Reflections From a DBA: Embracing the Cloud and Unlocking the Potential of Optimized Solutions
In this article, take a deep dive into clouds and discuss their optimal suitability based on different types of organizational or individual needs.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeThis is an article from DZone's 2023 Database Systems Trend Report.
For more:
Read the Report
The cloud is seamlessly integrated with almost all aspects of life, like business, personal computing, social media, artificial intelligence, Internet of Things, and more. In this article, we will dive into clouds and discuss their optimal suitability based on different types of organizational or individual needs.
Public vs. Private Cloud Evaluation
Mixing and matching cloud technologies provides a lot of ease and flexibility, but it comes with a lot of responsibilities, too. Sometimes it is difficult to make a choice between the types of cloud available, i.e., public, private, or hybrid cloud. An evaluation based on providers, cloud, and project demand is very crucial to selecting the right type.
When evaluating a public and private cloud, it is important to consider the factors listed in Table 1:
|
PUBLIC VS. PRIVATE CLOUD
|
||
|---|---|---|
| Public Cloud | Private Cloud | |
| Best use cases |
|
|
| Cost |
|
|
| Workload |
|
|
| Infrastructure |
|
|
| Services |
|
|
| Presence |
|
|
Table 1
Hybrid Cloud
Both public and private clouds are useful in various ways, so it is possible to choose both to gain maximum advantages. This approach is achieved by adopting a hybrid cloud. Let's understand some of the key factors to consider:
- Hybrid clouds are suitable when the workload is both predicted or variable. A public cloud provides scalability and on-demand resources during peak seasons, while a private cloud handles base workload during off-seasons.
- To save money, public clouds can be shut off during non-peak seasons and store non-sensitive data. Private clouds generally cost more, but it is necessary for storing sensitive data.
- Private clouds are used for confidential data; non-regulated or non-sensitive information can be stored in a public cloud.
- Hybrid cloud is suitable for businesses operating in multiple regions. Private clouds serve specific regions, while public cloud providers offer global reach and accessibility for other services.
Before adopting a hybrid approach, thorough analysis should be done, keeping factors such as workload patterns, budget, and compliance needs in consideration.

Figure 1: Hybrid cloud combines features of public and private cloud
Key Considerations for DBAs and Non-DBAs
To achieve overall operational efficiency, it is essential for DBAs and non-DBAs to understand the key considerations related to database management. These considerations will help in effective collaboration, streamlined processes, and optimized data usage within an organization.
Cost Optimization
Cost is one of the major decision-making factors for everyone. It is very crucial to consider cost optimization strategies surrounding data, backup and archival strategies, and storage.
Data is one of the most important factors when it comes to cost saving. It is always good to know your data patterns and to understand who the end user is so the classification of data is optimized for storage. No duplicates in data means no extra storage used. Also, an in-depth understanding of the types of storage available is required in order to get maximum benefit within budget. Classify your data into a structured or unstructured format.
It is important for DBAs to analyze data that is no longer actively used but might be needed in the future. By moving this data to archival storage, DBAs can effectively save primary storage space. Implementing efficient backup strategies can help minimize redundant storage requirements, hence less cost.
Data, storage, and cost are directly proportional to each other, so it is important to review these three for maximum benefits and performance with minimum costs from cloud providers. Available storage options include object storage, block storage, thin provisioning, and tiered storage.
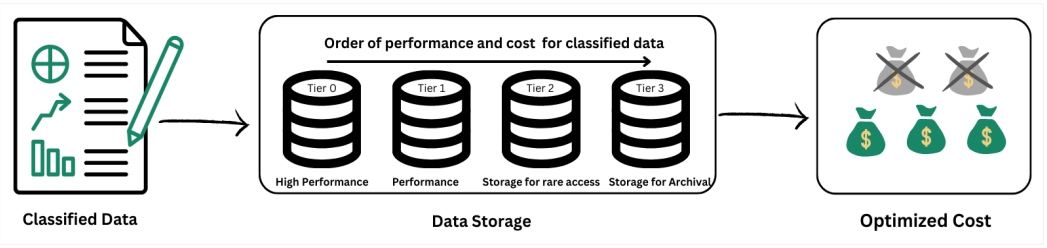
Figure 2: Data is directly proportional to the storage used and cost savings
Performance
To optimize storage speed, cloud providers use technologies like CDNs. Network latency can be reduced through strategies such as data compression, CDNs, P2P networking, edge computing, and geographic workload distribution. Larger memory capacity improves caching and overall performance.
Computing power also plays a vital role. Factors like CPU-intensive tasks and parallel processing should be considered. GPUs or TPUs offer improved performance for intensive workloads in machine learning, data analytics, and video processing.
Disaster Recovery
Data should be available to recover after a disaster. If choosing a private cloud, be ready with backup and make sure you will be able to recover! It's important to distribute data, so if one area is affected, other locations can serve and business can run as usual.
Security
Cloud providers have various levels of data protection:
- With multi-factor authentication, data will be secure by adding an extra layer of verification. A token will be sent to a mobile device, via email, or by a preferred method like facial recognition.
- The right data should be accessible by the right consumer. To help these restrictions, technologies like identity and access management or role-based access control assign permission to the users based on assigned roles.
- Virtual private networks could be your savior. They provide secure private network connections over public networks and encrypted tunnels between the consumer's device and the cloud that will protect data from intruders.
- With encryption algorithms, clouds protect data at rest and in transit within infrastructure. However, it is always a good idea for a DBA and non-DBA to configure encryption settings within an app to achieve an organization's required security.
Scalability
When working with a cloud, it is important to understand how scalability is achieved:
- Cloud providers deploy virtual instances of servers, storage, and networks, which result in faster provisioning and allocation of virtual resources on demand.
- Serverless computing allows developers to focus on writing code. Infrastructure, scaling, and other resources required to handle incoming requests will be handled by cloud providers.
- Cloud providers suggest horizontal scaling instead of vertical scaling. By adding more servers instead of upgrading hardware in existing machines, the cloud will develop a distributed workload, which increases capacity.
Vendor Lock-In
For organizations looking for flexibility and varying cloud deployments, the risk of vendor lock-in can be limiting. To minimize this risk, implementing a hybrid cloud approach enables the distribution of data, flexibility, and easy migration. Using multiple cloud providers through a hybrid model helps avoid dependence on a single vendor with diverse capabilities. Open data formats and vendor-independent storage solutions will help in easy porting. In addition, containerization technologies for applications allow flexible vendor selection. It is essential for organizations to consider exit strategies, including contractual support, to ensure smooth transitions between vendors and to reduce challenges.
Next Steps
Cloud computing is a huge revolution for not only the IT industry but also for individuals. Here are some next steps based on the features and extensive usage.
Extensive Acceptance
Cloud computing is a long-term deal. It offers flexibility and the ability for developers to focus on code alone, even if they don't have prior knowledge or a dedicated team to maintain infrastructure. Other benefits include increased innovation, since most of the hustle is taken care by the cloud providers, and little-to no downtime, which is great for businesses that operate 24/7.
Database Options To Mix and Match in the Cloud
When we talk about cloud computing, there are many databases available. The following are some popular database options:
|
DATABASE OPTIONS
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NoSQL | Relational | Serverless | Managed Database Services | |
| Purpose | Structured and unstructured data | Structured and complex queries | Unpredictable workloads | Simplify database management |
| Pros | Scalability, flexibility, pairs well with cloud computing | Strong data consistency, robust query capabilities | Pay per usage, server management | Scaling, automated backups, maintenance, cost-effective |
| Cons | Data consistency | Scalability, fixed schema | Vendor lock-in | Dependent on providers |
| Prevalence | Will grow in popularity | Will continue to stick around | Will grow in popularity | Will be a secure choice |
| Examples | MongoDB, Cassandra | MySQL, Postgres, Oracle | Google Cloud Firestore, Amazon Aurora Serverless | |
Table 2
Conclusion
It is important to note that there are scenarios where a private cloud might be preferred, such as when strict data security and compliance requirements exist, or when an organization needs maximum control over infrastructure and data. Each organization should evaluate its specific needs and consider a hybrid cloud approach, as well.
Cloud providers often introduce new instances, types, updates, and features, so it is always good to review their documentation carefully for the most up-to-date information. By mindfully assessing vendor lock-in risks and implementing appropriate strategies, businesses can maintain flexibility and control over their cloud deployments while minimizing the challenges associated with switching cloud providers in the future.
In this article, I have shared my own opinions and experiences as a DBA — I hope it offered additional insights and details about cloud options that can help to improve performance and cost savings based on individual objectives.
This is an article from DZone's 2023 Database Systems Trend Report.
For more:
Read the Report
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments