Secrets Manager in Anypoint Platform
Learn more about Secrets Manager in Anypoint Platform.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeWe can use the secrets manager to write, read, and manage your secrets, keys, and Transport Layer Security (TLS) certificates within a unique source that allows access to other authorized platform services on your behalf.
This is the central and secure repository to manage the secrets. Please note that the Secrets manager is supported on Runtime Fabric and API Manager only. Secrets manager uses secure vault technology to store and control access to private keys, passwords, certificates, and other secrets.
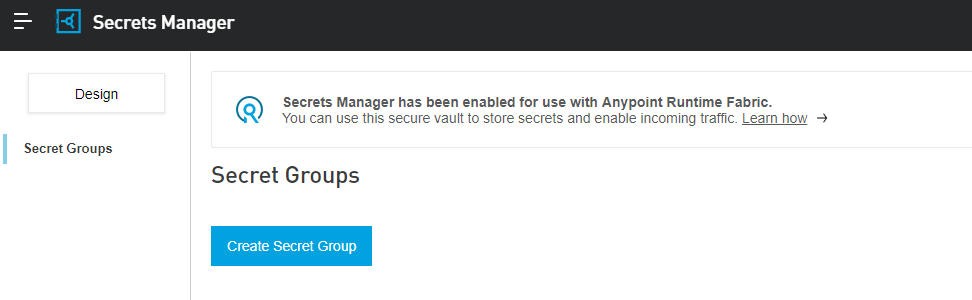
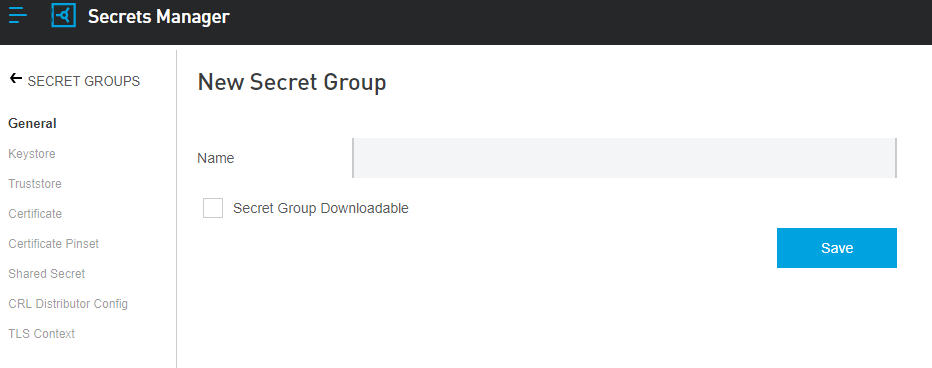
Anypoint Secrets Manager lets you store these secrets in secret groups, which are vaults associated with your environment and business group.
Each secrets group has unique encryption keys with per-instance access rules for read, write, and manage. You can configure your applications or platform services to request those secrets, and you can control which services are authorized to access them.
This basic task is handled by two microservices:
- Secrets Manager: This service handles the upload and storing of your secrets. Every time you upload a secret to your vault, the Secrets Manager establishes a reference to it, so it can be shared or read without revealing its contents.
- Secrets Provider: This service handles the secrets for consumption by platform services. This is the only service that can read actual secrets, and due to its nature, this is an internal service and not accessible from the public network. This service is used by the requesting client to consume the secret.
Secrets Manager can store and manage the following secret types:
Shared Secrets
Shared secrets are used for symmetric encryption and decryption, where the secret is known by both the message sender and the message recipient. Please find the below process in the Anypoint Platform.
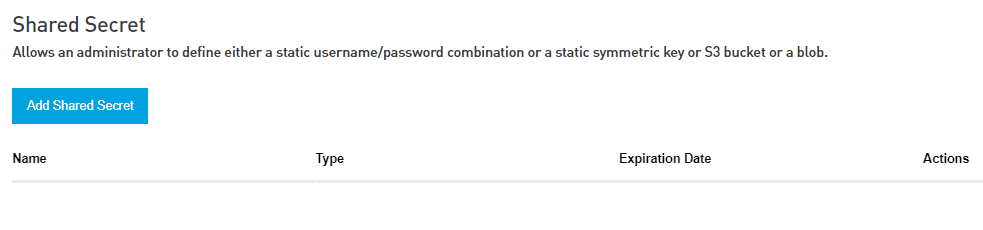
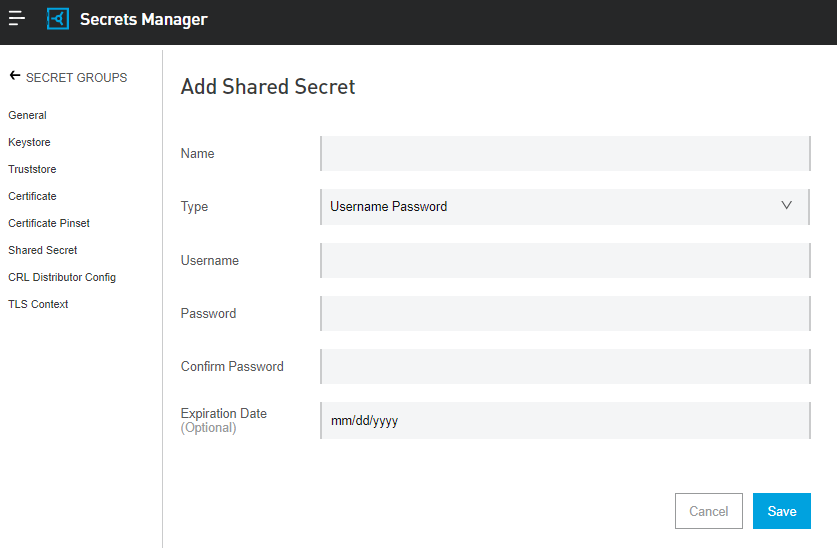
Anypoint Secrets Manager lets you store the following secret types to use as shared secrets.
- Passwords: A password used by the sender and recipient to encode and decode the message.
- Symmetric Keys: A public key cryptography used by the sender and recipient to encode and decode the message.
- S3 Credentials: A pair of security keys to access AWS S3 buckets.
- Blob: A free-form and application-specific secret. Blobs are base64 encoded data used by specific applications. For example, a blob could store a base64-encoded JSON object. The secret is stored through an API call and must be base64 encoded.
Certificates
Public X.509 certificates, electronic documents that bind together a public key with an identity (hostname, organization, or individual).
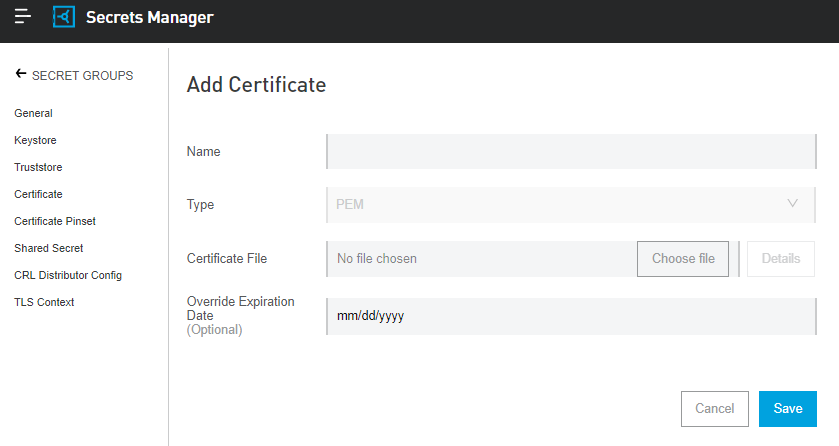 Private Keys
Private Keys
A secret key value paired with a public key to set off algorithms for encryption and decryption.
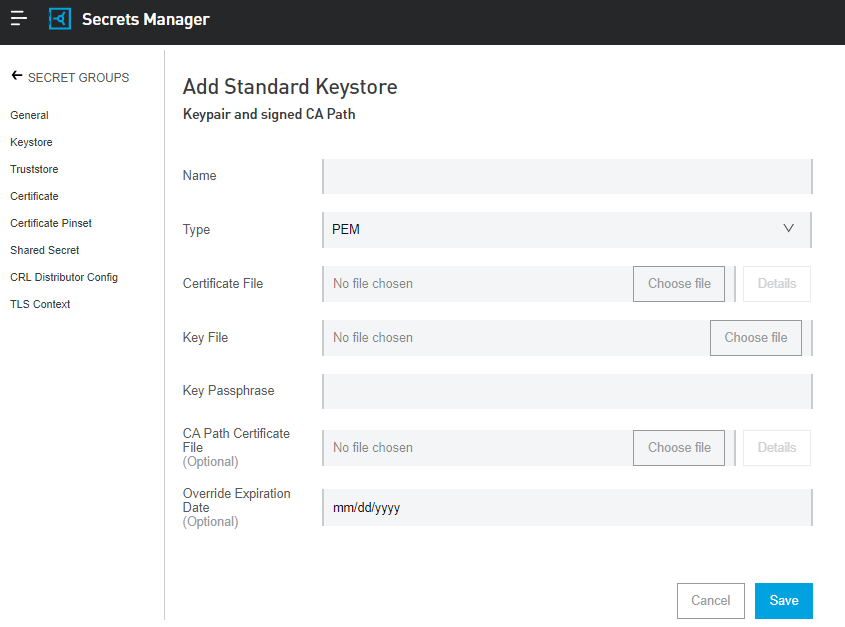
Keystore
A repository of security certificates (either authorization certificates or public key certificates) along with their corresponding private keys.

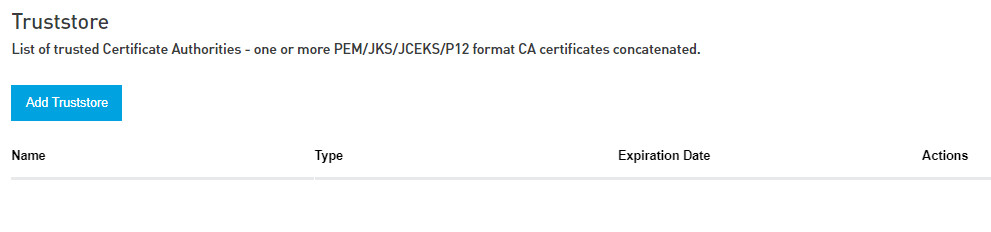
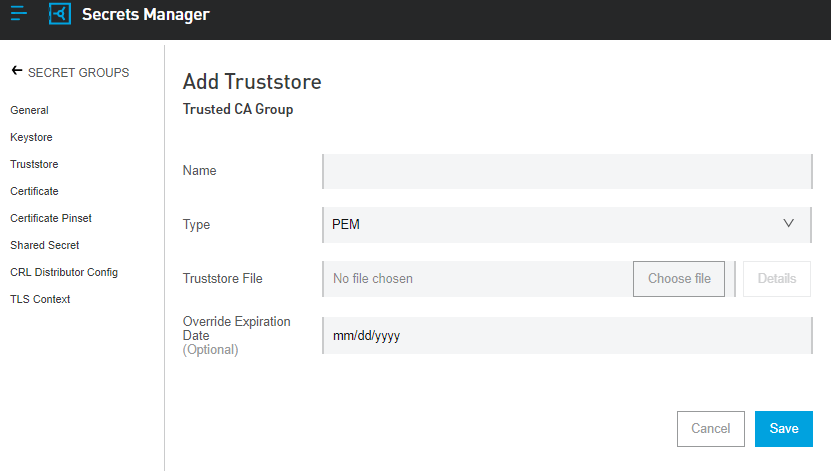
Truststore
A repository of security certificates from other parties with which you expect to communicate or from Certificate Authorities that you trust to identify other parties.
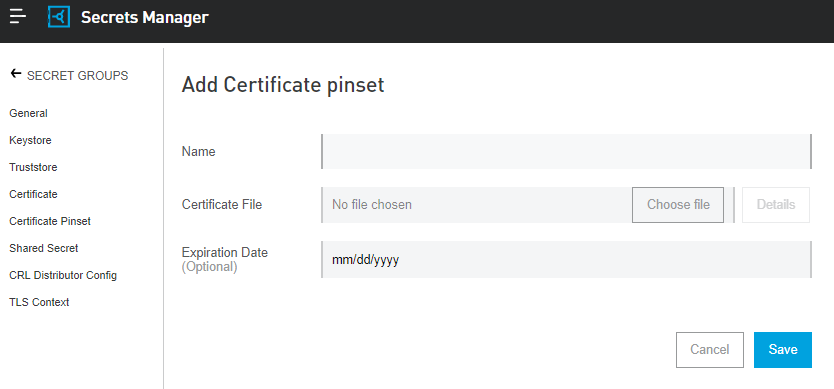
Certificate Pin Set
A repository of security certificates from other parties that associate a client or host with their expected X.509 certificate or public key.
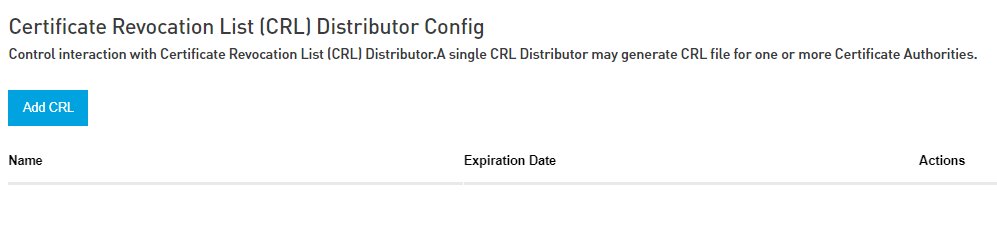
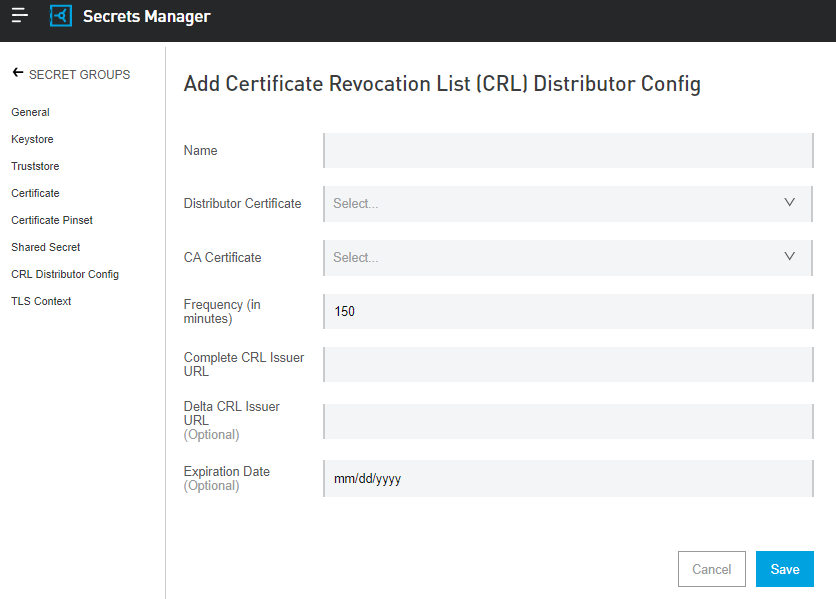
CRL Distributor
An entity that creates and maintains a list of CA certificates that are no longer trusted because their associated private keys, or a signing CA, were compromised.
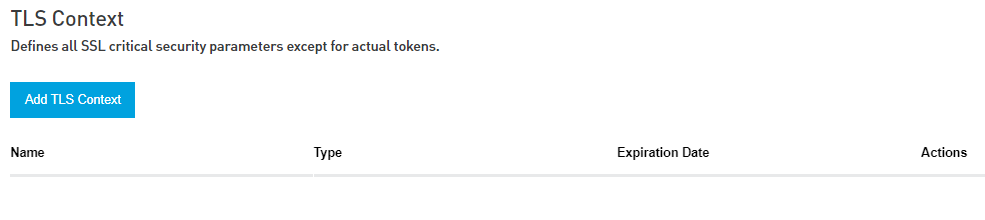
TLS Context
SSL Security Parameters (ciphers to use, TLS version, and so on).
Anypoint Secrets Manager does not save the actual values of your secrets within your application bundle. It saves a placeholder for those values, which is later replaced by the actual secret accessed only by the secrets provider when an authorized client requests it.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments