Top 20 Spring MVC Interview Questions for Java Programmers
Interviewing for a position developing Spring MVC-based applications? You'll want to know these questions and answers first.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeThe Spring MVC framework is one of the most popular Java frameworks for developing web applications. If you have been working in Java and developing web-based applications, then there is a good chance that you have already used Spring MVC in your projects. In the last decade, it has become the defacto framework for developing Java web applications. Spring MVC is based on classic MVC (Model-View-Controller) design pattern, but it is much more than that. It leverages the Spring framework's strength in terms of its dependency injection and Inversion of control and promotes a loosely coupled architecture, similar to the Spring framework. Because of its immense popularity and usefulness, most of the Java development role requires a good knowledge of Spring and Spring MVC.
There is a high demand for good Java developers with knowledge and experience in Spring and Spring MVC. One way to prepare yourself for such job interviews is to look for potential interview questions.
These questions not only help you to prepare for interviews but also help you to better understand the fundamental concepts and encourage you to learn more — that's why I am always in search of good Spring MVC Interview questions.
Recently, I was preparing for the Spring Core Professional Certification when I came across some Spring certification guides from Pivotal. These guides contain some interesting questions on Spring MVC.
Even though these questions are provided below just to give you an idea about the syllabus of Spring certification, I actually found many of such questions have already been asked to myself and friends in various Spring job interviews.
On request to a couple of my friends, I thought to share answers to these questions here. So if you are preparing for either a Spring Certification or Java developer interview, you will find this list of Spring MVC interview questions very useful for your preparation.
20 Spring MVC Interview Questions for Java Programmers
Without further ado, here is my list of some of frequently-asked Spring MVC questions from Java interviews, particularly from the web development positions.
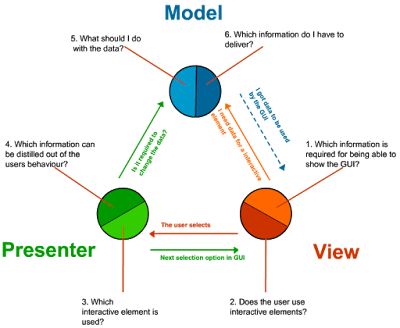
1. MVC is an abbreviation for a design pattern. What does it stand for and what is the idea behind it?
Answer: MVC is an abbreviation for Model-View-Controller design pattern. This pattern is based upon the separation-of-concerns design principle that promotes handling different functionality at different layers and loose coupling between layers.
In the MVC pattern, the Model contains data that is rendered by the View and Controler help in request processing and routing.
Neither Model knows about View, or that View is dependent upon Model, which means the same model can be rendered by different views, e.g. JSP or FreeMarker, or it can be even be written as JSON or XML in case of RESTful web services. You can learn more about MVC in my favorite course Spring Framework 5: Beginner to Guru. If you are serious about Spring, this is the course you should check out.
2. Do you need spring-mvc.jar in your classpath or is it part of spring-core?
The spring-mvc.jar is not part of spring-core, which means that if you want to use Spring MVC framework in your Java project, you must include spring-mvc.jar in your application's classpath. In a Java web application, spring-mvc.jar is usually placed inside the /WEB-INF/lib folder.
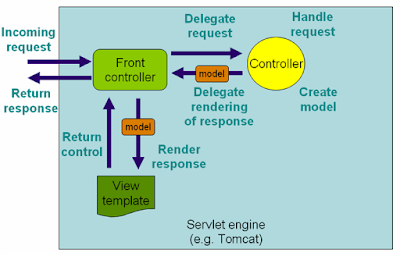
3. What is the DispatcherServlet and what is it used for? (answer)
The DispatcherServlet is an implementation of the Front Controller design pattern that handles all incoming web request to a Spring MVC application. A Front Controller pattern (see Enterprise application design pattern) is a common pattern in web applications whose job is to receive all request and route it to different components of application for actual processing.
In case of Spring MVC, the DispatcherServlet route web requests the Spring MVC controllers.
In Spring MVC, DispatcherServlet is used for finding the correct Controller to process a request, which it does with the help of handler mapping, e.g. the @RequestMapping annotation.
It is also responsible for delegating logical view name to ViewResolver and then sending the rendered response to the client.
4. Is the DispatcherServlet instantiated via an application context? (answer)
No, the DispatcherServlet is instantiated by Servlet containers like Tomcat or Jetty. You must define the DispatcherServlet into the web.xml file as shown below.
You can see that load-on-startup tag is 1, which means DispatcherServlet is instantiated when you deploy the Spring MVC application to Tomcat or any other Servlet container. During instantiation, it looks for a file servlet-name-context.xml and then initializes beans defined in this file.
5. What is the root application context in Spring MVC? How is it loaded? (answer)
In Spring MVC, the context loaded using ContextLoaderListener is called the "root" application context, which belongs to the whole application, while the one initialized using DispatcherServlet is actually specific to that servlet.
Technically, Spring MVC allows multiple DispatcherServlet in a Spring MVC web application, and so, multiple contexts are each specific for the respective servlet. But, having the same root context may exist. You can further check out this Introduction to Spring MVC course on Pluralsight to learn more on the fundamentals of Spring.
6. What is the @Controller annotation used for? How can you create a controller without an annotation? (answer)
The @Controller is a Spring MVC annotation to define a Controller, but in reality, it's just a stereotype annotation. You can even create a controller without @Controller by annotating the Spring MVC Controller classes using the @Component annotation. The real job of request mapping to handler method is done using the @RequestMapping annotation.
7. What is the ContextLoaderListener and what does it do? (answer)
The ContextLoaderListener is a listener that helps to bootstrap Spring MVC. As the name suggests, it loads and creates the ApplicationContext, so you don't have to write explicit code to do create it.
The application context is where Spring bean leaves. For a web application, there is is a subclass called WebAppliationContext.
The ContextLoaderListener also ties the lifecycle of the ApplicationContext to the lifecycle of the ServletContext. You can get the ServletContext from the WebApplicationContext using the getServletContext() method.
8. What are you going to do in the web.xml? Where do you place it?
The ContextLoaderListener is configured in web.xml as listener and you put that inside a tag as shown below:
<listener>
<listener-class>
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener
</listener-class>
</listener>When the Spring MVC web application is deployed, the Servlet container created an instance of the ContextLoaderListener class, which loads the Spring's WebApplicationContext. You can also see Spring MVC For Beginners to learn more about the ContextLoaderListener and WebApplicationContext and their role in Spring MVC.
9. How is an incoming request mapped to a controller and mapped to a method? (answer)
Sometimes, this question is also asked: how does DispatcherServlet know which Controller should process the request? Well, the answer lies in something called handler mappings.
Spring uses handler mappings to associate controllers with requests. Two of the commonly used handler mappings are BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping and SimpleUrlHandlerMapping.
In BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping, when the request URL matches the name of the bean, the class in the bean definition is the controller that will handle the request.
On the other hand, in SimpleUrlHandlerMapping, the mapping is more explicit. You can specify the number of URLs and each URL can be explicitly associated with a controller.
If you are using annotations to configure Spring MVC, which you should, then @RequestMapping annotations are used to map an incoming request to a controller and a handler method.
You can also configure the @RequestMapping annotation by the URI Path, query parameters, HTTP methods of a request, and HTTP headers present in the request.
10. What is the @RequestParam used for? (answer)
The @RequestParam is a Spring MVC annotation that is used to extract a request parameter or query parameters from the URL in the Controller's handler method as shown below:
public String personDetail(@RequestParam("id") long id){
....
return "personDetails";
}The @RequestParam annotation also supports data type conversion, e.g. you can see here a String is converted to log automatically, but it can also result in an exception if query parameter is not present or in case of type mismatch. You can also make the parameter optional by using requried=false, e.g. @RequestParam (value="id", required=false )
11. What are the differences between @RequestParam and @PathVariable ? (answer)
Even though both @RequestParam and @PathVariable annotations are used to extract some data from URL, there is a key difference between them.
The @RequestParam is used to extract query parameters, e.g. anything after "?" in the URL while the @PathVariable is used to extract the part of the URI itself. For example, if the given URL is http://localhost:8080/SpringMVC/books/3232233/?format=json, then you can access the query parameter "format" using the @RequestParam annotation and /books/{id} using the @PathVariable, which will give you 3232233.
Here is another example of @PathVariable:
@RequestMapping("/persons/{id}" )
public String personDetail (@PathVariable ("id" ) long id) {...}This code can extract person id=123 from /persons/123. It is particularly used in RESTful Web Services because their ID is usually part of the URI or URL path.
12. What are some of the valid return types of a controller method?
There are many return types are available for a controller method in Spring MVC, which is annotated by @RequestMapping inside the controller. Some of the popular ones are:
- String
- void
- View
- ModelAndView (Class)
- Model (Interface)
- Map
- HttpEntity<?> or ResponseEntity<?>
- HttpHeaders
You can see the full list of valid return types for a Spring MVC controller here.
Every return type has its specific use. For example, if you are using String, then it means that the Controller will just return the View Name and this view name will be resolved by ViewResolver.
If you don't want to return any view name, mention return type void. If you want to set a view name as well as want to send a object, use ModelAndView as a return type.
13. What is a View and what's the idea behind supporting different types of View? (answer)
A View is an interface in Spring MVC application whose implementations are responsible for rendering context and exposing the model. A single view exposes multiple model attributes. Views in Spring MVC can be beans.
They are likely to be instantiated as beans by a ViewResolver. As this interface is stateless, view implementations should be thread-safe. By using ViewResolver, a logical name of view can be resolved into different types of View implementation, e.g. JstlView for displaying JSP or other view implementations for FreeMarker and Velocity.
If you are new to Spring MVC and not familiar with these basic classes, then I suggest you learn Spring by joining one of these free Spring courses.
14. How is the right View chosen when it comes to the rendering phase?
The right View is chosen by the ViewResolver in Spring MVC. When Controller returns a logical view name to DispatcherServlet, it consults to ViewResolver to find the right View.
The ViewResolver, depending upon its implementation, resolves the logical view into a physical resource, e.g. a JSP page or a FreeMarker template.
For example, InternalResourceViewResolver is a default ViewResolver that converts a logical view name, e.g. "hello" to "/WEB-INF/hello.jsp" using the prefix and suffix.
15. What is the Model?
Model is a reference to encapsulate the data or output for rendering. Model is always created and passed to the view in Spring MVC. If a mapped controller method has Model as a method parameter, then a model instance is automatically injected by Spring framework to that method.
Any attributes set on the injected model are preserved and passed to the View. Here is an example of using Model in Spring MVC:
public String personDetail(Model model) {
...
model.addAttribute("name", "Joe");
...
}16. Why do you have access to the model in your View? Where does it come from?
You need to have access to the model in your View to render the output. It's the model that contains the data to be rendered. The Model comes with the Controller, which processes their client request and encapsulates the output into a Model object.
17. What is the purpose of the session scope? (answer)
The purpose of the session scope is to create an instance of the bean for an HTTP Session. This means the same bean can serve multiple requests if it is scoped in session. You can define the scope of a Spring bean using scope attribute or the @Scope annotation in a Spring MVC application.
18. What is the default scope in the web context? (answer)
The singleton scope is the default scope for a Spring bean, even in the web context. The other three web context-aware scopes are a request, session, and global-session, which are only available in a web application aware ApplicationContext object. See Spring Master Class - Beginner to Expert to learn more about ApplicationContext in Spring.
19. Why are controllers testable artifacts?
In Spring MVC, Controllers are testable artifacts because they are not directly coupled with any View technology. They just return a logical View name, which can be easily tested.
20. What does the InternalResourceViewResolver do? (answer)
In Spring MVC, a ViewResolver returns View to handle an output rendering based on the logical view name (provided by the controller) and locale. This way, the Controller is not coupled to specific view technology, e.g. JSP or FreeMarker. It only returns the logical view name.
InternalResourceViewResolver is the default ViewResolver configured in Spring MVC, and DispatcherServlet uses it to find the correct view. InternalResourceViewResolver is used to render JSPs ( JstlView).
It Configures the prefix and suffix to a logical view name, which then results in a path to a specific JSP as shown below:
<bean class= "org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver" >
<property name= "prefix" value= "/WEB-INF/" />
<property name ="suffix" value =".jsp" />
</bean>So if Controller returns "hello" as the logical view name, the InternalViewResolver will return /WEB-INF/hello.jsp, and the DispatcherServlet will forward the request to this JSP page for rendering.
That's all for now about the frequently-asked Spring MVC interview questions. If you know answers to these questions, you have a good foundation of the Spring MVC framework and its different components e.g. DispatcherServlet, handler mappings, Controllers, Views, and Model.
Good luck at your interviews!
Further Reading
Spring Framework 5: Beginner to Guru
Spring Master Class - Beginner to Expert
Spring Framework Interview Guide - 200+ Questions & Answers
Other Spring-related articles you may like to explore:
- 3 Ways to Learn Spring Framework (article)
- How Spring MVC Works Internally? (answer)
- What Is the Use of the DispatcherServlet in Spring MVC? (answer)
- How to Enable Spring Security in a Java Application? (answer)
- Does Spring Certification Help in Job and Career? (article)
- How to Prepare for Your Spring Certification? (guide)
- 3 Best Practices Java Developers Can Learn From Spring (article)
- Difference Between
@Autowiredand@Injectionannotations in Spring? (answer) - 5 Spring and Hibernate Online Courses for Java Developers (list)
- 5 Spring Boot Courses for Java Developers (courses)
- 5 Courses to Learn Microservices With Spring Boot and Spring Cloud (courses)
If you want to learn how to develop RESTful Web Services using Spring Framework, check out Eugen Paraschiv's REST with Spring course. He has recently launched the certification version of the course, which is full of exercises and examples to further cement real-world concepts.
Published at DZone with permission of Javin Paul, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments