Spring Cloud Gateway - Configuring a Simple Route
Spring Cloud Gateway can help implement the gateway pattern for your API, especially in a microservices environment. Learn how to make use of it by way of an example.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
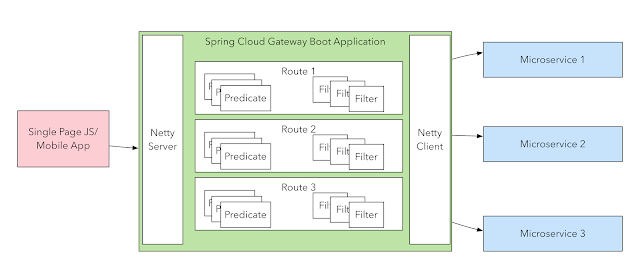
Join For FreeSpring Cloud Gateway can be considered a successor to the Spring Cloud Netflix Zuul project and helps in implementing a Gateway pattern in a microservices environment. It is built on top of Spring Boot 2 and Spring Webflux and is non-blocking end to end - it exposes a Netty based server, uses a Netty based client to make the downstream microservice calls and uses reactor-core for the rest of the flow.
My objective here is to show how a small Spring Cloud Netflix Zuul based route can be translated in multiple ways using Spring Cloud Gateway.
Spring Cloud Netflix Zuul
Spring Cloud Zuul allows simple routing rules to be configured using property files expressed as a YAML here:
zuul:
routes:
sample:
path: /zuul/**
url: http://httpbin.org:80
strip-prefix: trueThis route would expose an endpoint in Zuul which intercepts any requests made to URIs with a prefix of "/zuul" and forwards it to the downstream system after stripping out the "zuul" prefix.
Spring Cloud Gateway
Spring Cloud Gateway allows an equivalent functionality to be coded in three ways - using a Java-based DSL, using a Kotlin-based DSL and using simple property based configuration.
A starter project can be generated using the excellent http://start.spring.io site:
Java-Based DSL
A Java-based DSL that creates a route similar to the Zuul route is the following:
import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.RouteLocator;
import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.builder.RouteLocatorBuilder;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class GatewayRoutes {
@Bean
public RouteLocator routeLocator(RouteLocatorBuilder builder) {
return builder.routes()
.route(r ->
r.path("/java/**")
.filters(
f -> f.stripPrefix(1)
)
.uri("http://httpbin.org:80")
)
.build();
}
}
This is a readable DSL that configures a route which intercepts URIs with a prefix of "java" and sends it to a downstream system after stripping out this prefix.
Kotlin-Based DSL
A Kotlin based DSL to configure this route looks like this.
import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.RouteLocator
import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.builder.RouteLocatorBuilder
import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.builder.filters
import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.builder.routes
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration
@Configuration
class KotlinRoutes {
@Bean
fun kotlinBasedRoutes(routeLocatorBuilder: RouteLocatorBuilder): RouteLocator =
routeLocatorBuilder.routes {
route {
path("/kotlin/**")
filters { stripPrefix(1) }
uri("http://httpbin.org")
}
}
}
I had originally submitted the PR for Kotlin based DSL for Spring Cloud Gateway routes and so have a bias towards using Kotlin for configuring Spring Cloud Gateway. The route takes in URLs with a prefix of "kotlin" and strips it out before making the downstream microservice call.
Property-Based Route
And finally, the property-based one:
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- predicates:
- Path=/props/**
filters:
- StripPrefix=1
uri: "http://httpbin.org"
This route like the Java and Kotlin version takes in a URL with a prefix of "props" and strips this prefix out before making the downstream call. The properties based version has the added advantage of being refreshable at runtime.
Conclusion
This is a very quick intro to Spring Cloud Gateway by comparing how a typical configuration from Spring Cloud Netflix Zuul maps to Spring Cloud Gateway.
Published at DZone with permission of Biju Kunjummen, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.


Comments