The Critical Role of Data at Rest Encryption in Cybersecurity
Data at rest encryption is vital in cybersecurity, securing stored data from unauthorized access and breaches. It ensures that even if data is stolen, it remains unreadable.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeSecuring information is crucial as cyber-attacks are getting more sophisticated. Data residing in an unprotected state at rest (databases, stored files, and backups) pose one of the most significant risks.
Data at rest encryption is necessary to guarantee that information is safe and unreadable even in the event of illegal access. This discussion highlights why encrypting data is seen as an indispensable part of bolstering overall cyber security and keeping assets safe from unwanted entry.
Deciphering Dormant Data
Unlike data in transit, where data is continuously moving between systems and over networks, data at rest refers to information that exists on a piece of hardware or within any digital storage system.
Their backup systems have an entirely different set of security challenges to keep out malicious actors as opposed to data in transit that is protected through well-defined protocols during movement.
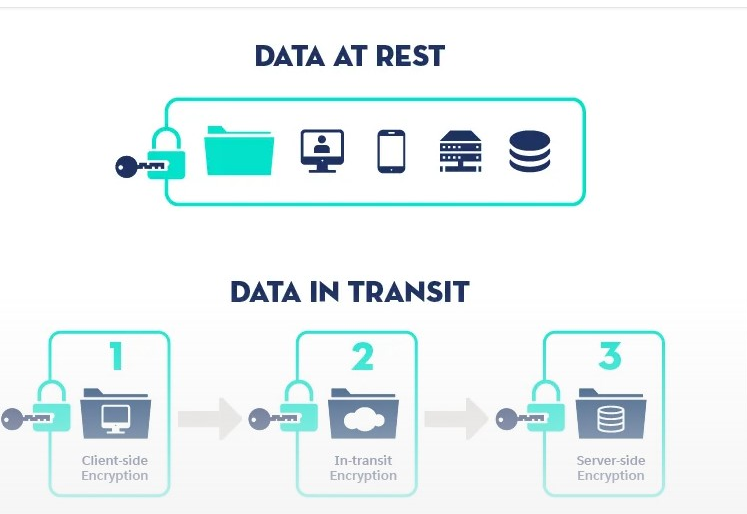
Examples of data at rest include files on hard drives, structured organized groups of records (including database tables), and archived backups. This data could be available through alternate apps or interfaces that are static.
Varonis's World in Data Breaches report stated that 7 million unencrypted data records are compromised daily. Data at rest is mandatory in some sectors such as healthcare and finance. This guarantees that it meets applicable regulations like HIPAA, providing security to healthcare industry data. It also secures private financial information in finance against theft and unlawful use.
Government entities make use of strong encryption to safeguard confidential information and prevent illegal access. Data at rest protection remains a linchpin to a full spectrum of cyber security.
The Growing Threat Landscape
A pressing issue in cybersecurity advancements is the growing array of high-level assaults being aimed directly at data at rest. Some of these technologies are currently being used by hackers.
Malicious actors can encrypt the victims' data and hold it for ransom thus denying them access, or sell confidential information. Additionally, social engineering attacks are often employed to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information or credentials. In the case of ineffective data-at-rest encryption, these attacks can result in a large-scale breach that puts private information organizations at risk.
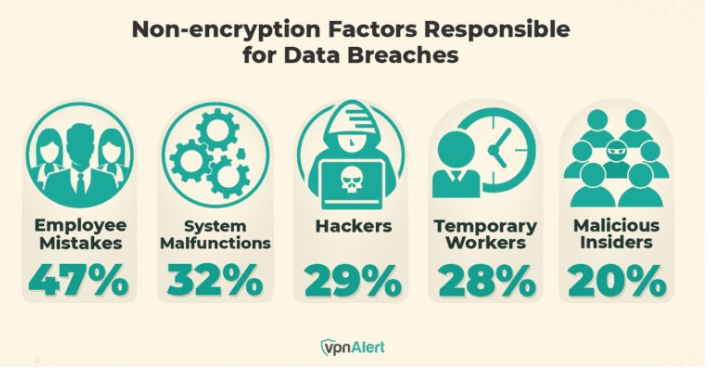
The hazards connected to unprotected data at rest are sharply brought to light by the Capital One data breach of 2019. In this incident, more than 100 million personal details of the bank’s clients were leaked when a hacker breached the institution’s cloud-stored data due to a misconfigured firewall. The attack’s impact could have been significantly reduced by stronger data storage encryption that would make the stolen information worthless without the decryption key.
The repercussions of data at rest compromise are catastrophic; businesses may experience financial losses directly through fines and legal fees and indirectly through negative brand recognition and loss of consumer trust.
Furthermore, as the process of recovering after such hacking typically entails costly implementations of new security systems and processes, the consequences for a company’s daily functioning in the long term are severe. Any business that seeks to defend its most vital property from an escalating hazard profile must start implementing data-at-rest encryption today. This is no longer an option.
How Data at Rest Encryption Works
Shielding inactive data stored on physical devices such as hard drives, databases, or cloud storage requires data-at-rest encryption. It guarantees that no one can read or make the most of this saved data when exposed to illicit reach without suitable encryption keys. This is how it works:
A. Encryption Algorithms
Two main algorithms are employed in encrypting stored data. They are:
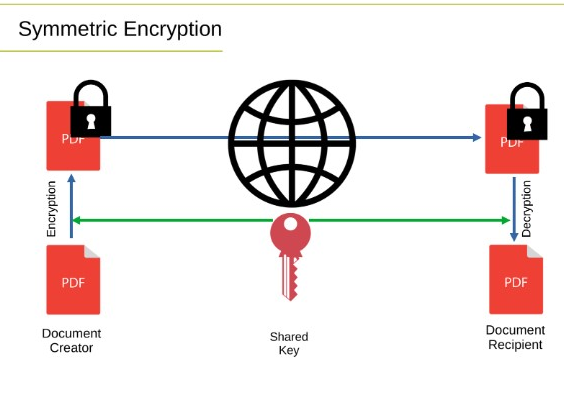
Symmetric Encryption
This technique uses a single key for both encryption and decryption. It is a fast approach and helpful for large datasets. But the difficulty lies in sharing the key between parties safely.
Asymmetric Encryption
This encryption technique uses two keys, the public key to encrypt and the private key to decrypt. This method improves security by eliminating secret keys that need to be shared though it is slower.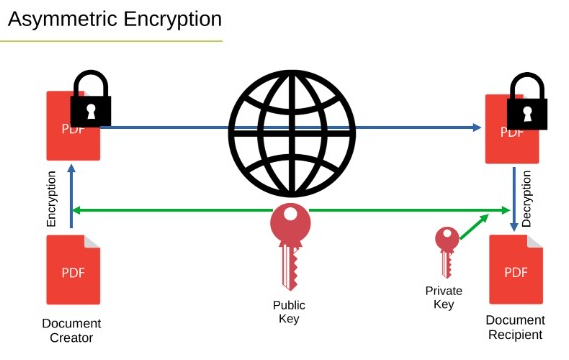
B. Encryption Keys
Stored data encryption security is more dependent on the safety of the access keys. Strong key management processes such as secure storage, rotation, and access control are required to be in place. Key protection ensures the data stays useless even when encrypted data is stolen.
The best password managers are among the greatest key protection additions you can make. It is helpful to have these tools and help you store the keys securely ensuring that none other than authorized personnel can access them.
C. Implementing Encryption
Data at rest is encrypted using two main methods: Software-Based Encryption and Hardware-Based Encryption.
Software-based encryption means specialized software used to save data to any device. This type of data encryption is customizable and may be used for various storage systems. However, software-based encryption systems require processor power to encrypt data themselves, which might raise latency and system issues.
The second type is hardware-based encryption, built into hardware storage itself. This technique encrypts and decrypts information more quickly and demands fewer system resources. Self-encrypting drives is an example.
Regulatory Compliance and Data Protection Laws
Without a doubt, compliance and data protection are crucial. Standards such as GDPR(General Data Protection Regulation) and HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), have made the security of sensitive information an integral part. These laws dictate tough data security measures for personal and health information.
Data at rest encryption is essential to ensure compliance with these mandates. When data is encrypted at rest, businesses can secure their stored data in case of a breach where unauthorized access has been properly controlled. This helps keep sensitive data inaccessible to anyone without the appropriate decryption keys, and therefore compliant with GDPR privacy rules and HIPAA protections for personal health information.
Encryption is employed by 42% of respondents for customer data, ranking it as the fifth most commonly encrypted type of information in businesses. Implementing data at storage encryption helps in regulation and most importantly the trust of customers.
Businesses can strengthen customer relationships by investing in protecting personal information. At the same time, strong protection systems prevent fines and legal issues as a result of data leaks, ultimately saving organizations from financial losses and reputational damage.
Integrating Data at Rest Encryption into a Comprehensive Security Strategy
Static data encryption fits seamlessly into a defense-in-depth strategy by providing an additional layer of security. While firewalls and intrusion detection systems (IDS) safeguard against unapproved network access and monitor suspicious activity, encryption ensures that even if these shields are breached, the data remains inaccessible. Encrypting data at rest adds a crucial safeguard, rendering stolen or intercepted data unreadable without the proper decryption keys.
Encryption complements firewalls, IDS, and multi-factor authentication (MFA). Firewalls protect against unsanctioned access from the outside, and IDS detects and alerts users to potential threats, while MFA provides additional identity authentication for user account access. Blockchain technology further enhances this security framework by offering a decentralized ledger that ensures data integrity and transparency, making it nearly impossible for unauthorized parties to alter information.
Combining them is a holistic security solution. Therefore, encryption keeps any information intercepted safe; firewalls and IDSs on the other hand help secure the data from being accessed or exploited in the first place.
Stored data encryption combined with other security factors strengthens overall data security thereby minimizing risk. It constructs a complete solution for external attacks and internal data security providing full-fledged protection against standard threats or possible inside jobs. Embedding encryption into a larger security strategy creates an adaptable safeguard that narrows the attack surface and strengthens data against many types of threats.
Securing the Foundation of Data Protection With Encryption
In this era of growing cyber threats and data breaches, encrypting data at rest is an essential extra layer of defense. Encrypting at rest secures stored data by protecting against unauthorized access providing improved safety, compliance, and privacy of the data.
Due to developing cyber threats, it is becoming increasingly necessary rather than optional for organizations to establish themselves with encryption solutions to secure their assets and maintain confidence within the digital realm.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments