Overcoming the Data Silo Challenge: How Industry 4.0 Paves the Way for Seamless Data Interoperability
Data silos hinder data sharing and collaboration, obstructing the flow of valuable insights and hindering effective decision-making.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIndustry 4.0 is the playground where innovation and interconnectivity converge, turning possibilities into realities and preparing us for the future of machines.
It is testifying the applicability of intelligent automation and addressing one of the most significant challenges of our digital age, data silos.
Data silos have long plagued organizations, hindering their ability to leverage the full potential of their data assets. These remote information repositories restrict data sharing and collaboration between different departments or systems, impeding the flow of valuable insights and inhibiting effective decision-making. This has given rise to a potential new market for integration.
According to the latest research report, the global data integration market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 11.0% from 2021 to 2026. The market, estimated at $11.6 billion in 2021, is expected to reach a revenue value of $19.6 billion by 2026. The report includes an industry trend analysis, providing insights into the market's growth potential and future prospects.
A Quick Run Through the Critical Challenges Posed by Data Silos
- Lack of standardization: Different systems use different data structures and formats, hindering communication and interoperability.
- Data quality issues: Inconsistent or incomplete data affects interoperability and can lead to errors during data exchange.
- Integration complexity: Integrating systems, especially legacy ones, can be complex and time-consuming, impacting interoperability.
- Lack of governance: The absence of clear guidelines and policies for data interoperability leads to confusion and inconsistency.
- Data inaccessibility: Silos prevent easy access and sharing of information between departments or systems.
- Redundancy and duplication: Silos result in redundant data storage and increased costs due to separate databases or systems.
- Lack of data consistency: Data definitions, formats, and quality inconsistencies hinder accurate analysis and decision-making.
It further leads to siloed analytics and reporting. Data silos restrict comprehensive and centralized reporting and analytics.
However, Industry 4.0 enables organizations to break free from the constraints of data silos and unlock the transformative power of interconnected data. By promoting interoperability and seamless integration, Industry 4.0 empowers businesses to harness the wealth of their data, leading to enhanced efficiency, innovation, and competitiveness in the digital age.
How Can Industry 4.0 Tech Address These Issues?
Industry 4.0 technologies, such as AI, IoT, Blockchain, Edge computing, and others, enable interoperability, play a crucial role in addressing the challenges posed by data silos and enable seamless data integration and collaboration.
Given the hockey-stick growth in the awareness of AI products off-late (thanks to chatGPT), discussing AI competency in emerging tech is imperative. While a separate post is required to acknowledge products, I recently read Parso's brilliant whitepaper, which dives deep into the data silos challenge.
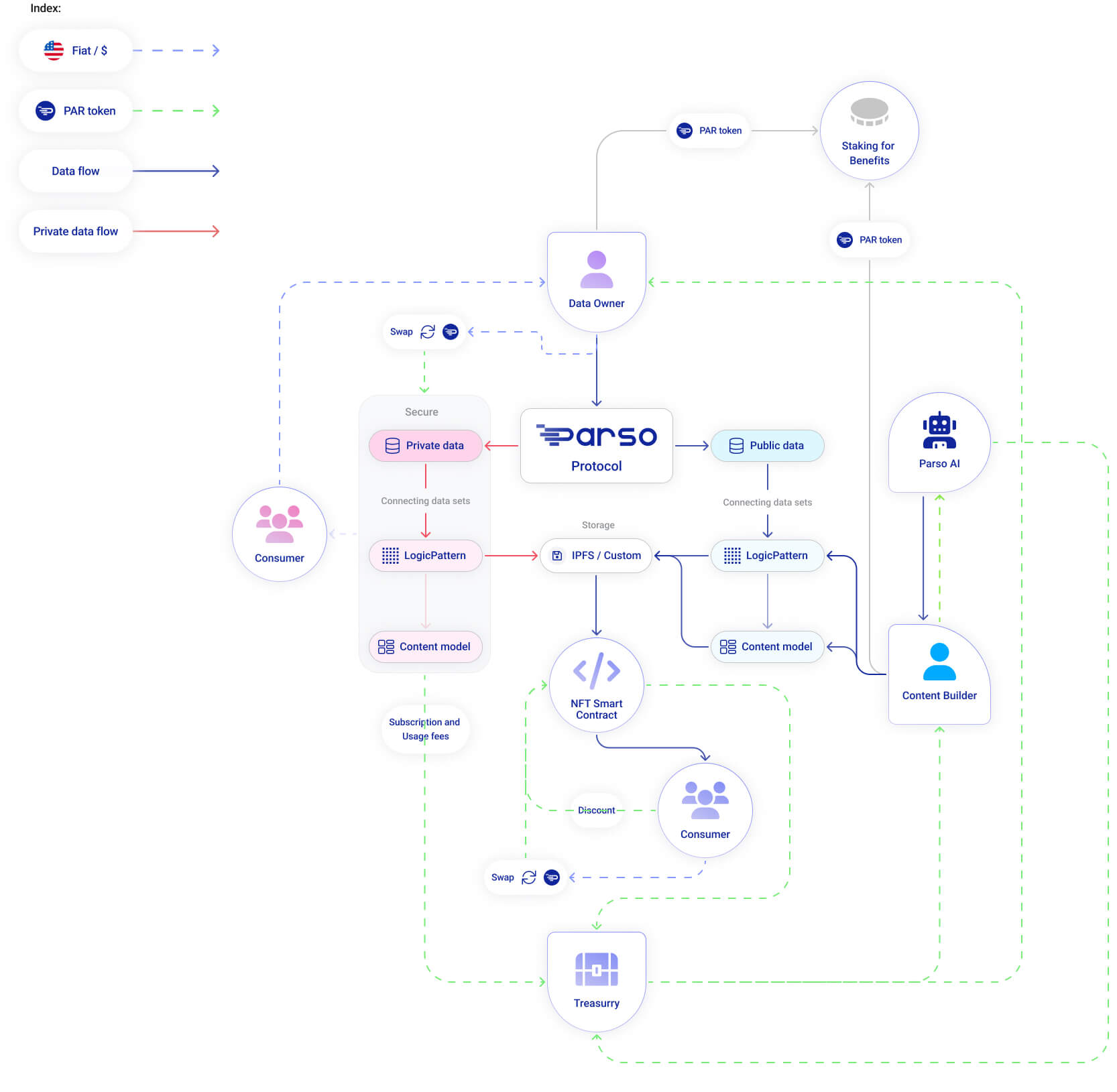
Parso overcomes data silos through its user-friendly Interaction Layer. Users can navigate and explore multiple data silos, accessing correlated use cases and applications in a unified interface akin to "Google Earth." The Parso market enables active participation, while Request Content allows users to obtain relevant data based on their geospatial location. Builder Apps empower users to create customized applications using open-source SDKs and integrate them seamlessly into the data interoperability solution, which promotes data exchange.
The content and data layer focuses on data ingestion, leveraging the FLOW SDK and the Elastic Knowledge GraphTM for data interoperability. Parso Logic PatternsTM enables semantic modeling for meaningful connections. Content Creation involves federating content and implementing a cloud-native infrastructure, breaking down data silos. The Transaction Layer handles subscriptions, protocol taxation, voting, and staking, ensuring a well-functioning market ecosystem. The Identity Layer establishes virtual ownership and trust of data origins. Their solution enables data contextualization, M/L-driven interoperability, developer access, and visualized data node interoperability.
Speaking more on Industry 4.0 challenges, Bruno Kocher, CEO of Parso, says, "Today, more than ever, the technology industry faces challenges such as cybersecurity threats, ethical concerns related to AI, and accelerating technological possibilities. Addressing these challenges requires collaboration between people in open ecosystems, robust security measures, ethical frameworks, and prioritizing data interoperability. This vision also includes striving for overall efficiency gains while aligning with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) to ensure the positive impact of technology on society and the environment."
Next, the IoT is another integral component of the web3 stack in optimizing data utilization from different sources.
Industry 4.0 leverages IoT to connect various devices, sensors, and machines in an industrial setting. IoT platforms facilitate data collection, analysis, and sharing across the value chain, reducing data silos. By enabling devices to connect and share data, IoT promotes interoperability and collaboration between different components of the industrial ecosystem.
Moreover, IoT connectivity extends beyond the boundaries of an organization. It enables data sharing and collaboration with external stakeholders, such as suppliers, customers, and partners. Organizations can establish seamless connections through secure data exchange protocols, breaking down silos between different entities and fostering collaboration across the value chain.
For example, in a smart factory setting, IoT sensors in machinery collect data on various parameters like temperature, vibration, energy consumption, and production output. This data is transmitted to the IoT platform, which is processed and made available to relevant stakeholders. The manufacturing team can access real-time data on machine performance, while the maintenance team can receive alerts for potential issues. This connectivity and data-sharing level improves operational efficiency, enables predictive maintenance, and facilitates collaboration among different teams.
Industry 4.0 utilizes cloud computing and edge computing technologies to process and store data from various sources.
Cloud platforms provide a centralized repository where data from different systems can be collected, integrated, and analyzed. Edge computing enables data processing and analysis at the edge of the network, closer to the data source, reducing latency and enhancing real-time decision-making. For example, In a smart energy grid, data from sensors installed on power generation, transmission, and distribution equipment are collected and processed in real time. This data is stored in the cloud, allowing utilities to monitor the grid's health, predict and prevent failures, and optimize energy distribution.
Conclusion
As we embark on the future of Industry 4.0, the journey toward a data-driven and interconnected world holds immense promise. With the ability to overcome the challenges posed by data silos, organizations will harness the true power of their data assets. Seamless data integration and interoperability will pave the way for transformative insights, informed decision-making, and unprecedented collaboration.
The breaking down of data barriers will unlock new opportunities for innovation, efficiency, and growth across industries. Industry 4.0's vision of a connected ecosystem, where data flows seamlessly and boundaries between systems dissolve, will propel us towards a future where data silos become relics of the past and the true potential of our digital era is fully realized.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments