Usability Testing: A Comprehensive Guide With Examples And Best Practices
Learn how usability testing is a great way to discover unexpected bugs, find what is unnecessary, and have unbiased opinions from an outsider.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeUsability testing is a technique of evaluating the user experience of a web product or service by testing it with representative users. It is an approach to identify issues that users may encounter when using the product and to collect feedback about how to enhance the product's usability.
Over the years, with increasing competitors, organizations are actively researching and spending on understanding usability. And, merely design and content aren't adequate; the software or website's engaging, intuitive, and responsive user experience, which an average person can use to achieve specific goals, has become important too.
What Is Usability Testing?
According to ISO 9241: Usability is the extent to which a product can be used by specified users to achieve specific goals with effectiveness, efficiency, and satisfaction in a specified context.
Usability testing is a method used by organizations to get direct insight into how people interact with a product. It is a qualitative research method that helps identify usability issues and determine whether the solution is user-friendly.
It has two main objectives: determining whether a product or website is easy to use and finding ways to improve interaction design. It involves testing prototypes of websites and software programs with real users, who provide feedback on their experience. This must be done in person, as it is difficult to replicate the exact conditions that the user will be using the product, such as time constraints, distractions, or environmental factors.
Usability testing provides valuable information about what the user needs from an interface, which can help guide developers when creating a new interface. It also gives insight into how users behave while interacting with interfaces, which can help inform future modifications of an existing interface.
Usually, the tests consist of learnability, memorability, efficiency, satisfaction, and errors as parameters.
- Learnability: The ease of performing a successful task for a new user.
- Memorability: Recall the value of the functioning of your website after a long time.
- Efficiency: How quickly a user executes tasks once familiarized with your website.
- Satisfaction: Did the user enjoy using the design of the website?
- Errors: Frequency of errors users made, their severity & how to solve them.
Why Perform Usability Testing?
A great system is built on a great user experience. With rapid technology growth, organizations have started relying upon their online presence to achieve their goals. This leads to cutting-edge competition where there are so many websites that people will go to the following site if the first one they visit is not usable. It might be a beautiful website, but a lack of user-friendliness will usher users to hop on next.
Many websites generally make the mistake of running usability testing at last. Rectifying these problems at an early stage saves organizations both time and money. Furthermore, as developers don't have to rebuild from scratch, the project will likely be released on schedule.
Apart from website testing, mobile app testing is becoming crucial too. Many users usually stop using an app due to unsatisfactory performance, resulting in lower customer engagement. A successful app is intuitive and easy to understand. Adding a well-streamed instruction manual while onboarding users to use the app is essential; if it gets complicated for the user, they start losing interest. Mobile app usability testing is an essential way of learning the ultimate mobile experience of the user.
In the testing world, 'usability' refers to a quality attribute (QA) that decodes how easy the user interface is to use for a user. It enriches the performance, dependability, and delight with which specific users achieve their objectives. It helps achieve deeper valuable insights before developing a website or app in the design phase.
3 Aims of Usability Testing
1. Identify the problem: Review and research thoroughly to find challenges.
2. Discover new opportunities: With test results, you shall find new prospects for enhancing websites.
3. Behavioral learning: This will allow understanding of target users better.
What Do We Need Usability Testing For?
It is widely accepted that user experience is one of the most important aspects of making an online business successful. Thus, usability testing has become a vital practice for all companies. It helps understand the target audience and learn about their needs, behavior, problems, and preferences by letting them witness the product. If skipped, it will directly affect your conversion rate, ultimately determining whether your business succeeds or fails. Here are the five E's of performing usability testing.
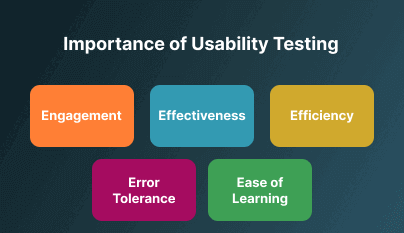
1. Engagement: Want to have a successful website? Engagement plays a crucial role; it measures how captivating your website is and how much time users spend on it. The website should have clean and minutest details (design elements, micro-interactions, chat-bots, etc.) that elevate users' experience
2. Effectiveness: Relevant. Has the goal you decided been achieved or not? usability testing ensures the website solves the core values of its foundation and that the enabled features are working as intended.
3. Efficiency: Fast and well-structured. Efficiency denotes how fast and effective goals are achieved. It monitors how your navigation works and how concise and well-structured the design layout is. usability testing measures efficiency in terms of the number of keystrokes; the fewer the keystrokes, the better the opportunity to achieve goals faster.
4. Error Tolerance: Unambiguous and minimized error with faster recovery. Always check the error and how to resolve it faster. The usability testing checks how fast and efficiently your website allows users to reverse the errors.
5. Ease of Learning: Quick to understand. The goal is to enable the new and existing users with continued learning that is easy to remember.
Example: Online streaming OTT platforms have rapidly become a favorite pass time, and you are planning to launch one soon too. As we know, an OTT platform has multiple filters and searchability tabs; thus, results will be released for each command.
In this case, you will ask your users to perform multiple tests like.
- Search the genres/language of content you want to watch.
- Sharing command functioning.
- Save or upvote and downvote button functioning.
- Performance on various network speeds.
- Sign-in and sign-out functions working.
- Remember me command functioning.
- Feasibility to choose and continue in the selected language.
These are a few framed questions you can ask the users during the usability testing. The environment can be set according to you, as in this situation, qualitative remote usability testing conditions can opt to check the performance in diverse locations, devices, OS, and networks.
Types of Usability Testing
There are three major actionable ways to perform usability testing:
1. Moderated vs. Unmoderated
| Moderate | Under Moderate |
|---|---|
| Administered under human presence (on-site or virtually). | Done without the direct presence. |
| Queries are answered & follow-up questions are asked. | Virtual overview and no distraction |
| Performed in labs. | Performed on participants' devices (OS, browser). |
| Results are in-depth. | Only mentioned queries are answered. |
| Expensive. | In-expensive. |
| Time-Consuming | Comparatively faster |
| Interact with participants in person and then select participants. | Third-party software to recruit target participants. |
2. Remote vs. In-person
| Remote | In-person |
|---|---|
| Can't control the test environment. | Can control the test environment. |
| The website is made available for the participants to access and analyze. | Tests locally hosted websites (might not be accessible to the participant's device). |
| A large number of tests can be conducted at once. | Conducting tests in large numbers can be expensive. |
| Websites can be checked across multiple geographical locations | Restriction to the site. |
| Tests are run on the participant's familiar device giving the freedom to explore. | Restriction to exploring as the device is new and not user-friendly. |
| Technical glitches can occur. | If technical glitches occur, the device can be changed in quickly. |
3. Qualitative vs. Quantitative
| Qualitative | Quantitative |
|---|---|
| Focuses on collecting insights, findings, and anecdotes. | Focus on collecting metrics. |
| Best for discovering problems in the user experience. | Best for setting benchmarks. |
Usability Testing Methods
Usability testing is an area of expertise for UX/UI designers and developers as the team collects necessary details about the website's usability using various usability testing methods.
- A/B Testing: Also known as split testing, it is a method of experimental analysis in which two versions of a website or its components (such as color, text, or interface difference) are compared to determine which performs best and help decide which version should be used on the website.
- Hallway Testing: Performed with people having no prior experience or knowledge. As a result, the response is more reliable and helps find the bugs in crucial environments, which can be unproductive and lag the website.
- Expert Review: For usability testing, skilled professionals are selected to perform the test on the website. The expert review of usability testing is implemented rapidly and takes less time than other types of usability testing because the professionals can easily identify the loopholes and discover flaws in the product. However, this type of testing is more costly because it requires a skilled person.
- Automated Expert Review: Automated expert review is a technique in which tests are executed by a script rather than a human. An automation expert writes scripts and develops an automation framework, then tests are executed, and results are recorded.
- Moderated Usability Testing: In this, the focus is on live feedback. Live feedback is an excellent way to test new designs as this method allows moderators to see the users' reactions, hear their live comments, and answer their questions in real-time, which leads the participants to feel more engaged and interested in participating in this study.
- Unmoderated Remote Usability Testing: This method is an efficient way to test as the users carry out their tasks, perform tasks, and report to the provider in real time, using the data gathered to analyze findings. This form of usability testing is usually done remotely without the help of a human moderator or tester. It is much simpler, faster, and easier to handle.
- Surveys: Surveys are widely used methods by which usability tests are conducted. This method includes the use of questionnaires and different question patterns, which the user has to answer, and on this basis, the developers get the required information. The best part of surveys is that they can be conducted on a large scale and therefore help gather huge data, which helps analyze better.
- User Persona: The aim of this approach is to create a unique brand that reflects an idealized version of the user. It involves a fictional representation of an ideal consumer and focuses on the goals of the users depending on their features, which they particularly process, and their attitudes which they have. The consumer is the focus of the process, and all the aspects that influence and affect them must be included in the development process. The developers also examine the expectations that the users have regarding any particular product or service.
- Eye-Tracking: It is a method to capture physiological data of users' unconscious and conscious experiences using a website. The eye's motion, movement, and position are tracked while interacting with the interface. The data collected is then analyzed in real-time to provide immediate feedback on users' reactions.
Steps/Process of Usability Testing
Performing usability tests require a small group of participants. But, before dwelling on the steps, let's look at the three core elements for executing tests.
1. Facilitator: A facilitator is a guide for participants. They carefully observe the participant's behavior, listen to their feedback, answer their queries, and guide them through the test. Further, they may ask follow-up questions to elicit detail from the participant.
2. Task: A realistic activity the participants perform. Each word mentioned in the tasks holds a strong meaning because it directly impacts the question's nature and the users' behavioral response.
3. Participant: A real person performs the test. Usually, participants are selected with similar domains to the nature of the product.
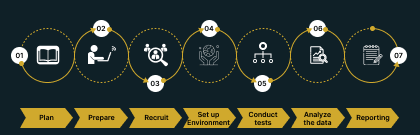
A Breakdown of Steps For Performing Usability Testing
- Plan
- Prepare
- Recruit
- Set-up Environment
- Conduct Tests
- Analyze The Data
- Report The Data
- Plan: Define your goals before initiating the tests in this stage. It will help you build a suitable type of test. Understanding executing tests is not your objective; the purpose is to determine the vital functionalities and objectives of the system. Be specific about your goals, as these will help in the objective and decide the format of your test.
- Prepare: Usability tests need to be done at the initial stage, as they will help identify challenges or changes that would get expensive in the final stages of development. Be precise with functionalities and features you want to ensure are performing.
- Recruit: Finding the right participant is the hardest part of usability testing. Identify a good mix of users that should correspond to your target audience's demographic (age, sex, etc.) and professional ( education, job, etc.) profile. It is crucial to have candidates relate to the issue you are trying to resolve and accordingly screen the number of desired numbers of testers. But be careful not to hire participants that can be biased, as it might fulfill your response number; however, it would eliminate your chances of finding honest criticism.
- Set up Environment: Layout the design of the actual environment where the tests will be conducted. As the purpose is defined, you shall script everything. You'll decide if you want to record the tests and how each task will be tracked and executed. And to make your study uniform, impartial, and scientific, moderators should follow the same script in each user session. You shall also decide the method of performing usability testing, lab testing (in-person at your offices), and remote testing (where participants can log in to your test from anywhere). And choose the style that is relevant to your goals.
- Conduct tests: Execute these tests in a quiet room or distraction-free. Try not to influence your opinion of the participant. For example, do not ask them queries that direct them to a particular response. Do you like the flow of subcategories? Before the final test, run a dry run before the final tests. And during the tests, do not look for feedback; instead, check the response the participant has to give.
- Analyze the data: Based on your test results, work with your team to study all data gathered from your usability test. It is to derive meaningful hypotheses and give actionable recommendations on how you can improve the overall usability of your product. Be open-minded toward the test, as it will highlight the issues that can come up in your tests and use them as a starting point for the next versions.
- Reporting: Finally, after extracting insights from your data, report the key takeaway points to relevant stakeholders across your team. Also, it will suggest improvements that will help lay out the next steps for improving your website's design.
Tools for Usability Testing
The following are the most popular usability testing tools. Pick the suitable one according to your needs.
- Crazy Egg: This is an innovative, easy-to-use tool that allows you to track your customers' scroll and click behavior on your website or mobile app. It provides features like User Recordings, A/B Testing, and Heatmaps. With filters, you can easily understand detailed customer segments & use cases, while the recording will help you learn an individual's journey through your website. Evaluate how they engage with your site, experience it the user's way, and discover the shortcomings where they get stuck.
- Userlytics: This tool is known for its extensive and unique features that allow users to dig deep into test response data based on details about each participant in every study. Its advanced feature can help set tests up in minutes, and results can be concluded in hours. One of its kind, it is a platform that records the webcam, audio, and screen of the user's device while also permitting an infinite number of annotations, users/admins, testers per session, highlight reels, and the number of concurrent studies.
- Qualaroo: This is an automated research platform that is designed to help teams collect valuable insights from their users at scale. It prompts site visitors to answer surveys and helps teams understand their users in real time. It relieves teams of the burdens that come with user research. It can be deployed from mobile to web apps to use features like advanced targeting, dynamic insight reporting, sentiment analysis, and more.
- Clicktale: One of its kind Clicktale is a platform that allows you to report "crash trends" to help research which user actions cause your application to crash. It provides a suite of visual reports such as session replays, heatmaps, error reports, form and funnel analysis, and more to help brands see and understand the individuals behind their numbers. It allows you to build multiple dashboards for different users or departments in your organization. Apart from that, the platform records participants' behavior in detail and offers several different ways of processing that information. Users can see what participants did and how by recording and chronological breakdown of participants' actions within the app.
- LambdaTest: Test orchestration and execution platforms like LambdaTest allow you to perform usability testing of your websites and mobile apps on an online device farm of 3000+ real devices and OS combinations.
How to Perform Usability Testing of Websites?
With the number of competitors growing rapidly, design and content are no longer enough to retain users. Businesses are learning that creating engaging, intuitive, and responsive user experiences are necessary to compete in today's marketplace. Thus designers and developers must start incorporating usability testing from the development phase. The ultimate goal is to get real-user feedback and ensure the applications' real-world success.
There are two ways to perform usability testing of your website.
- Set up an in-house physical device, which is costly and comes with on-premise challenges and scalability issues.
- Get a real device cloud that eliminates the need for an in-house device lab and reduces operational costs instantly.
With cloud-based testing platforms like LambdaTest, you can perform live interactive web testing running on real browsers and operating systems.
Below are the steps on how to perform usability testing of websites.
- In case you don't have a LambdaTest account, register for free.
- From the left menu, select Real Time Testing > Browser Testing.
- Enter the URL, select Desktop, VERSION, OS, and RESOLUTION. Click START.
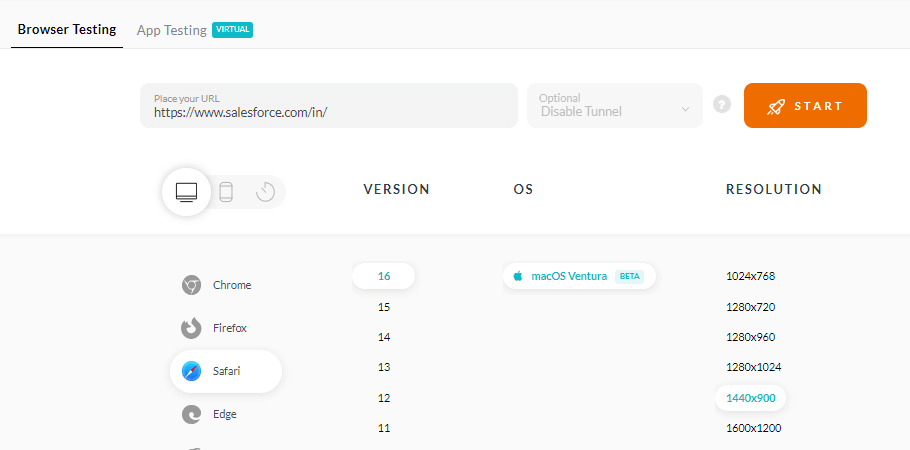
- A new virtual machine will open based on the selected browser-OS combinations where you can test websites or web applications for usability issues.
How to Perform Usability Testing of Mobile Apps?
With LambdaTest mobile app testing, you can test mobile applications manually on real devices and virtual testing cloud as per your requirements.
In this guide, we will use a real device cloud to test the usability of mobile applications.
Below are steps to perform usability testing of mobile apps on the LambdaTest platform.
- Sign up and log in to your LambdaTest account. To get real device cloud access, contact sales.
- Go to Real Device > App Testing.

- Choose OS type (Android or iOS), upload your app, and select BRAND and DEVICE/OS. Then click START.

- It will launch a real device cloud in which you can test the usability of your mobile apps.

Advantages of Usability Testing
Some of the significant advantages of usability testing are:
- Unbiased and accurate results. With usability testing, the tests are performed with users without prior experience; thus, the responses are fair and help to understand where the modifications are required.
- Usability testing verifies the product meets expectations.
- It helps discover usability bugs prior to the final release.
- It helps you create a highly effective and efficient website and improves the end-user experience.
- The large-scale release can be challenging; a new set of fresh minds promotes rectifying minor errors, if any.
- Saves cost and time; if executed from the initial stage, it helps detect poor UI experiences and helps build something more suitable.
- It gives a clear and broader picture of what users do on your site and why they take these actions.
- Implementing usability testing results enriches the satisfactoriness and consistency of the product.
Common Mistakes That Happen During Usability Testing
In the pursuit of quality assurance, testers or observers are expected to observe, report, and analyze the application to search for potential defects. Often, they can make certain mistakes that can be costly and time-consuming to fix. Therefore here are a few mistakes you must avoid before executing usability testing
- Lack of Proper Planning: Planning is one of the most important aspects of usability testing. Every team member is involved in it and contributes to effective testing. The entire testing phase must be planned properly with all the stages involved. Without proper planning, any amount of user experience testing would make little difference in finding critical bugs or improving user experience.
- Misinterpretation of the Goal: Most testers have a misconception about usability testing. They use it to improve the look, feel, and design of an application. But usability testing goes beyond that; it tests how people use the software. Usability testing aims to determine where users get frustrated, either with design or functionality.
- Testing with Incorrect Audience: The process of usability testing is to bring in the actual users of the application. To save time, testers often execute usability testing with friends or co-workers. However, this leads to results that are not properly validated. Therefore, proper screening is carried out before selecting the users. If the client provides the users, equip them with requirements that clearly state the type of users to choose and those to avoid.
- Last Moment of Testing: A large percentage of projects fail. Some fail due to technical issues, but mostly because bugs are only identified at the final moment. Thus, it is essential that usability testing is ideally carried out from the development phase to make informed and smart decisions throughout the project. This will result in faster and misunderstood usability and increased productivity.
- One-Way Testing: The one-way-mirror testing method is exemplary for observing users while they test the application. This certifies participants to test the application under usual conditions, with no knowledge that they are being observed.
- Creating Interruptions: The objective of usability testing is to gather information from end users and, from that feedback, develop a more desirable product for the customer. With this in mind, it should be noted here that you cannot push the user to use your product or follow your guidelines, or be forced (in any way) to finish the task. Letting them explore the product alone would be better if they are comfortable with it. You can instruct them and attract their attention to a specific feature if necessary, but try not to interrupt their exploration process.
- Conducting Only One Test: In order to make usability testing effective, it is essential to conduct tests at multiple stages during the development process. It helps in saving time in finding potential problems early on, making the development process more efficient. For example, when a bug is encountered during the designing phase, it is easier to fix than after completion.
- Missing Pilot: Pilot testing is a form of usability testing that allows the designer to test a product. It enables the tester to test at the early stages of development when prototypes or mockups rather than the final product are being tested. It will help eliminate last-minute planning errors during the final test procedure.
- Improper Designed Tasks: Test task design significantly impacts test results outcomes. The most critical aspect is uniquely arranging tasks so participants execute them correctly. Employing proper guidelines can help the participants know precisely what they need to do and assist in streamlining performance testing.
- Testing Wrong Potential Solutions: It is the best way to test the performance of new features, ensure interface elements work, and ensure that tasks are intuitive for all types of users. Testers see usability testing as a valuable exercise that helps create better products and boost revenue by making it more effortless for customers to do what they want with products.
Best Practices for Usability Testing
From tools to processes, you have learned everything about usability testing. As testing with real users allows you to compile data needed to identify usability issues, improve the design and ensure it's easy to use. Here are some best tricks and practices to adhere to when you validate your product with real users and can help you avoid mistakes that can happen during usability testing
- Test early: The earlier you test, the easier it is for the team to make the changes, as delaying would have a greater impact on the quality of the product. It is not necessary to wait for a prototype or final product; in fact, it can be as soon as after the inception of the idea.
- Stick to common design elements: When running a usability test, ensure that the elements across the platform are the same, which will help users navigate easily.
- Establish evaluation criteria: You know the product better; thus, with an open mind, define the benchmark to determine the website's success.
- Make sure your content is ambiguous: Be clear and neat with the content.
- Remember, it's a constant loop of learning: Businesses often treat launching as a linear process that starts with research, followed by prototyping, and ends with testing. However, it's an iterative process. Each team has to test in every phase for success.
- Be inclusive: Wide audience gives different opinions; to have a better prospect on your website, perform usability testing with the target audience for whom it will resolve an issue.
- Be mindful: Time is valuable for participants as well. Understand that they are spending time on this; the lengthier tests would give less time for feedback, and too many questions will not give precise data to you.
- Testing environment: Before final deployment, check your product in all the testing environments to understand performance in diverse audiences
- Think quality over quantity: Usability testing doesn't have to be about numerous users; rather, invest in testing in each phase with a focused target group. It will enable us to undertake tests at multiple stages and save time analyzing data.
- Solve one bug at a time: Trying to solve everything at once is quite impossible. Instead, fix each issue at a time, prioritizing the critical first. It is a constant learning process, so fix issues to the best of your ability, ship the product, learn from the feedback, and iterate accordingly.
Conclusion
Throughout the article, we understood that usability testing is a great way to discover unexpected bugs, find what is unnecessary or unused before going any further, and also unbiased opinions from an outsider.
Often considered an expensive and time-consuming process, usability testing is a favorable process before final implementations. You might not implement at a larger scale; an internal team or close group can run tests on different prototypes, from a journey of rough ideas to fully functioning products. Also, by the end of the tests, always ask for recommendations (be polite and take feedback positively).
Remember to include your quality assurance team in usability testing. It gives them a fresh perspective on users, acknowledges how they operate the set, and examines ways to bridge what the product can do. It will also profit the users as quality assurance will help them learn the best way to engage and use features. This infinite loop will profit you in making a better product and understanding what your target audience needs.
Published at DZone with permission of Kavita Joshi. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments