New Open-Source Multi-Cloud Asset to Build SaaS
Development and automated deployment of SaaS for multiple tenants, using Red Hat OpenShift/Kubernetes and DevSecOps
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeOver the last months I’ve worked with many companies who want to build SaaS (Software as a Service) to scale their solutions to new markets and to save costs. To address these needs, our team has produced an asset that demonstrates how to build cloud-native applications that can be deployed to multiple clouds and how they can be exposed in multiple marketplaces. Red Hat OpenShift is a perfect technology to address these requirements.
Check out the SaaS repo.
Introduction
When software is provided as a managed service (SaaS), using a multi-tenant approach helps minimise costs for the deployments and operations of each tenant. In order to leverage these advantages, applications need to be designed so that they can be deployed to support multiple tenants, while maintaining isolation for security reasons. At the same time, common deployment and operation models are required so that new SaaS versions can be deployed to existing tenants, or to onboard new tenants, in a reliable and efficient way.
A new open-source project from IBM developers aims to support a DevSecOps approach to building multi-tenant SaaS for different platforms including Kubernetes, Red Hat OpenShift, IBM Code Engine (serverless), IBM Satellite, and public clouds including IBM Cloud, AWS and Azure. The asset includes DevSecOps toolchains to automate the process for deploying a sample cloud native application to a common platform and create per-tenant cloud services for persistence and authentication.
The initial release uses Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) toolchains on IBM Cloud to deploy SaaS to IBM Code Engine, Red Hat OpenShift on IBM Cloud, or IBM Kubernetes Service on IBM Cloud. We have plans to extend the deployment to support multi-cloud using Red Hat OpenShift on AWS (ROSA) and Azure Red Hat OpenShift (ARO).
This asset has been created by IBM’s Build Labs:
Challenges
Organizations offering SaaS will need to deliver rapidly and often, while maintaining a strong security posture and continuous state of audit-readiness. Achieving this goal involves several teams including developers, IT operations and security. DevSecOps integrates a set of security and compliance controls and makes application and infrastructure security a shared responsibility for all these teams, and automatically bakes in security at every phase of the software development lifecycle, bringing speed and security. This is of particular importance for SaaS where the challenges and benefits are a factor of the number of tenants!
The project provides a starting point for learning how to create an application which is ready for SaaS, using best practices for DevSecOps such as detecting code or container vulnerabilities, and using CI/CD pipelines to automate deployments. The key value of this asset is that it shows how to reuse the same application code, containers, and CI/CD, with the flexibility to deploy to a dedicated or shared Kubernetes cluster, while maintaining isolation and security.
Support for Multiple Platforms
The following diagram shows the different deployment platform options, currently including several alternatives for IBM Cloud, as indicated by the grey and blue boxes. The white and light grey boxes represent planned future developments, including the addition of IBM Cloud Satellite which will allow the SaaS application to be deployed on-premises at client data centers, while still taking advantage of an OpenShift cluster managed by IBM Cloud. Additionally, the same SaaS application could be deployed to other managed OpenShift services like AWS ROSA and Azure ARO.
The easiest way to get started is with serverless, using the fully managed IBM Code Engine platform to run the application. For more advanced cloud-native applications, a dedicated Kubernetes or OpenShift cluster can be used. Compute isolation can be achieved with a shared cluster using Kubernetes namespaces/OpenShift projects, or by having dedicated clusters for each SaaS tenant.
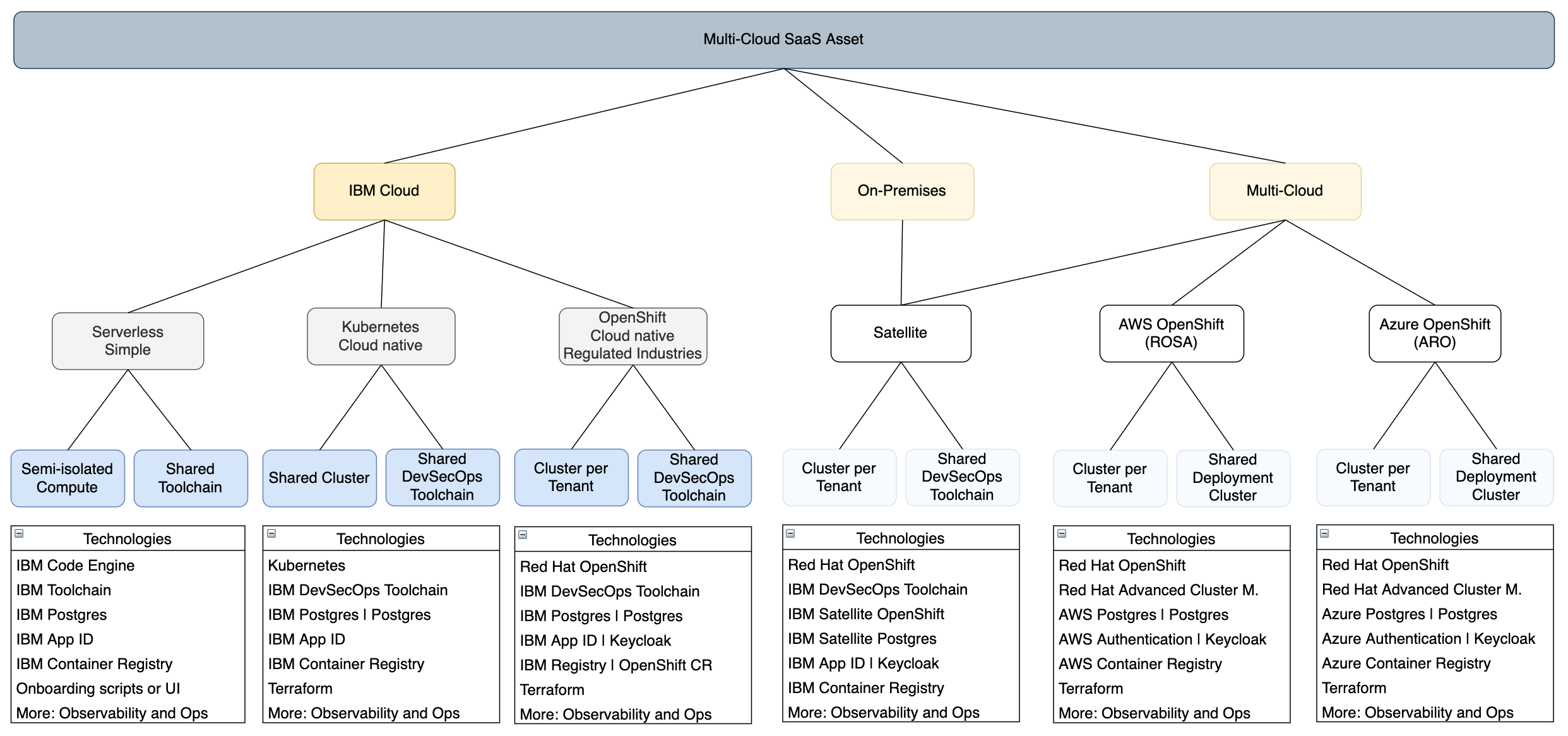
Core technologies used:
- Kubernetes using either IBM Kubernetes Service or OpenShift on IBM Cloud
- IBM Code Engine (serverless)
- IBM Continuous Delivery CI/CD pipelines using Tekton
- IBM Cloud Databases for PostgreSQL
- IBM App ID
- IBM Container Registry
- Terraform
Sample eCommerce Application
A sample e-commerce application is provided, which is deployed as two containers. A frontend web application displays a catalogue of products. The data for the catalogue is provided by a backend microservice. Configuration properties are used extensively to customise both the frontend and backend at deployment time, including titles, connection details for the PostgreSQL database and authentication service etc. This means the same e-commerce sample application can easily be used for multiple tenants, perhaps one selling books, the other shoes.
Automation first
Everything in this project embraces automation and a series of approaches to deploy SaaS are provided, each with an increasing degree of capability. You are able to start with any of the following approaches:
- Simple bash scripts to create and deploy the sample application container images, and the PostgreSQL and AppID cloud services.
- A simple DevOps toolchain with CI/CD pipelines which deploys to IBM Code Engine. The pipelines orchestrate build, test, and deployment jobs (optionally across multiple environments) as changes progress from the developer to production.
- A more comprehensive DevSecOps toolchain which deploys to a Kubernetes cluster. This brings a more robust process where the CI/CD pipelines ensure that code is scanned for security vulnerabilities (e.g. secrets or credentials), and repository branch protection prevents a developer from directly updating the main branch without first issuing a pull/merge request to be approved by a second developer. In addition, the container images are scanned for vulnerabilities, a dynamic application security testing tool looks for vulnerabilities in the deployed application, and application acceptance tests all contribute to a secure and quality assured release.
Any of these approaches are ready to deploy the multiple tenancies of a SaaS application. Simply change the externalised properties and re-run the script or trigger the pipelines.
For deployments to IBM Kubernetes Service or OpenShift, terraform templates are also provided to automate the cluster creation on IBM Cloud.
Ready for Regulated Industries
Regulated industries such as financial institutions, insurance, healthcare and more, all want the advantages of a hybrid cloud, but need assurance they can protect their assets and maintain compliance with industry and regulatory requirements. The key to hosting regulated workloads in the cloud is to eliminate and mitigate the risks that might be standing in the way of progress. In regulated industries, critical risks fall into the general categories of compliance, cybersecurity, governance, business continuity and resilience.
The DevSecOps approach of our CI/CD pipelines are based an IBM DevSecOps reference architecture, helping to address some of the risks faced by regulated industries. The CI/CD pipelines include steps to collect and upload deployment log files, artifacts, and evidence to a secure evidence locker. In addition, a toolchain integration to IBM Security and Compliance Center verifies the security and compliance posture of the toolchain by identifying the location of the evidence locker, and the presence of the evidence information.
What’s Next?
Our project is constantly evolving. You can expect more supported platforms including IBM Cloud Satellite and other public clouds including support for their native database and authentication services. We still have some work to do on the documentation, e.g. explaining how to observe multi-tenant runtime logs, and understand how much cloud resource each tenant is consuming, to help calculate the bills.
In the meantime, we invite you to explore the repo and give it a try. Why not start by using our most simple script-based approach with IBM Code Engine, and see for yourself how easy it is is to be a SaaS provider!
We would also be happy to work together with you on using this asset to build your SaaS.
If you have feedback or comments, please don’t hesitate to get in touch via our social media links above.
Published at DZone with permission of Niklas Heidloff, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments