What Are Ephemeral Environments?
This article will discuss ephemeral environments and how they work to test and scale your deployments.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeThe world of DevOps today is characterized by exciting new approaches and tools revolving around developer experience and productivity. Gone are the days when manual testing and deployment used to take days to complete. Instead, these new tools automate and streamline the software development pipeline. Whenever any application is created, it’s typically entered into a continuous integration (CI) tool or platform that tests the code through various frameworks. If the tests are passed, the code will be deployed.
However, increasing velocity is difficult if your processes and tools are tedious and complex to configure. That’s why ease of use is non-negotiable for every developer evaluating any new tool. Developers like a CI tool that’s not only easy to set up but can also scale to test their applications. Configuring infrastructure and other related tasks is daunting and time-consuming, taking resources away from deployments.
This is where a concept called ephemeral environments comes in. Ephemeral environments can be used to test your applications much faster by spinning up short-lived environment instances and automatically destroyed after the work is done. This article will discuss ephemeral environments and how they work.
What Are Ephemeral Environments?
Ephemeral environments are an excellent way for engineering and development teams to collaborate and test new features quickly and efficiently. They provide a temporary, isolated environment for running tests and previewing features without worrying about making any permanent changes that may impact production systems. This allows for rapid iteration and development without committing to long-term changes.
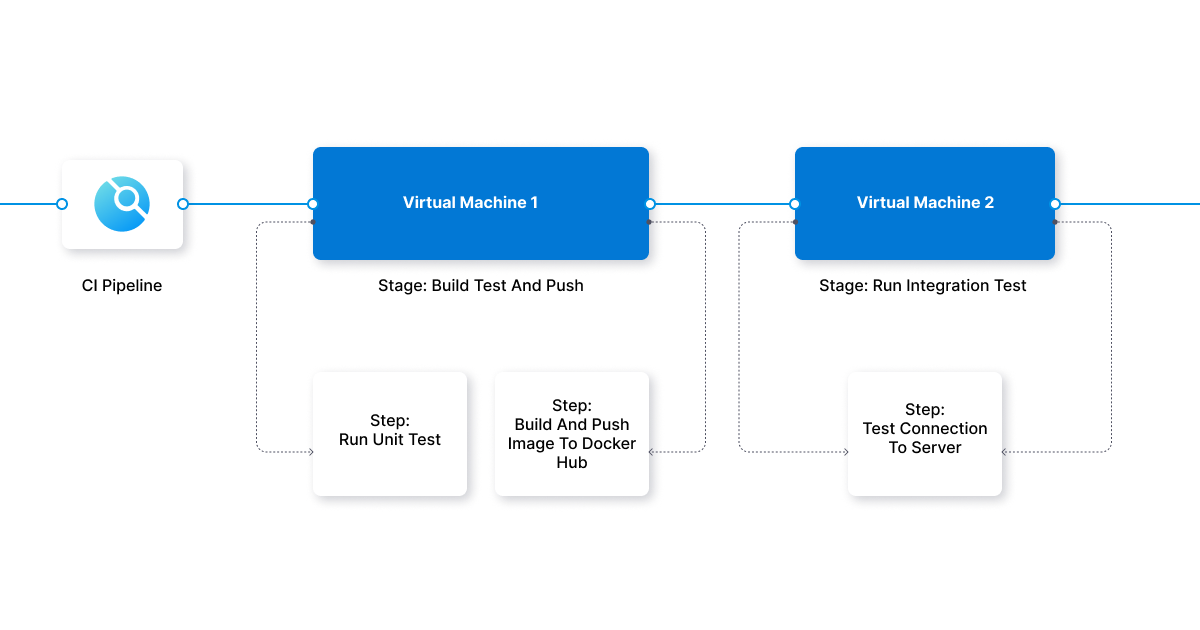
Configuring an ephemeral environment allows you to customize the environment to meet specific needs and preferences, such as the preferred operating system, number of servers, or type of memory and storage. Once the environment is set up, you can utilize that environment to run tests and experiments on your application.
Running an application in an ephemeral environment is relatively simple. All of the necessary files and configurations will be packaged into a single deployable artifact. This can then be deployed to the ephemeral environment and quickly spun up, allowing for rapid application development and testing.
The process is usually automated, allowing for continuous deployments and the environment to be easily rolled back if necessary. Additionally, the process can be configured to run certain tests or other checks before the deployment is finalized. This helps ensure that the application runs as expected and is free of errors or issues.
Advantages of Ephemeral Environments
Overall, ephemeral environments provide a robust, on-demand platform for quickly testing and previewing new features. Let’s dive into some of their distinct advantages over traditional static or shared staging environments.
Asynchronous Collaboration
Ephemeral environments make it easier for teams to collaborate asynchronously. This is especially useful when teams are distributed across different time zones. Setting up an ephemeral environment allows teams to share their work and collaborate on projects without having to work simultaneously. They are also commonly used for previewing features as teams can quickly spin up a new environment to test out new ideas without affecting existing services.
Cost Effective
Ephemeral environments are cost-effective, simple to set up, and can be destroyed and recreated when needed, making them an excellent choice for teams collaborating across multiple projects. In addition, they give the developers temporary environments that can be efficiently utilized to test, experiment, and destroy after the experiment is finished. As a result, developers don’t need to worry about adding additional costs by running resources directly from their cloud providers.
Agile and Flexible
The ephemeral environment is far more agile and flexible than conventional environments, allowing developers to quickly spin up an application instance with the exact specifications they need. This makes deploying and testing changes easier without waiting for a new application version to be built and deployed. Additionally, ephemeral environments allow teams to quickly scale up their applications to meet the demands of their users and reduce operational costs by automatically shutting down instances that are no longer needed. Finally, ephemeral environments also provide increased security and reliability, as they are entirely isolated from other instances and automatically destroyed after a specific period.
Conclusion
In conclusion, using ephemeral environments in a CI/CD pipeline offers several benefits to development teams. Developers can more easily reproduce issues by creating disposable environments for each pipeline stage and ensuring consistent and reliable results. Ephemeral environments also reduce the risk of conflicts and interference from other ongoing development work, as each environment is self-contained and isolated.
Furthermore, ephemeral environments can help reduce costs by using only the resources needed for each specific stage of the pipeline, rather than maintaining dedicated infrastructure for each stage. This allows teams to scale their development and testing resources more efficiently and cost-effectively.
In summary, using ephemeral environments in a CI/CD pipeline is a best practice to help development teams achieve faster, more reliable, and cost-effective software development and delivery.
Published at DZone with permission of Pavan Belagatti, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments