Reactive vs. Synchronous Performance Test With Spring Boot
The author conducts two tests with differing service delay times to measure any difference in performance between reactive and synchronous programming.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeAuthor's note: This is a modified repost of a test done back in 2018.
Reactive is a programming paradigm that uses asynchronous programming. It inherits the concurrency efficiency of the asynchronous model with the ease of use of declarative programming.
Multithreading is able to parallelize work on multiple CPUs, but when an IO operation is issued, the thread blocks waiting for the IO to complete.
Reactive/Async does not parallelize work on multiple CPUs, but when an IO operation is issued, the CPU is handed over to the next task in the event loop.
Typically, using multiple processes or threads is better for CPU-bound systems and async/reactive is better for IO-bound systems.
Easier Asynchronous Programming
Let’s see an example of a method that fetches a user from a database, does some conversions, transformations, and then displays the results.
The synchronous version looks like this:
User user = getUserFromDBSync(id);
user = convertUser(user);
user = processResult(user);
displayResults(user);Pretty straightforward.
The async version with callbacks has deeply nested code, essentially the “callback hell."
getUserFromDB(id, user -> {
convertUser(user, convertedUser -> {
processResult(convertedUser, processedUser -> {
displayResults(processedUser);
});
});
});Now, let's see the same example with the reactive approach. It is much more readable and maintainable than the async/callback version.
getUserFromDBAsync(id)
.map(user -> convertUser(user))
.map(user -> processResult(user))
.subscribe(user -> displayResults(user));Performance on High Concurrency Scenarios
On the concurrency topic, I’ve decided to do a small test to evaluate the difference between the reactive versus the synchronous version for IO-bound operations.
You can get the test project on GitHub.
The test setup is as follows:
- Load testing client (Gatling)
- Test Service (Spring Boot)
- External backend service (simulated)
Load Testing Client
The following components were used:
- AWS EC2 t2.small 1vCPU / 2GB RAM
- Gatling 2.3.0
- Continuous request loop without any delay between requests
- 2 configurations of external service: one with 500ms response time; another with 2.000ms response time
Load Test #1: External Service Delay 500ms

With <=100 concurrent requests, the response times are very similar between the 2 versions.
After 200 concurrent users, the synchronous/tomcat version starts deteriorating the response times, while the reactive version with Netty holds up until 2.000 concurrent users.
Load Test #2: External Service Delay 2.000ms
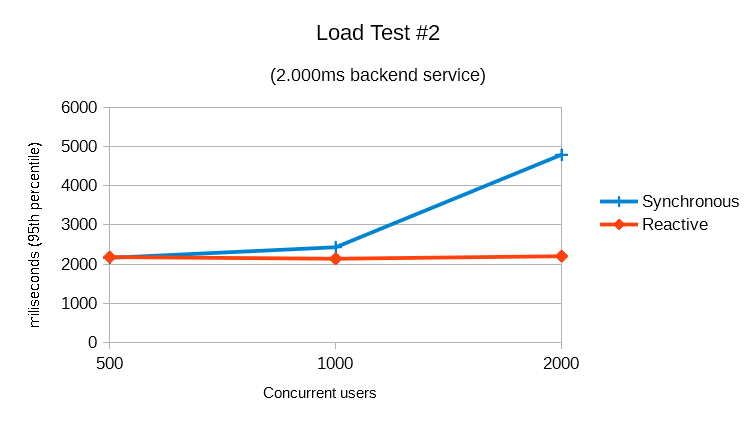
This test uses a much slower backing service (4x slower) and the service handles a much larger load. This happens because, although the number of concurrent users are the same, the number of req/sec is 4x lower.
In this test, the synchronous version starts deteriorating with 4-5x the number of concurrent users than the prior 500ms delay test.
Test Service
The test service simulates a query to an external service (ex: database) which takes some time to return a list of records. For simplification, the test doesn’t send a query to a real database, but instead, it simulates the response delay.
The synchronous version uses the following:
- A Spring Boot 2.0 (2.0.0.RC1) application/Spring MVC framework
- Embedded Tomcat container with max threads=10.000 (large number to avoid queued requests)
- Hosted on AWS ECS/Fargate with 256 mCPU/2GB RAM
NOTE: In a typical environment, having this many threads would lead to DB connection pool exhaustion and queries would start getting queued, thus increasing the response time.
The reactive version uses the following:
- A Spring Boot 2.0 (2.0.0.RC1) application/Spring Webflux framework
- Netty framework
- Hosted on AWS ECS/Fargate with 256 mCPU/2GB RAM
Hope you enjoyed the post.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments