Navigating the Skies: Cloud Vendors and the Need for Scalability, Security, and Services for Cloud Databases
In an in-depth look at primary cloud vendors, analyze crucial factors that set them apart: scalability, security, and cloud services for cloud databases.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeThis is an article from DZone's 2023 Database Systems Trend Report.
For more:
Read the Report
In today's rapidly evolving digital landscape, businesses across the globe are embracing cloud computing to streamline operations, reduce costs, and drive innovation. At the heart of this digital transformation lies the critical role of cloud databases — the backbone of modern data management. With the ever-growing volume of data generated for business, education, and technology, the importance of scalability, security, and cloud services has become paramount in choosing the right cloud vendor.
In this article, we will delve into the world of primary cloud vendors, taking an in-depth look at their offerings and analyzing the crucial factors that set them apart: scalability, security, and cloud services for cloud databases. Armed with this knowledge, businesses can make informed decisions as they navigate the vast skies of cloud computing and select the optimal vendor to support their unique data management requirements.
Scaling in the Cloud
One of the fundamental advantages of cloud databases is their ability to scale in response to increasing demands for storage and processing power. Scalability can be achieved in two primary ways: horizontally and vertically. Horizontal scaling, also known as scale-out, involves adding more servers to a system, distributing the load across multiple nodes. Vertical scaling, or scale-up, refers to increasing the capacity of existing servers by adding more resources such as CPU, memory, and storage.
Benefits of Scalability
By distributing workloads across multiple servers or increasing the resources available on a single server, cloud databases can optimize performance and prevent bottlenecks, ensuring smooth operation even during peak times.
Scalability allows organizations to adapt to sudden spikes in demand or changing requirements without interrupting services. By expanding or contracting resources as needed, businesses can maintain uptime and avoid costly outages.
By scaling resources on-demand, organizations can optimize infrastructure costs, paying only for what they use. This flexible approach allows for more efficient resource allocation and cost savings compared to traditional on-premises infrastructure.
Examples of Cloud Databases With Scalability
Several primary cloud vendors offer scalable cloud databases designed to meet the diverse needs of organizations. The most popular releases encompass database platforms from licensed versions to open source, such as MySQL and PostgreSQL. In public clouds, there are three major players in the arena: Amazon, Microsoft Azure, and Google.
The major cloud vendors offer managed cloud databases in various flavors of both licensed and open-source database platforms. These databases are easily scalable in storage and compute resources, but all controlled through service offerings.
Scalability is about more power in the cloud, although some cloud databases are able to scale out, too.
Figure 1: Scaling up behind the scenes in the cloud
Each cloud vendor provides various high availability and scalability options with minimal manual intervention, allowing organizations to scale instances up or down and add replicas for read-heavy workloads or maintenance offloading.
Securing Data in the Cloud
As organizations increasingly embrace cloud databases to store and manage their sensitive data, ensuring robust security has become a top priority. While cloud databases offer numerous advantages, they also come with potential risks, such as data breaches, unauthorized access, and insider threats. In this section, we will explore the security features that cloud databases provide and discuss how they help mitigate these risks.
Common Security Risks
Data breaches aren't a question of if, but a question of when. Unauthorized access to sensitive data can lead to data access by those who shouldn't, potentially resulting in reputational damage, financial losses, and regulatory penalties. It shouldn't surprise anyone that cloud databases can be targeted by cybercriminals attempting to gain unauthorized access to data. This risk makes it essential to implement strict access controls at all levels — cloud, network, application, and database.
As much as we don't like to think about it, disgruntled employees or other insiders can pose a significant threat to organizations' data security, as they may have legitimate access to the system but misuse it for malicious or unintentional abuse.
Security Features in Cloud Databases
One of the largest benefits of a public cloud vendor is the numerous first-party and partner security offerings, which can offer better security for cloud databases. Cloud databases offer robust access control mechanisms, such as role-based access control (RBAC) and multi-factor authentication (MFA), to ensure that only authorized users can access data. These features help prevent unauthorized access and reduce the risk of insider threats.
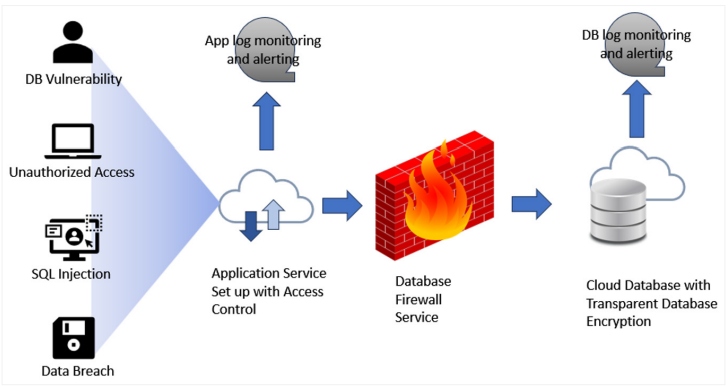
Figure 2: Database security in the public cloud
The second most implemented protection method is encryption and data level protection. To protect data from unauthorized access, cloud databases provide various encryption methods. These different levels and layers of encryption help secure data throughout its lifecycle. Encryption comes in three main methods:
- Encryption at rest protects data stored on a disk by encrypting it using strong encryption algorithms.
- Encryption in transit safeguards data as it travels between the client and the server or between different components within the database service.
- Encryption in use encrypts data while it is being processed or used by the database, ensuring that data remains secure even when in memory.
Compliance and Regulations
Cloud database providers often adhere to strict compliance standards and regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), and the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS). Compliance with these regulations helps ensure that organizations meet their legal and regulatory obligations, further enhancing data security.
Integrating cloud databases with identity and access management (IAM) services, such as AWS Identity and Access Management, Azure Active Directory, and Google Cloud Identity, helps enforce strict security and access control policies. This integration ensures that only authorized users can access and interact with the cloud database, enhancing overall security.
Cloud Services and Databases
Cloud databases not only provide efficient storage and management of data but can also be seamlessly integrated with various other cloud services to enhance their capabilities. By leveraging these integrations, organizations can access powerful tools for insights, analytics, security, and quality. In this section, we will explore some popular cloud services that can be integrated with cloud databases and discuss their benefits.
Cloud Machine Learning Services
Machine learning services in the cloud enable organizations to develop, train, and deploy machine learning models using their cloud databases as data sources. These services can help derive valuable insights and predictions from stored data, allowing businesses to make data-driven decisions and optimize processes.
With today's heavy investment in artificial intelligence (AI), no one should be surprised that Cloud Services for AI are at the top of the services list. AI services in the cloud, such as natural language processing, computer vision, and speech recognition, can be integrated with cloud databases to unlock new capabilities. These integrations enable organizations to analyze unstructured data, automate decision-making, and improve user experiences.
Cloud Databases and Integration
Integrating cloud databases with data warehouse solutions, such as Amazon Redshift, Google BigQuery, Azure Synapse Analytics, and Snowflake, allows organizations to perform large-scale data analytics and reporting. This combination provides a unified platform for data storage, management, and analysis, enabling businesses to gain deeper insights from their data.
Along with AI and machine learning, cloud databases can be integrated with business intelligence (BI) tools like Tableau, Power BI, and Looker to create visualizations and dashboards. By connecting BI tools to cloud databases, organizations can easily analyze and explore data, empowering them to make informed decisions based on real-time insights. Data streaming and integrating cloud databases with services like Amazon Kinesis, Azure Stream Analytics, and Google Cloud Pub/Sub enable organizations to process and analyze data in real time, providing timely insights and improving decision-making.
By integrating cloud databases with monitoring and alerting services, such as Amazon CloudWatch, Azure Monitor, and Google Cloud Monitoring, organizations can gain insights into the health and performance of their databases. These services allow businesses to set up alerts, monitor key performance indicators (KPIs), and troubleshoot issues in real time.
Data Pipelines and ETL Services
Data pipelines and ETL services are the final services from the category of integration, such as AWS Glue, Azure Data Factory, and Google Cloud Data Fusion, that can be integrated with relational cloud databases to automate data ingestion, transformation, and loading processes, ensuring seamless data flow between systems.
Conclusion
The scalability of cloud databases is an essential factor for organizations looking to manage their growing data needs effectively. Along with scalability, security plays a critical aspect of cloud databases, and it is crucial for organizations to understand the features and protections offered by their chosen provider. By leveraging robust access control, encryption, and compliance measures, businesses can significantly reduce the risks associated with data breaches, unauthorized access, and insider threats, ensuring that their sensitive data remains secure and protected in the cloud.
Finally, to offer the highest return on investment, integrating cloud databases with other services unlocks the powerful analytics and insights available in the public cloud. By leveraging these integrations, organizations can enhance the capabilities of their cloud databases and optimize their data management processes, driving innovation and growth in the digital age.
This is an article from DZone's 2023 Database Systems Trend Report.
For more:
Read the Report
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments