10 Best Frameworks and Libraries for AI
Look at some high-quality libraries that are used for artificial intelligence, their pros and cons, and some of their features.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeArtificial intelligence has existed for a long time. However, it has become a buzzword in recent years due to huge improvements in this field. AI used to be known as a field for total nerds and geniuses, but due to the development of various libraries and frameworks, it has become a friendlier IT field and has lots of people going into it.
In this article, we will be looking at top-quality libraries that are used for artificial intelligence, their pros and cons, and some of their features. Let's dive in and explore the world of these AI libraries!
1. TensorFlow
"Computation using data flow graphs for scalable machine learning."
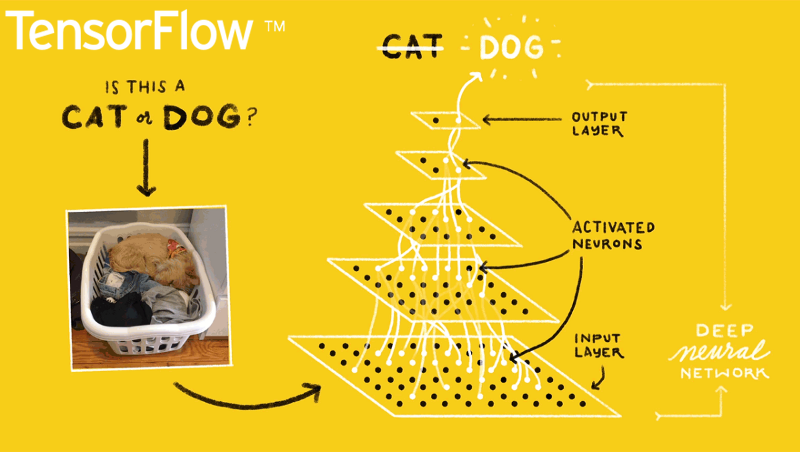
Language: C++ or Python.
When getting into AI, one of the first frameworks you'll hear about is Google's TensorFlow.
TensorFlow is an open-source software for carrying out numerical computations using data flow graphs. This framework is known for having an architecture that allows computation on any CPU or GPU, be it a desktop, a server, or even a mobile device. This framework is available in the Python programming language.
TensorFlow sorts through data layers called nodes and makes decisions with whatever information it gets. Check it out!
Pros:
- Uses an easy-to-learn a language (Python).
- Uses computational graph abstraction.
- Availability of TensorBoard for visualization.
Cons:
- It's slow, as Python is not the fastest of languages.
- Lack of many pre-trained models.
- Not completely open-source.
2. Microsoft CNTK
"An open source-deep learning toolkit."

Language: C++.
We could call this Microsoft's response to Google's TensorFlow.
Microsoft's Computational Network ToolKit is a library that enhances the modularization and the maintenance of separating computation networks, providing learning algorithms and model descriptions.
CNTK can take advantage of many servers at the same time in a case where lots of servers are needed for operations.
It is said to be close in functionality to Google's TensorFlow; however, it is a bit speedier. Learn more here.
Pros:
- It is very flexible.
- Allows for distributed training.
- Supports C++, C#, Java, and Python.
Cons:
- It is implemented in a new language, Network Description Language (NDL).
- Lack of visualizations.
3. Theano
"A numerical computation library."

Language: Python.
A strong competitor to TensorFlow, Theano is a powerful Python library that allows for numerical operations involving multi-dimensional arrays with a high level of efficiency.
The library's transparent use of a GPU for carrying out data-intensive computations instead of a CPU results in high efficiency in its operations.
For this reason, Theano has been used in powering large-scale computationally intensive operations for about a decade.
However, in September 2017, it was announced that major developments of Theano would cease after the 1.0 release, which was released in November 2017.
This doesn't mean it is a less powerful library in any way. You can still carry out deep learning research with it any time. Learn more here.
Pros:
- Properly optimized for CPU and GPU.
- Efficient for numerical tasks.
Cons:
- Raw Theano is somewhat low-level compared to other libraries.
- Needs to be used with other libraries to gain a high level of abstraction.
- A bit buggy on AWS.
4. Caffe
"Fast, open framework for deep learning."
Language: C++.
Caffe is a powerful deep learning framework.
Like the other frameworks on this list, it is very fast and efficient for deep learning research.
With Caffe, you can very easily build a convolutional neural network (CNN) for image classification. Caffe works well on GPU, which contributes to its great speed during operations. Check out the main page for more information.
Caffe main classes:
Pros:
- Bindings for Python and MATLAB are available.
- Great performance.
- Allows for the training of models without writing code.
Cons:
- Bad for recurrent networks.
- Not great with new architectures.
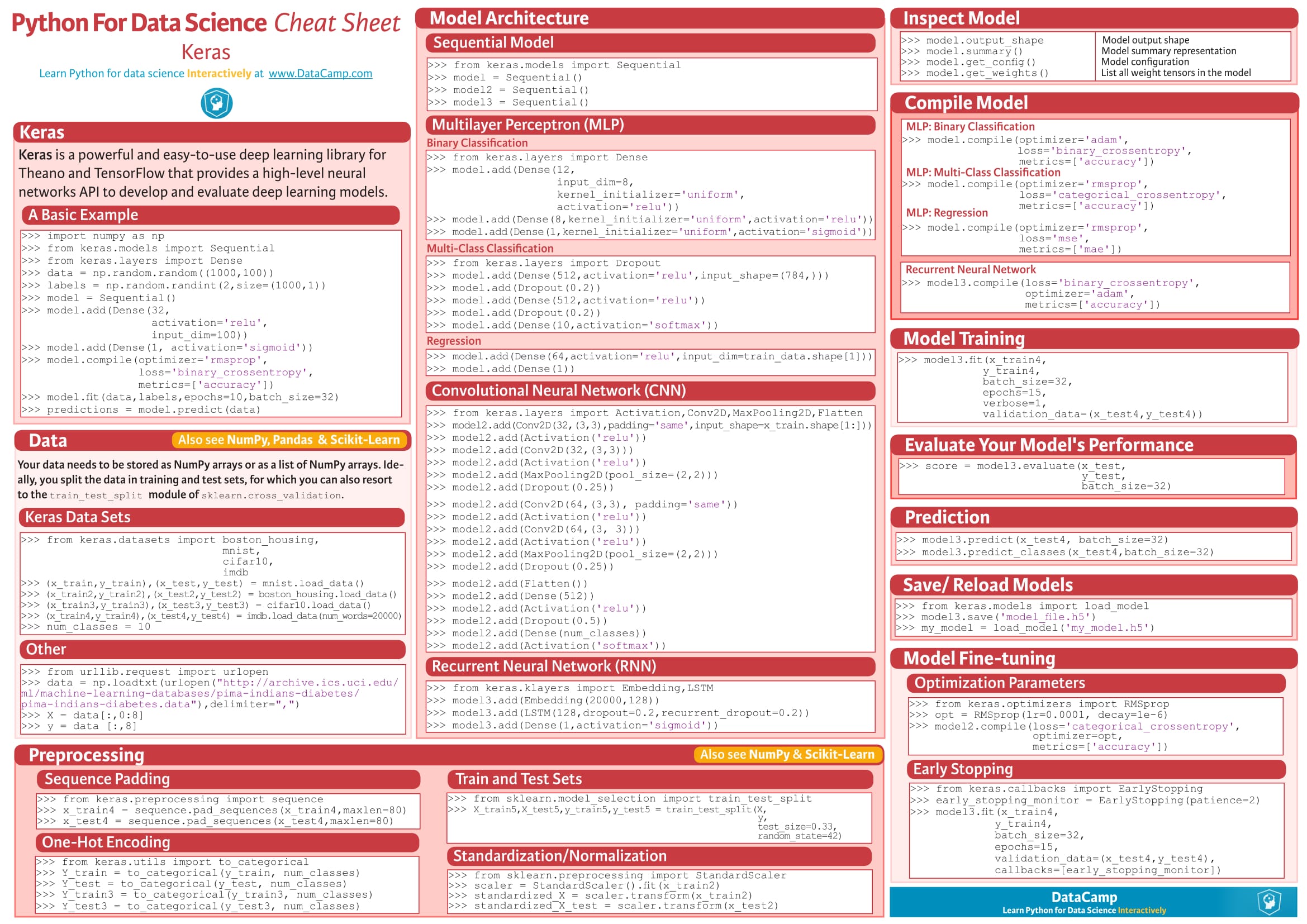
5. Keras
"Deep learning for humans."
Language: Python.
Keras is an open-source neural network library written in Python.
Unlike TensorFlow, CNTK, and Theano, Keras is not meant to be an end-to-end machine learning framework.
Instead, it serves as an interface and provides a high level of abstraction, which makes for easy configuration of neural networks regardless the framework it is sitting on.
Google's TensorFlow currently supports Keras as a backend, and Microsoft's CNTK will do the same in little or no time. Learn more here.
Pros:
- It is user-friendly.
- It is easily extensible.
- Runs seamlessly on both CPU and GPU.
- Works seamlessly with Theano and TensorFlow.
Cons:
- Can't be efficiently used as an independent framework.
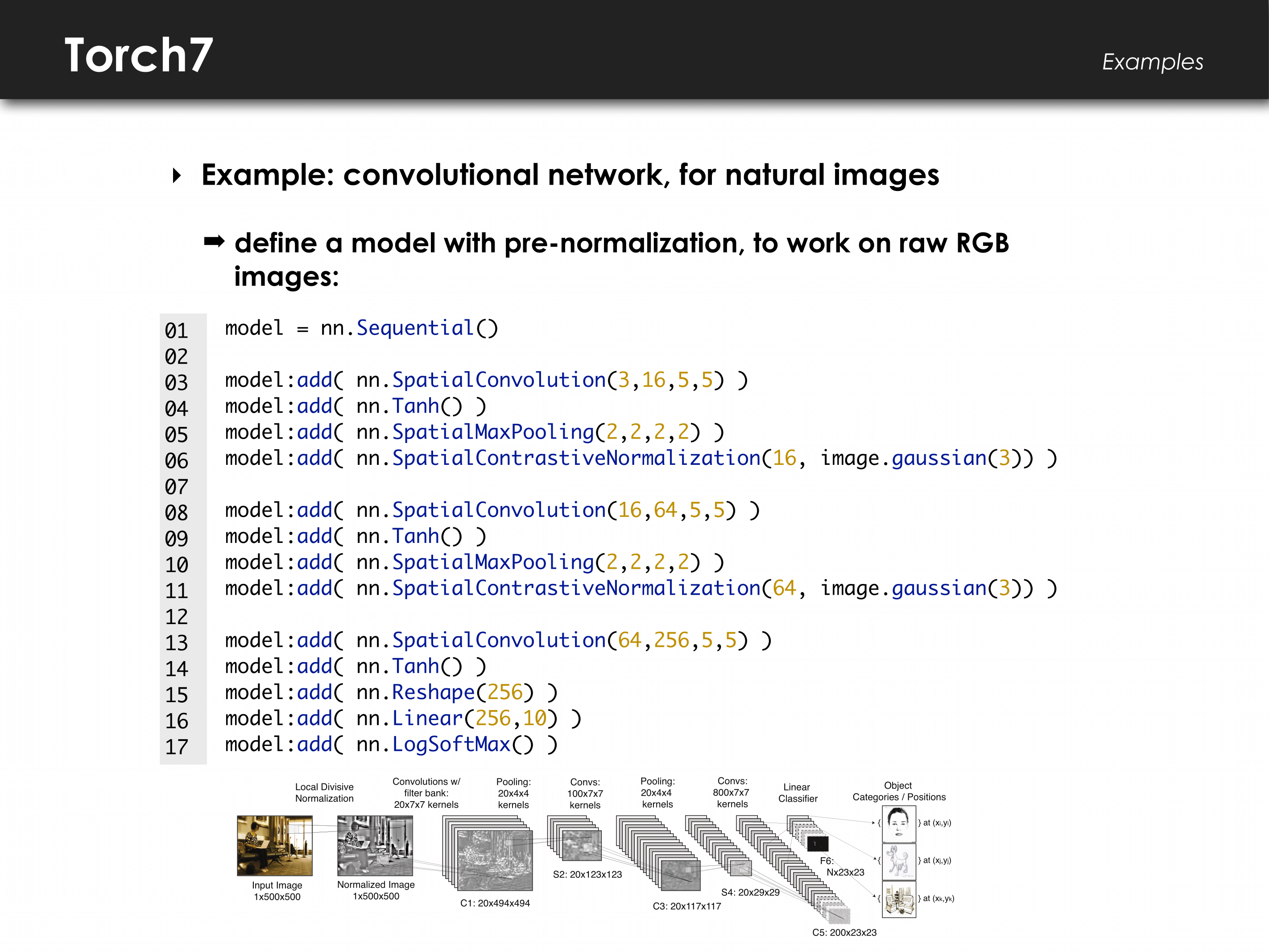
6. Torch
"An open-source machine learning library."
Language: C.
Torch is an open-source machine learning library for scientific and numerical operations.
It's a library based on — no, not Python — the Lua programming language.
By providing a large number of algorithms, it makes for easier deep learning research and improved efficiency and speed. It has a powerful N-dimensional array, which helps with operations such as slicing and indexing. It also offers linear algebra routines and neural network models. Check it out.
Pros:
- Very flexible.
- High level of speed and efficiency.
- Lots of pre-trained models available.
Cons:
- Unclear documentation.
- Lack of plug-and-play code for immediate use.
- It's based on a not-so-popular language, Lua.
7. Accord.NET
"Machine learning, computer vision, statistics, and general scientific computing for .NET."
Language: C#.
Here is one for the C# programmers.
The Accord.NET framework is a.NET machine learning framework that makes audio and image processing easy.
This framework can efficiently handle numerical optimization, artificial neural networks, and even visualization. Aside from this, Accord.NET is powerful for computer vision and signal processing and also makes for an easy implementation of algorithms. Check the main page.
Pros:
- It has a large and active development team.
- Very well-documented framework.
- Quality visualization.
Cons:
- Not a very popular framework.
- Slow compared to TensorFlow.
8. Spark MLlib
"A scalable machine learning library."
Language: Scala.
Apache's Spark MLlib is a very scalable machine learning library.
It is very usable in languages such as Java, Scala, Python, and even R. It is very efficient, as it interoperates with the numpy in library Python and R libraries.
MLlib can easily be plugged into Hadoop workflows. It provides machine learning algorithms such as classification, regression, and clustering.
This powerful library is very fast when it comes to processing of large-scale data. Learn more on the website.
Pros:
- Very fast for large-scale data.
- Available in many languages.
Cons:
- Steep learning curve.
- Plug-and-play available for Hadoop only.
9. Sci-kit Learn
"Machine learning in Python."
Language: Python.
Sci-kit learn is a very powerful Python library for machine learning that is majorly used in building models.
Built using other libraries such as numpy, SciPy, and matplotlib, it is very efficient for statistical modeling techniques such as classification, regression, and clustering.
Sci-kit learn comes with features such as supervised learning algorithms, unsupervised learning algorithms, and cross-validation. Check it out.
Pros:
- Availability of many of the main algorithms.
- Efficient for data mining.
Cons:
- Not the best for building models.
- Not very efficient with GPU.
10. MLPack
"A scalable C++ machine learning library."
Language: C++.
MLPack is a scalable machine learning library implemented in C++. Because it's in C++, you can guess that it is great for memory management.
MLPack runs with great speed, as quality machine learning algorithms come along with the library. This library is novice-friendly and provides a simple API for use. Check it out.
Pros:
- Very scalable.
- Python and C++ bindings available.
Cons:
- Not the best documentation.
Wrapping It Up
The libraries discussed in this article are very efficient and have proven over time to be of high quality. Big companies like Facebook, Google, Yahoo, Apple, and Microsoft make use of some of these libraries for their deep learning and machine learning projects — so why shouldn‘t you?
Can you think of any other library that you make use of very often that isn't on this list? Kindly share with us in the comments section!
Published at DZone with permission of . See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.


Comments