Using R on Jupyter Notebook
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For Free
Overview
R is an interpreted programming language for statistical computing and graphics supported by the R Foundation. It is widely used among statisticians and data miners for developing statistical software and data analysis.
R is available as Free Software under the terms of the Free Software Foundation’s GNU General Public License in source code form. It compiles and runs on a wide variety of UNIX platforms and similar systems (including FreeBSD and Linux), Windows, and macOS.
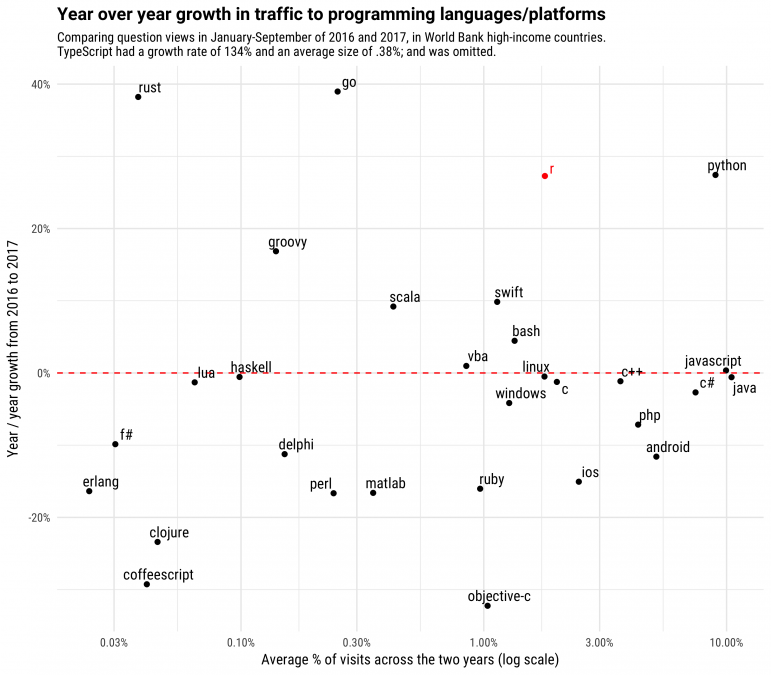
According to the information from stack overflow in 2017, the R programming language had shown outstanding growth from 2016 to 2017. The growth of R could be explained by the popularity of data science.
Typically, most R developers use R Studio as a tool to develop R applications and display results. This article provides an alternative via Jupyter Notebook.
Jupyter Notebook
Jupyter Notebook is an open source web application that allows you to create and share documents that contain live code, equations, visualizations, and narrative text. It can be used as a tool for interactively developing and presenting data science projects. Mostly, it is used with Python, but it is possible to use Jupyter Notebook with different programming languages, including R. For a list of supported programming languages, please refer to the Jupyter kernels page in GitHub.
This article explains steps to setup Jupyter Notebook for R on Windows 10 and provides links to R examples that demonstrate how to use Refinitiv’s APIs with Jupyter Notebook.
Setting Up Jupyter Notebook for R
There are several ways to setup Jupyter Notebook for R. The following steps are suitable for Windows 10 machines, which don’t have any versions of R and Python installed. For other installation methods, please refer to R, Python, and Jupyter websites.
1. Install R
The precompiled binary distributions of R packages (Linux, Mac OS X, and Windows) are available at the Comprehensive R Archive Network [CRAN]. Download R for Windows and then install it on the machine. After that, both R 32bit and 64bit are installed on the machine. In this article, R 3.6.1 64bit is used.
2. Install Python
Python packages are available at the Python website. It supports many operating systems, such as Windows, Linux/Unix, and Mac OS X.
Download the Windows version and then install it on the machine. In this article, Python 3.7.4 64bit is used. You need to verify the installation path or choose the Add Python 3.7 to PATH option to add the Python installation path to the PATH environment variable.
However, the Add Python 3.7 to PATH option may introduce version conflicts among the installed Python versions. If you have multiple versions of Python installed on the machine, please beware of this option.
After installing, open the Windows Command Prompt to verify the version of Python (python -- version).
You may install different Python Distributions, such as Anaconda. Please refer to the Anaconda website for more information.
3. Install Jupyter Notebook
Jupyter Notebook can be installed with the pip command. Open the Windows Command Prompt and use the following commands to install Jupyter Notebook.
python -m pip install --upgrade
pip python -m pip install jupyter
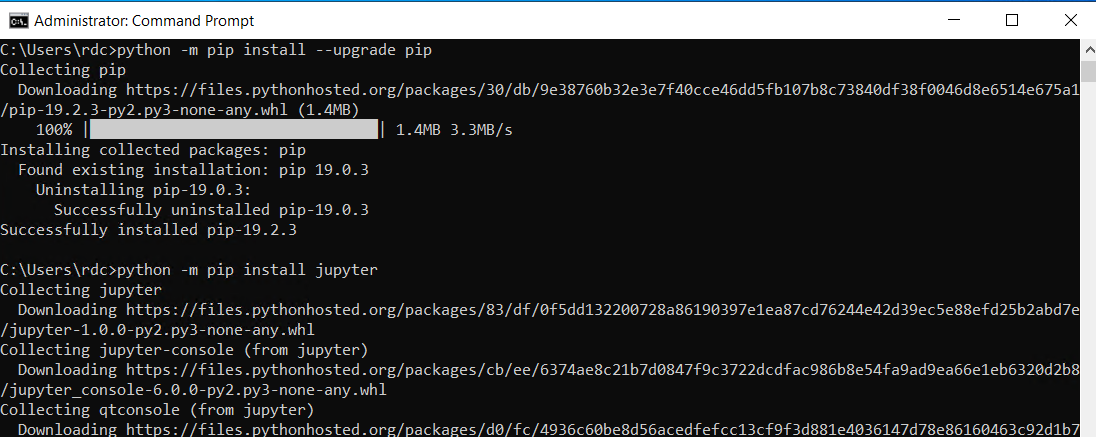
Then, run jupyter notebook from the Windows Command Prompt to start the Jupyter Notebook.
At this time, the Jupyter Notebook only supports Python 3.
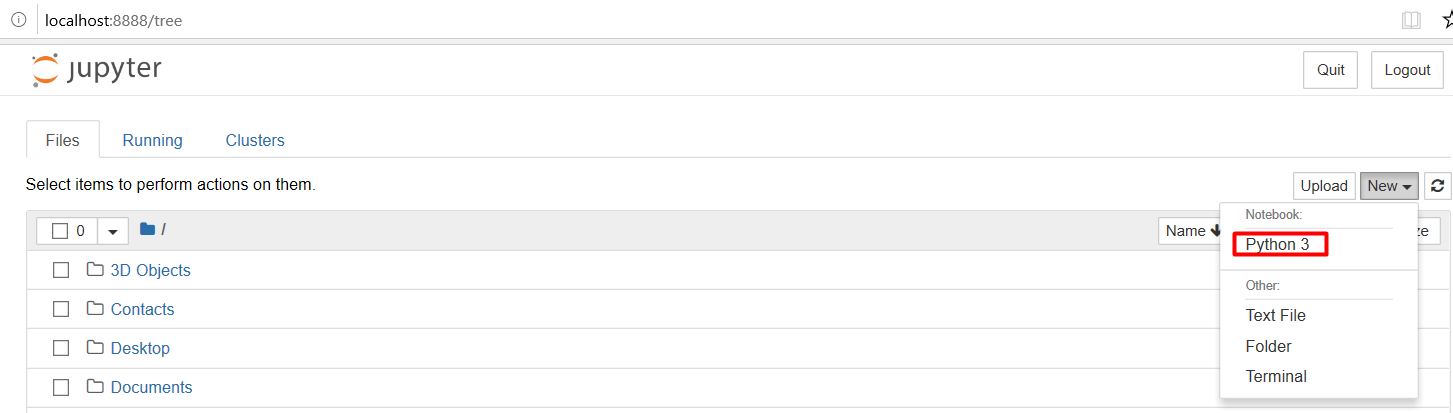
For different Python distributions, please refer to the distribution websites regarding how to install Jupyter Notebook.
4. Install R kernel for Jupyter Notebook
Jupyter Notebook has kernels that are processes that run interactive code in a particular programming language and return output to the user. IRkernel is an R kernel for Jupyter Notebook.
IRkernel can be installed via the Comprehensive R Archive Network [CRAN]. Open the R x64 GUI and follow these steps.
Installing via CRAN
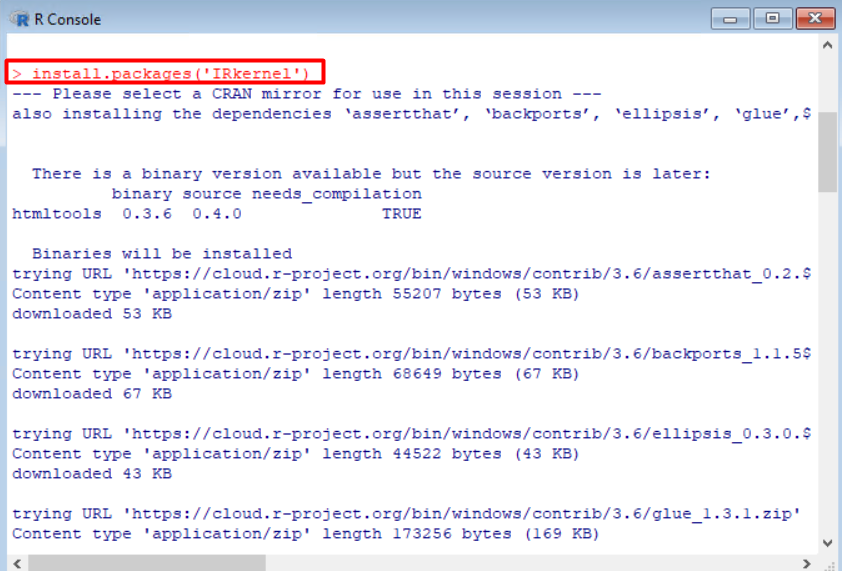
You can install the IRkernel package by running to the following command in an R console:
install.packages('IRkernel')
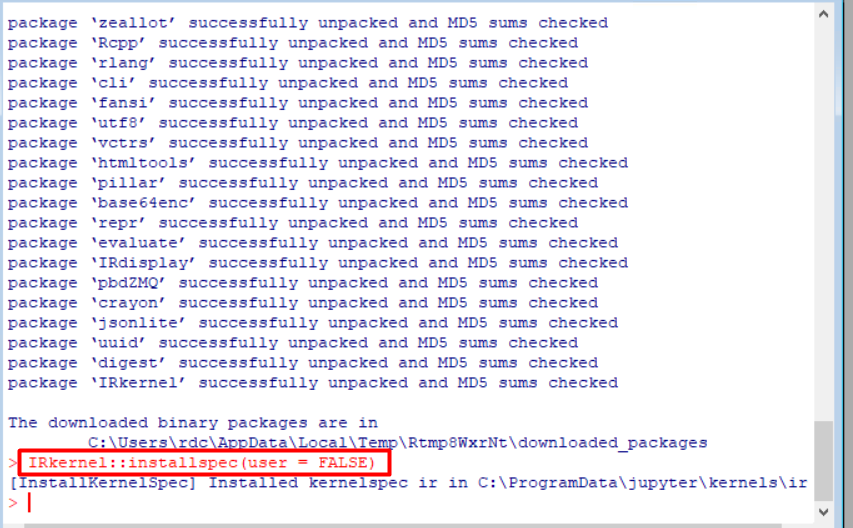
Making the kernel available to Jupyter
Then, you will have to make Jupyter see the newly installed R kernel by installing a kernel spec. To install system-wide, set user to False in the installspec command:
IRkernel::installspec(user = FALSE)
Then, run jupyter notebook via the Windows Command Prompt. Now, the Jupyter Notebook supports both Python 3 and R programming languages.
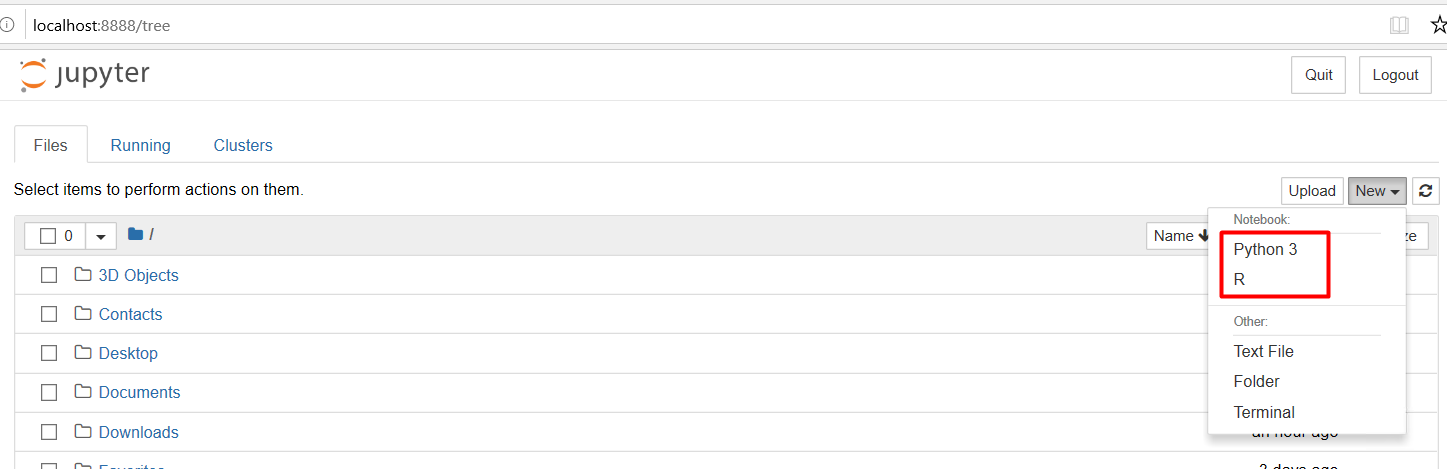
Refinitiv’s APIs Examples
The section provides links to R examples that use different Refinitv’s APIs to retrieve and display financial data on Jupyter Notebook. The examples are available GitHub and the valid credentials are required to run the examples.
Eikon is a set of software products provided by Refinitiv for financial professionals to monitor and analyze financial information. It provides access to real-time market data, news, fundamental data, analytics, trading, and messaging tools.
It also provides Eikon Data API to access Eikon data directly from any application running on the same Eikon desktop. The data retrieved by Eikon Data API includes real-time, fundamental, historical, symbology, and news data.
This example demonstrates how to use Eikon Data API with R on Jupyter Notebook to retrieve the latest data, historical data, symbology, and news. It uses the eikonapir package to retrieve data from Eikon and uses the Plotly package to draw charts. It also uses the IRDisplay package to display news in HTML format.
Datastream is the world’s leading time-series database, enabling strategists, economists, and research communities access to the most comprehensive financial information available. With histories back to the 1950s, you can explore relationships between data series; perform correlation analysis, test investment and trading ideas and research countries, regions, and industries.
It provides the Datastream Web Service (DSWS) API to access Datastream content based on SOAP/XML, REST/JSON, and .NET.
This example demonstrates how to use DataStream Web Service with R on Jupyter Notebook. It uses the DatastreamDSWS2R package to retrieve data from DataStream Web Service and uses the Plotly package to draw charts.
3. Refinitiv Data Platform R Example
Refinitiv Data Platform (RDP) is a cloud-based product from Refinitiv. This product provides financial data and associated analytics that’s used by financial professionals globally. This data includes real-time data from various stock exchanges around the world as well as reference and historical data.
RDP includes simple standard REST-based APIs for accessing this financial data. The requested data is delivered using a Request-Response mechanism. An application uses a web request (HTTP GET, POST, PUT or DELETE) to convey the request message and parameters, and the RDP service responds with data synchronously.
This example demonstrates how to retrieve historical data from the Refinitiv Data Platform with R on Jupyter Notebook. It uses the httr package to send HTTP request messages and uses the Plotly package to draw charts.
References
- “R (programming language)”, Wikipedia, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/R_(programming_language).
- “The R Project for Statistical Computing”, https://www.r-project.org/.
- “The Python official website”, https://www.python.org.
- “Anaconda Distribution”, https://www.anaconda.com/distribution/.
- “Installing the Jupyter Software”, https://jupyter.org/install.
- “R kernel for Jupyter Notebook”, https://irkernel.github.io/.
- “Refinitiv Eikon Data API”, https://developers.refinitiv.com/eikon-apis/eikon-data-api.
- “Refinitiv Datastream Web Service”, https://developers.refinitiv.com/eikon-apis/datastream-web-service.
- “Refinitiv Data Platform”, https://developers.refinitiv.com/refinitiv-data-platform/refinitiv-data-platform-apis
- “Getting Started with Plotly in R”, https://plot.ly/r/getting-started/.
- Robinson, David. “The Impressive Growth of R”, stack overflow, 10 October 2017, https://stackoverflow.blog/2017/10/10/impressive-growth-r/.
- Pryke, Benjamin. “Jupyter Notebook for Beginners: A Tutorial”, Data Science Tutorials, 22 August 2019, https://www.dataquest.io/blog/jupyter-notebook-tutorial/.
Further Reading
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments