Top 12 Technical Skills Every Software Tester Must Have
As a software tester, it’s essential to possess some technical skills, which make apps better. Let’s look at skills that are essential for any software tester.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeNobody can become a software tester like that. To gain that profession, there are some technical skills that every tester has to go through. As the renowned computer scientist and testing expert Jerry (Gerald) Weinberg once said, “If you are not learning something new each day, you are not testing.” Well, when the technology, agile, and DevOps methodologies are advancing rapidly, while accelerated development and continuous deployments are getting more complex, testing becomes quite a critical phase. This allows testers to work harder and demands more deliberation.
Learning about the latest trends and advancing in technical skills becomes inevitable to keep up with the trends and avoid becoming obsolete. In this scenario, every tester needs to be well-versed with the technical skills—to get greater insight, a great degree of effectiveness, and effectively communicate the failures and defects in the system to developers.
A tester with a good understanding of requirements analysis, design, and coding, has great insight into the defect life cycle. They can easily understand which area of code has the maximum defects and how it could be resolved by helping developers. There are some good technical skills of a tester that help in preventing defects from getting introduced in the delivered code.
1. Agile Testing
The software testing process—agile testing follows the principles of agile software development. Agile testing aligns with iterative development methodology in which requirements develop gradually from customers and testing teams. The development is aligned with customer requirements.
Agile testing is a continuous process, but not sequential. The testing starts from the beginning of the project, and there is ongoing integration between testing and development. The main and common goal of agile development and testing is to achieve high product quality.
2. Automation Testing
By leveraging the latest technologies, increasing complexities in software, and integrations in the application, using manual testing alone cannot take you to the right path. For testing browser compatibility, performance, headless, as well as database, and integration layers, software testers or QA engineers should learn automation skills since it imparts higher accuracy because of the business logic and technicalities it can serve. Plus, several test automation tools completely support the testing type and have the features to get the tasks done quickly and effectively.
3. Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
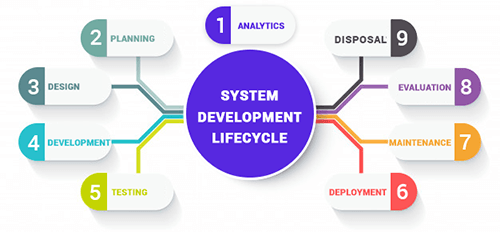
It’s one of the important and preferable things—if a tester is willing to learn software development life cycle management skills. The whole structure of SDLC will help them understand the application development tasks and plan the testing cycle accordingly. Having a strong and deep knowledge of the SDLC cycle will also help testers anticipate complexities in the application, which can guide them in taking the right measures beforehand. Along with this, testers must also learn other development mythologies like Kanban, Waterfall, Scrum, Lean, etc.
4. Technologies in Web and Mobile
Every tester must be aware of the latest technologies that are trending in web and mobile. Hence, they can understand the type of application, its build, and scalability and apply a suitable course of action for its testing. Testers must keep an eye on the latest technologies of web and mobile and what’s trending since it guides them in comprehending the coding architecture and technical challenges to deliver effective QA solutions.
5. Testing Tools and Techniques
Every tester needs to be armed with the latest and different testing techniques and the usage of tools. The other testing types, like black-box testing, penetration testing, security testing, system testing, unit testing, etc., help testers work on any sort of project irrespective of the domain and application type. Apart from this, the other testing tools available in the market, like bug tracking tools, management tools, GUI testing tools, automation tools, etc., will help testers serve different requirements and complexities of the project.
6. Defect Tracking and Test Case Management Tools
Defect tracking and defect life cycle are the key roles of any software testing phase. It’s very difficult to manage defects properly and systematically track them. The tester with a wide knowledge of defect tracking and test case management tools, like QC, Bugzilla, Jira, etc., will help them lock the defect, including managers, developers, and testers.
7. Database or SQL
Over the last four decades, SQL has been the standard programming language for database management. Since then, the software systems have had a massive amount of data in the background. Since the data is stored in different types of databases like Oracle, MySQL, etc., in the backend, testers must understand the query and manipulate the data. So, if testers are versed in databases or SQL, that becomes easier for them to give proper solutions when this data needs to be validated. A single database or SQL query can be encountered to check whether the proper data is stored in the backend database.
8. Cross-Browser Testing Skills
Due to the demand for various browsers along with multiple devices and variations in different screen sizes for smartphones, the need for browser compatibility testing is more than ever.
This cross-browser testing skill allows testers to test their developed application across different browsers. This test ensures the delivery of the product without any bugs or errors, which could work on every platform smoothly.
9. Project Management
Software testing skills are a mixture of technical and professional aspects. To manage both, testers need to be able to take ownership of the project. This means a tester delivers the project after the completion of testing. Learning project management skills will instill problem-solving abilities in testers. In this way, testers will be accountable and answerable for their work to the concerned person and carry the responsibility and management of the end-to-end testing project. Project management skills also play an important role to promote a sense of responsibility. This way, the tester can improve the entire testing process and deliver quality results to the client.
10. Basic Programming Knowledge
When we talk about programming, that doesn’t mean every tester should work as a developer. However, it’s very important to understand the insights of the application so it becomes easy for a tester to understand its functionality and create tests accordingly. The basic knowledge of programming will help testers identify possible errors in the application code, which further reduces the chances of bugs and application inefficiencies. It’s advisable for every tester to learn at least a few programming languages since there are good chances for them to know the workarounds of the application.
11. General Operating Systems Knowledge
This also includes core IT skills. If you are keen to learn and explore more in your field, you will find it easy to learn and use new operating systems. Of course, it’s mandatory to learn OS, Windows, Linux, and Mac, and know what the basic differences are across desktop OS and spot the difference.
On the mobile platform, it’s also good to be familiar with iOS and Android. Since wearable devices are booming, you should sneak into the scene—Tizen and Android Wear OS.
12. Domain Knowledge
Knowing different domains is essential for every QA or software tester. Testers can become more creative with the knowledge of software testing domains. So, it helps in increasing the value of the software product. Having good domain knowledge will assist every tester in an improved manner to have a clear understanding of the testing techniques that are required by the client or which meet the client’s requirements. The knowledge of multiple domains for every QA opens the door to multiple jobs as sometimes some clients require people who have domain expertise in a specific domain like legal, health, finance, banking, etc.
Every tester needs to balance all the skill activities so that all product aspects will get addressed.
Conclusion
Regardless of the educational background and years of experience, testers should always strive to learn and improve their technical software testing skills and knowledge. Be it self-learning or engaging in a training program, testers should always be eager to learn more methods and processes to improve their performance in testing and keep implementing the new skills and learning to keep themselves ahead of the completion.
Published at DZone with permission of Kiran Beladiya. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments