permissions are required, you can also modify them during the deployment process to different environments so that if there is a code change by the developer, the visual representation of Build and you can see Deploy automation.
AWS Code Commit
CodeCommit is a secure online version control service that hosts private Git repositories. Instead of using AWS CodeCommit to store their source code or even binaries such as the WAR / JAR / EAR files created from the build, a team does not need to maintain their version control repository.
You build a repository with AWS CodeCommit and each developer copies it to their local machine, adds files to it, and moves it back to the AWS CodeCommit repository. With the AWS CodeCommit repository, one uses the standard GIT commands.
For example, once the AWS CodeCommit repository is cloned to a local machine, commands such as 'git pull,' 'git add,' 'git commit,' 'git move,' etc.
Illustrative AWS CodeCommit created empty repository AWS CodeCommit created an empty repository.
Copy repository to local computer Clone repository to local machine Files added to repository AWS CodeCommit Files added to repository AWS CodeCommit
AWS CodeBuild
As we have seen the source code and other objects for the project are held in the repository of AWS CodeCommit.
To implement Continuous Integration AWS CodeBuild like Jenkins gets the latest changes to source code from AWS CodeCommit or GitHub repository as configured and based on the build specification YAML file (created as buildspec.yml) the commands are run based on the four phases such as Install, Pre-build, Build and Post-build.
version:10.0
Os: Linux
Files:
-source: /opt/deploy/index.html
Destination:/var/www/html/
Hooks:
BeforeInstall:
-location:scripts/before_install
runas:niranjan
AfterInstall:
-location:scripts/restart_server
runas:niranjan
The objects (WAR / ZIP / JAR / EAR) are stored in the AWS Storage which is an S3 bucket until the construction is complete.
AWS CodeDeploy
As the name suggests AWS Codedeploy is the deployment software that automates the program deployment (in this case WAR file) to the Linux or Windows instances of Amazon EC2.
As we now have the artifacts stored in the S3 bucket, which was completed using AWS CodeBuild, the artifacts are then picked up from the S3 bucket and correctly deployed in the AWS EC2 instance provisioning to the Tomcat or JBoss system server, etc.
AWS CodeDeploy relies on a YAML file called appspec.yml that has instance deployment instructions for the EC2 instances.
Conclusion
I hope you decide to try AWS DevOps technology. You can learn more from industry experts at AWS online training.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments