What Is Continuous Testing?
Continuous Testing helps us build the right product by implementing testing at every phase of the Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC). Read to learn more.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeTesting is a crucial part of the Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC). Testing should be included in every stage of the SDLC to get faster feedback and bake the quality within the product. Test automation can get you excellent results if it is implemented and used in an efficient way and continuous testing is the right approach.
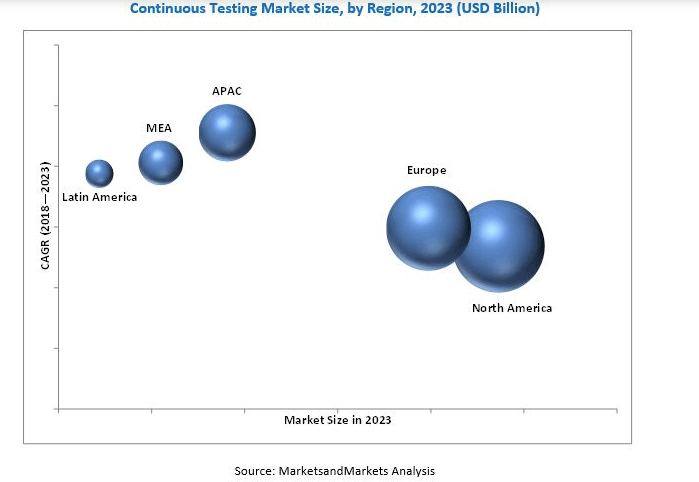
According to Markets and Markets, the continuous testing market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 15.9% during the forecast period of 2018-2023 and reach $2.41 billion by 2023. 2017 was considered the base year for estimating the market size.
In this article, we will discuss what continuous testing is, how to implement it, and what benefits we can get out of it.
What Is Continuous Testing?
Continuous testing helps provide faster feedback in all stages of the Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC). In most SDLC cases, it is seen that minimal automated tests are written at the core level, hence, increasing the pressure on the top level of the test pyramid to perform manual exploratory testing.
This actually hits the quality because catching an error after the development is complete is very costly. The table below shows the cost to fix a bug at Google and you can see it costs a whopping $5000 when a bug is discovered in the “System Testing” phase.

Continuous testing helps us evaluate this fear of software failing by providing early feedback as soon as the code is committed to the repository. The main goal of continuous testing is to test early at all stages of the SDLC with automation, test as often as possible, and get faster feedback on the builds.
You might know about the Go/No-Go meetings, which are set up before every release, this meeting helps you find out whether you are headed in the right direction. It helps you decide whether you are good to release the application with the respective features in the production or not.
Similarly, continuous testing works, it provides you the test results based on what you decide you can move to the next stage of development. Using continuous testing, we can fix all failures as soon as they occur before moving on to the next stage, which eventually helps save time and money.
Why Is Continuous Testing Needed?
In one of my previous projects, we were working on a mobile application to be developed for iOS and Android platforms. The client wanted everything to be automated from the inception itself. Any bug leakage into production meant it will impact the business directly and cost millions of dollars.
We were asked to present a plan for automation where testing would be carried out in every stage of the development to minimize the risk of bug leakage. Hence, we decided to implement the test pyramid and create a CI/CD pipeline where testing would be done continuously at every stage.
Here is the graphical representation of the CI/CD Pipeline that. can also be taken as a practical guide to implementing continuous testing in a project:
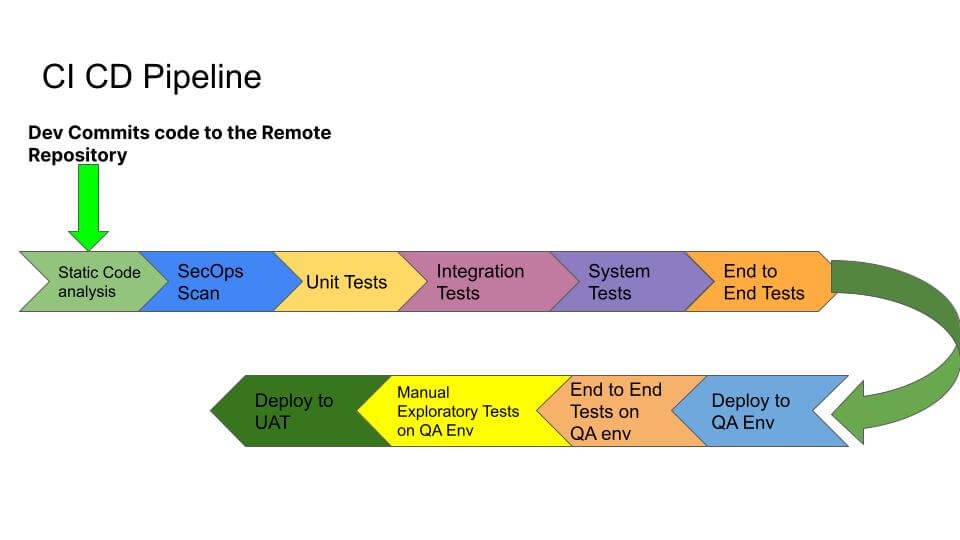
To bake the quality within the product, we came up with a plan to introduce testing at every stage in the pipeline, and as soon as any red flag appears, it should be fixed before we move on to another phase. So, as soon as the dev commits the code to the remote repository, the following scans would run:
- Static code analysis: This will ensure the best coding practices are followed and alert us with code smells in case of any errors.
- SecOps scan: This will scan the code and all the libraries used within the code for any security vulnerabilities and raise a red flag in case of “Critical,” “High,” “Medium,” or “Low” level vulnerabilities that should be taken care of.
Once the above scans are successful, the pipeline would move ahead and run the following tests in the development environment:
- Unit tests
- Integration tests
- System tests
- End-to-end tests
All of the above tests will ensure the code is working perfectly as expected.
If any of the above tests fails, the pipeline will break and a red flag will be raised. It is the developer’s responsibility to fix those respective failing tests. It’s not about playing the blame game, but finding the commit that broke the build and fixing it. The team will offer help to the developer to fix the issue.
After all the above-mentioned tests pass successfully, the build will be deployed to the QA environment where end-to-end automated tests will run on the QA build as a part of regression tests.
Once the end-to-end automated tests pass on a QA build, QA will pick up the build and perform manual exploratory tests to uncover any further defects in the build. Once QA signs off the build, it will eventually be deployed to the UAT env where further rounds of testing will be done by the UAT team of testers. Finally, after the sign off, the build will be deployed into production.
This plan worked for us tremendously as we uncovered many issues in the first and second stage of the pipeline when the unit and integration tests were run.
The Static Code Analysis and SecOps scan helped us implement the best coding practices and fixing vulnerable libraries by updating to the latest version or discarding and using the libraries that were less prone to vulnerabilities and also frequently updating them so the code is less prone to security risks.
Though we also discovered issues in the exploratory testing, which was done manually; however, those were not that critical. Most of the issues were resolved in the initial phase, which provided us faster feedback.
Continuous Testing: The Need of the Hour
No Longer Good but a Must Have in the SDLC Lifecycle
From my experience, the following points are derived, which states why continuous testing is needed:
- Requirements change frequently: With the requirement changing frequently, the need arises to change the code as well, and with every change we do, there is a risk involved. There are two risks involved here:
- Whether the changed code will work as expected.
- If this change impacts the existing code.
- With continuous testing, we can tackle both of these risks by setting up an automated pipeline, which will run the unit, integration, and, eventually, automated regression tests.
- Continuous integration:With agile development in place, continuous integration has gained a lot of popularity where developers merge their code to the main branch as often as possible, to make it production ready.
- Continuous testing helps us here because before merging takes place, the code goes through a pipeline where automated tests are run against the build. If there is a failure, the code does not merge and a red flag is raised.
- Production ready: With continuous testing, we can be production ready as all our checks and tests run on an automated pipeline as soon as the developer commits the code.
- Reduce human errors: In the case of regression tests, if an automated test is written, it can serve as a documentation proof for the feature and help reduce human errors in testing.
Advantages of Continuous Testing
- Fast feedback: In the traditional software development process, the team had to wait for the tester’s feedback, who would test the build manually after the developer completed writing the feature from their end. After the tester’s feedback, they had to rework to fix the issues that were time-consuming and more costly. With continuous testing, we can get faster feedback on the newly committed code and save time and money.
- Quality baked within the product: With all tests running in the automated pipeline, from unit, integration, functional, security, performance, and end-to-end user journeys, we can be sure that quality is baked within the product itself and need not worry about releasing it to production.
- Reduces bug leakage: Continuous testing helps in eliminating the chances of bugs occurring in the build by providing us with timely updates about software failures.
- Minimize the risks: It also helps find the risk, address them, and improve the quality of the product.
Important Types of Continuous Testing
- Unit tests: This involves testing a piece of code in isolation. Basically, testing every method written for the feature. The main objective of this test is to check that the code is working as expected, meaning all the functionalities, inputs, outputs, and performance of the code are as desired.
- Integration tests: This involves testing the two modules together. The goal of this test is to ensure the integration between the two components is working fine.
- Regression tests: This is the most widely used test and is used to ensure the existing functionality of the application is working as expected after the latest addition or modification to the code repository,
- End-to-end Journey tests: These tests are added to check the end-to-end working of the software. The goal of these tests is to ensure the end user is able to use the application end to end.
Future of Continuous Testing
With the ever-increasing demand for high-quality software and the economies flourishing with digitalization at its core, continuous testing is considered an important aspect. A software company is required to respond to frequent changes happening daily in the SDLC and continuous testing is the answer.
The following points are the benefits of continuous testing:
- To adapt to the frequent changes in the software.
- To achieve maximized automation in the delivery cycle and avoid loopholes in the process.
- Minimize human errors.
- To provide a cost-effective solution to the end customer.
- Beat the competition and outperform the competitors by releasing bug-free software.
- Baking the quality within the product.
As technology progresses, so is the need to upgrade the process. With continuous testing, best results can be achieved.
Role of Cloud Services Platform in Continuous Testing
Last year, I was working on a mobile application development project, which had iOS and Android versions to be rolled out. Now, as it was planned to be rolled out in different regions around Germany, we studied mobile phone usage in the different areas of Germany and came to know that Android and iPhones are used in all areas.
Hence, we concluded that we will need a combination of at least six devices (three Android devices and three iPhones) to test our build, two devices to test minimum supported versions, two devices with the latest versions, and two devices with random versions between the highest and minimum supported ones.
The hard part was to get these devices, as mobile phones and their versions are updated nearly every 2-3 months, so even if the organization invested and bought these devices, it would be required to update them occasionally when the new version launches. Here, the cloud platform services came to the rescue and we simply purchased the right plan as per our requirement and got access to the required real devices, which helped us test the applications smoothly by running automated and manual exploratory tests on the real devices on the cloud platform.
In today’s fast-paced world, there are multiple platforms where software works, from browsers to mobile phones and tablets. As we release the application to production, we need to make sure it runs on all the desired platforms and fix the things we find that are not working.
However, to do that, we need to test it on the respective devices/browsers to ensure it works hassle-free. This is possible but will cost money and time as we will have to purchase the hardware and provide the required resources to make it work. From hiring engineers to setting up the infrastructure.
As we are testing continuously, performing parallel runs on the different browsers and their respective versions OR on different mobile devices with different OS versions, these services help us test continuously by providing us with the required device, browsers/OS and their variety of versions, so we catch the bugs early and using the early feedback to fix the required issue and stop the bug leakage.
Conclusion
Quality is a crucial part of software and needs to be baked in the software. Continuous testing helps us build the right product by implementing testing at every phase of the Software Development Lifecycle.
We need to be production ready with every feature we build, which is necessary to get fast feedback with a fail-fast strategy. There are various testing types available that help us implement continuous testing using automated pipelines.
Cloud Services Platforms provide us with the right infrastructure to keep up the pace with testing continuously by providing the required infrastructure.
Published at DZone with permission of Faisal Khatri. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments