Understanding Zero Trust Security Building a Safer Digital World
This article delves into Zero Trust Security, its principles, and its implementation as we aim to build a safer digital world.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIn our rapidly evolving digital age where technology underpins almost every facet of our lives, cybersecurity has never been more critical. As the world becomes increasingly interconnected with personal devices and social networks to critical infrastructure and global business operations, the digital landscape has expanded and diversified, presenting new opportunities and unknown threats, bringing cybersecurity to the forefront of the global stage. Today, data is the lifeblood of our modern society, and it flows ceaselessly through the veins of the digital realm. It's the engine that powers our businesses, our governments, and our personal lives. We entrust it with our most sensitive information, from financial records to healthcare data and private conversations.
The interconnected world has created unparalleled convenience but has also introduced unprecedented risk. The digital realm has become a battleground where malicious actors, from cyber criminals to nation-states, continually seek to exploit vulnerabilities, steal sensitive information, disrupt critical services, and sow chaos. The consequences of a cybersecurity breach are far-reaching and can include financial loss, reputation damage, and even threats to national security. Cyber threats’ sheer volume and sophistication continue to increase daily, necessitating a proactive and comprehensive approach to safety. "Zero Trust Security" has become an effective strategy to safeguard our interconnected world.
What Is Zero Trust Security?
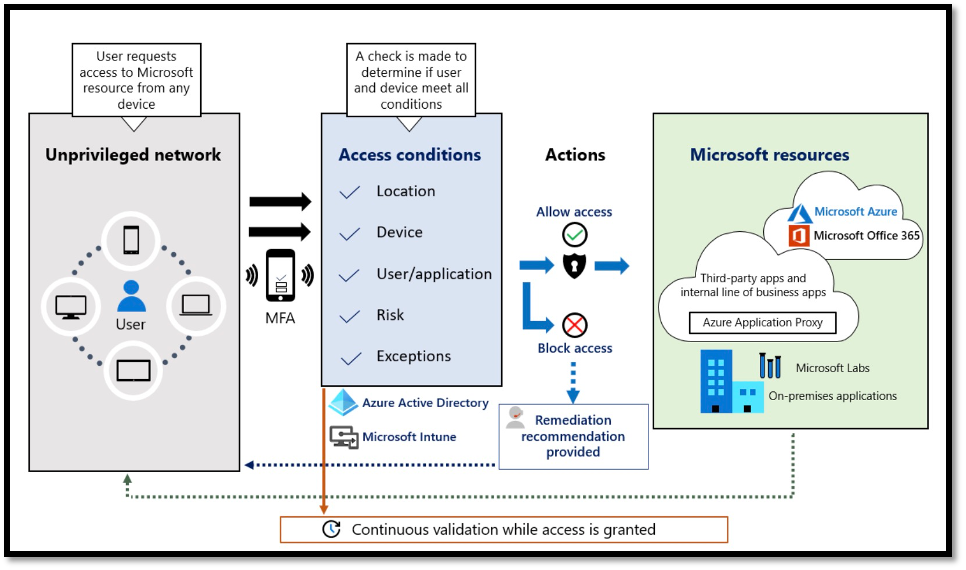
Zero Trust Security is a cybersecurity framework and philosophy that challenges the traditional trust model within a network. In the past, network security often relied on a "perimeter-based" approach, assuming that threats were primarily external. This model created trust within the network where users and devices were usually granted broad access to resources once inside. Zero Trust Security, on the other hand, operates under the assumption that no entity—whether inside or outside the network—can be trusted implicitly. It advocates continuous verification and strict access controls to protect critical assets and data.
The concept of Zero Trust Security has evolved in response to the changing cybersecurity landscape, characterized by an increasing number of data breaches, advanced persistent threats, and insider threats. Forrester Research analyst John Kindervag initially introduced the Zero Trust model in 2010. Kindervag's vision directly responded to the shortcomings of traditional security models, particularly the outdated "castle-and-moat" approach, which assumed that an organization's perimeter was secure and anyone inside it could be trusted. He recognized that this approach was no longer tenable in the face of increasingly sophisticated cyber threats. The Zero Trust model, conceived by Kindervag, represented a radical shift. It advocated a fundamental change in thinking, emphasizing that trust should not be automatically granted to anyone or anything, whether inside or outside the network. Instead, trust should be continuously earned through rigorous identity verification and monitoring.
The term "Zero Trust" may sound extreme, but it reflects the need for a profound shift in cybersecurity mindset. The approach gained traction as significant data breaches and security incidents highlighted the weaknesses of traditional models, and organizations began to realize the importance of a more proactive and adaptive security stance.
Key Principles of Zero Trust Security
Zero Trust Security is built on several fundamental principles crucial to its effectiveness. These principles collectively help organizations create a security framework that minimizes risk and provides a robust defense against cyber threats; below are some of the fundamental principles in detail:
Verify Identity
The foundation of Zero Trust Security is identity verification. Users and devices must prove their identity before accessing network resources, typically achieved through multi-factor authentication (MFA), strong passwords, and other authentication methods. By verifying identities, organizations ensure that only authorized individuals or devices can access critical systems and data.
Least Privilege Access
The principle of least privilege dictates that users and devices should only have access to the minimum set of resources and data required to perform their specific tasks; this limits the potential damage if an account or device is compromised. By adhering to the principle of least privilege, organizations reduce the attack surface and the potential impact of security breaches.
Micro-Segmentation
Micro-segmentation is dividing a network into small, isolated segments or zones. Each component has its own access controls and security policies. This approach minimizes lateral movement within the network, making it more challenging for cybercriminals to move freely if they breach one segment. Micro-segmentation helps contain and isolate security incidents.
Continuous Monitoring
Continuous monitoring involves real-time network traffic analysis, user behavior, and device activity. It allows organizations to detect anomalies and potential security threats as they happen. Organizations can respond promptly to emerging threats by continuously monitoring the network, preventing or minimizing damage.
Explicit Access Controls
Access to network resources should not be granted by default; it should be explicitly defined based on well-defined policies. Access controls must be precise and consistently enforced, and changes or escalations in access permissions should be carefully reviewed and authorized. Explicit access controls ensure that only authorized actions are allowed.
By adhering to these core principles, organizations can establish a security framework rooted in "never trust, always verify." This approach makes it much more difficult for cyber attackers to compromise systems, move laterally within the network, and gain access to sensitive data. It also aligns with the evolving threat landscape, where breaches can come from both external and internal sources. Zero Trust Security provides a proactive and adaptive strategy to protect against security threats.
Benefits of Zero Trust Security
Implementing a Zero Trust Security model offers numerous advantages, significantly enhancing an organization's cybersecurity posture. Here are the key benefits:
Improved Security Posture
Zero Trust Security provides a proactive and robust defense against evolving cyber threats. Organizations can better protect their digital assets and data by constantly verifying identities and reducing the attack surface through the principle of least privilege.
Enhanced Protection Against Data Breaches
Data breaches often result from unauthorized access to sensitive information. Zero Trust Security minimizes the risk of data breaches by ensuring that only authorized users and devices can access sensitive data. Because of micro-segmentation and least privilege access, potential damage is minimal, even if a breach occurs.
Support for Remote and Hybrid Work Environments
Post-pandemic, the modern workplace is increasingly remote and hybrid, with employees accessing company resources from various locations and devices. Zero Trust Security is well-suited for this environment, as it enforces strict access controls regardless of the user's location, device, or network.
Regulatory Compliance
Organizations are subject to stringent regulatory requirements concerning data security and privacy depending on which domains they operate, such as healthcare, banking, insurance, etc. Zero Trust Security helps organizations comply with these regulations by ensuring that sensitive data is accessed and handled according to the prescribed rules.
Threat Detection and Response
Continuous monitoring and real-time network traffic analysis enable organizations to identify and respond to security incidents as they happen. This rapid detection and response capability helps minimize the impact of security breaches.
Reduced Insider Threats
Whether intentional or accidental, insider threats pose a significant risk to organizations. Zero Trust Security mitigates this risk by applying the same strict access controls to all users and devices, regardless of their status within the organization.
Adaptability To Evolving Threats
The cybersecurity landscape constantly evolves, with new threats and vulnerabilities emerging regularly. Zero Trust Security is adaptable and can grow with the changing threat landscape, ensuring organizations remain resilient against emerging threats.
Minimized Attack Surface
Zero Trust Security minimizes the attack surface by segmenting the network and applying the least privileged access, making it more challenging for attackers to move laterally within the network and access critical systems.
Improved User Experience
Zero Trust Security enforces strict access controls but strives to maintain a positive user experience. Users are granted access to the needed resources, and authentication can be streamlined through single sign-on (SSO) and MFA solutions.
Zero Trust Security is an essential risk mitigation strategy, reducing the likelihood of costly security incidents and breaches. This can lead to lower financial losses, improved reputation, and better business continuity. Zero Trust Security is a comprehensive approach to cybersecurity that offers a wide range of benefits, from improved protection against cyber threats to regulatory compliance and adaptability in the face of evolving security challenges. Organizations that adopt Zero Trust Security are better positioned to secure their digital assets and data in an interconnected and increasingly complex world.
Implementing Zero Trust Security
Adopting a Zero Trust Security model involves a series of steps and considerations. Organizations should begin by comprehensively assessing their network architecture, security policies, and data flows.
The next step is to identify all physical and digital assets and all users and devices that interact with the network. Understanding organizations' existing security controls and policies is crucial in defining and documenting access control policies. Documentation on who should have access to which resources and under what circumstances is a critical consideration, ensuring access is based on the principle of least privilege, granting only the adequate access required for each user or device to perform their tasks.
Essential consideration should be focused on implementing robust authentication methods, including multi-factor authentication (MFA), requiring users and devices to provide multiple forms of identification to verify their identity. This step is crucial for ensuring that only authorized entities gain access. The best practice is to divide the network into smaller, isolated segments, using access controls based on the principle of least privilege, which limits the movement of adversaries within the network segmentation and requires explicit authorization of communications.
Implementing continuous monitoring tools to monitor network traffic, user behaviors, and device activities will help detect early threat detection and anomaly patterns in real-time. Organizations should invest in robust Identity and Access Management [IAM] solutions that help efficiently manage user identities, access policies, and authentication processes. IAM systems are critical in Zero Trust Security to secure endpoints, including laptops, smartphones, and IoT devices.
Implementing endpoint security will provide real-time threat detection and response capabilities that will guarantee that devices are secured from malicious actors. Data encryption at rest and in transit, data loss prevention (DLP), and data classification mechanisms to safeguard sensitive information are best practices to safeguard an organization’s digital assets. An organization’s detailed incident response plan that outlines how it will react to security incidents or breaches is critical in the Zero Trust Model, ensuring all stakeholders understand their roles and responsibilities in the event of an incident.
Organizations often need to evaluate the security of third-party vendors and service providers with whom they share data or collaborate. They need to ensure those external identities adhere to Zero Trust Security principles to prevent vulnerabilities in the network through external connections.
Consider a pilot implementation before rolling out Zero Trust Security across your organization. Start with a small, well-defined segment of the network to test the security controls' effectiveness and ensure that they align with the organization's requirements and goals. Once the pilot is successful, gradually expand the Zero Trust Security model to cover the entire organization.
Monitor, assess, and refine Zero Trust Security framework to adapt to evolving threats and organizational changes, and regularly review and audit security policies and controls to ensure they comply with relevant regulations and industry standards. Educating employees and users about the principles of Zero Trust Security and the importance of responsible and secure digital practices is essential for the success of this security model. Implementing Zero Trust Security is a journey that requires careful planning, commitment, and adaptability. Following the above-mentioned guidelines and continuously improving security measures can significantly enhance an organization's resilience to the ever-evolving threat landscape. Zero Trust Security provides a proactive and robust approach to safeguarding digital assets and data in an interconnected world.
Case Studies of Successful Zero Trust Security Implementation
To illustrate the effectiveness of Zero Trust Security, let's explore a few case studies of organizations that have successfully adopted this security model. These case studies highlight how organizations with diverse backgrounds and security needs have successfully implemented Zero Trust Security to overcome challenges and gain significant benefits. They have seen improvements in data protection, security resilience, user experience, and the ability to adapt to a changing threat landscape. These examples underscore the flexibility and effectiveness of Zero Trust Security as a modern approach to cybersecurity.
With its vast infrastructure and diverse user base, Google faced the challenge of securing its cloud-based services and protecting user data from various threats. It needed a solution that would work seamlessly with its distributed environment while preventing unauthorized access and lateral movement within the network. Google developed the BeyondCorp framework, which is a Zero Trust Security model. It shifted its security focus from the network perimeter to the user and device identity. BeyondCorp ensures that every access request is subject to rigorous identity verification and access controls. Google has experienced improved security, reduced risks, and enhanced user experiences with secure remote access, and it has shared its findings and model with the cybersecurity community.
Akamai
Akamai has developed a Zero Trust security strategy to eliminate traditional corporate VPNs and move away from the perimeter-based security model. The objective was to keep Akamai's business applications and data secure, ensuring lateral movement in the corporate network is prevented providing a better user experience. As part of the Zero Trust transformation, Akamai established a core set of principles. For example, in the transition to a perimeter-less environment where the Internet becomes the corporate network, every office must become a Wi-Fi hotspot, and application access is dynamically and contextually granted based on identity, environmental factors (such as location and time of day), and device signals (such as client-side certificates or device compliance to corporate security policy).
Security guidelines align with Zero Trust's tenets; no machine or user would be trusted by default. This approach was based on finding cost-effective technologies that support mobility, enhanced security, flexible access, and virtualization, also taking advantage of the simplicity of the cloud.
Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC)
The FDIC safeguards sensitive financial information. The organization faced challenges in protecting this data from external cyber threats and insider risks. FDIC adopted a Zero Trust Security approach to protect sensitive financial data and maintain the trust of the public and financial institutions. The organization has improved its data security and resilience to cyberattacks. Zero Trust Security helps the FDIC continuously monitor its network for potential threats, ensuring the security of the financial sector.
The Future of Zero Trust Security
The cybersecurity landscape continually evolves, driven by technological advancements, new threats, and changing user behaviors. Zero Trust Security, as a concept and practice, is expected to adapt and evolve to meet these challenges. As organizations continue to recognize the importance of robust cybersecurity measures, the adoption of Zero Trust Security is expected to rise. This trend will be driven by a growing awareness of the limitations of traditional security models and the need for a more adaptive approach to protect digital assets.
- The future of Zero Trust Security will involve the convergence of various technologies, such as identity and access management (IAM), artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML). These technologies will improve identity verification, anomaly detection, and automated responses to security incidents.
- Zero Trust Security will become more cloud-native with the shift to cloud-based services and remote work. Organizations will implement cloud security strategies that seamlessly integrate with Zero Trust principles, allowing secure access to cloud resources and applications.
- The proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices presents a unique challenge. Zero Trust Security must adapt to accommodate IoT devices’ diverse and often resource-constrained nature while ensuring secure network integration.
- Zero Trust Security will become even more user-centric, focusing on securing the identity and actions of individual users, regardless of their location or the device they use. User behavior analytics and contextual awareness will be pivotal in risk assessment and access control.
- Automation will play a significant role in Zero Trust Security, allowing organizations to respond quickly to threats. Automated threat detection, incident response, and policy enforcement will help reduce the burden on security teams and improve response times.
The concept of Zero Trust Security is inherently dynamic. It will continue to evolve to address emerging threats and vulnerabilities. As threat actors adapt and develop new tactics, Zero Trust Security must remain adaptable and responsive. With the introduction of more stringent data protection regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, Zero Trust Security will be vital for organizations aiming to maintain regulatory compliance. The model's emphasis on data protection and access control aligns well with these requirements. Organizations must invest in educating and training their employees to implement Zero Trust Security successfully. Cybersecurity awareness programs will become integral to ensuring that all users understand their role in maintaining security.
As the adoption of Zero Trust Security grows, collaboration within the cybersecurity community will be essential. Sharing best practices, threat intelligence, and insights will help organizations strengthen their security postures. Zero Trust Security is characterized by adaptability, technology integration, and a heightened focus on identity and data protection. As the threat landscape evolves, organizations must embrace Zero Trust Security as a foundational element of their cybersecurity strategy to protect their digital assets and data effectively.
Conclusion
Zero Trust Security has emerged as a foundational approach to cybersecurity in an interconnected and constantly evolving digital world. This proactive and adaptive model challenges the traditional notion of trust within a network, emphasizing rigorous identity verification and strict access controls.
Organizations can significantly enhance their security posture by verifying identity, implementing least privilege access, micro-segmentation, continuous monitoring, and explicit access controls. Zero Trust Security offers numerous benefits, including improved data protection, enhanced security against breaches, and support for remote work environments.
Real-world examples from organizations like Google, Akamai, and FDIC demonstrate the effectiveness of Zero Trust Security. These organizations have successfully implemented this model, overcoming challenges and reaping the rewards of improved security and resilience.
Zero Trust Security will continue to evolve, adapting to emerging technologies and threats and witnessing increased adoption across various industries. It will become more user-centric, integrate with cloud-native strategies, and leverage automation and AI for enhanced security.
As organizations navigate the complex and dynamic cybersecurity landscape, Zero Trust Security remains a valuable tool to secure digital assets, protect sensitive data, and respond effectively to the evolving threat landscape. By embracing the principles of Zero Trust, organizations can build a safer and more resilient digital world.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments