Microservices Architectures: What Is Fault Tolerance?
We explore why fault tolerance is essential in a microservices architecture and how it can be implemented at the code level using frameworks such as Hystrix.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIn this article, we discuss an important property of microservices, called fault tolerance.
You Will Learn
- What is Fault Tolerance?
- Why is fault tolerance important in microservices architecture?
- How do you achieve fault tolerance?
Cloud and Microservices Terminology
This is the last article in a series of six articles on terminology used with cloud and microservices. The first five parts can be found here:
Microservices Architecture: Centralized Configuration and Config Server
Microservices Architecture: Introduction to API Gateways
Microservices Architecture: The Importance of Centralized Logging
What Is Fault Tolerance?
Microservices need to be extremely reliable.
When we build a microservices architecture, there are a large number of small microservices, and they all need to communicate with one another.
Lets consider the following example:
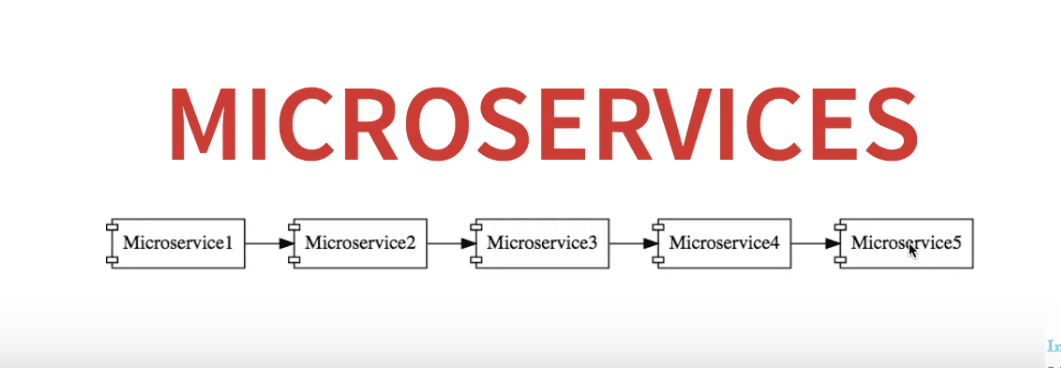
Let's say Microservice5 is down at some point in time.
All the other microservices are directly or indirectly dependent on it, so they all go down as well.
The solution to this problem is to have a fallback in case a microservice fails. This aspect of a microservice is called fault tolerance.
Implementing Fault Tolerance With Hystrix
A popular framework used to implement fault tolerance is Hystrix, a Netflix open source framework. Here is some sample Hystrix code:
@GetMapping("/fault-tolerance-example")
@HystrixCommand(fallbackMethod="fallbackRetrieveConfguration")
public LimitConfiguration retrieveConfiguration() {
throw new RuntimeException("Not Available");
}
public LimitConfiguration fallbackRetrieveConfiguration() {
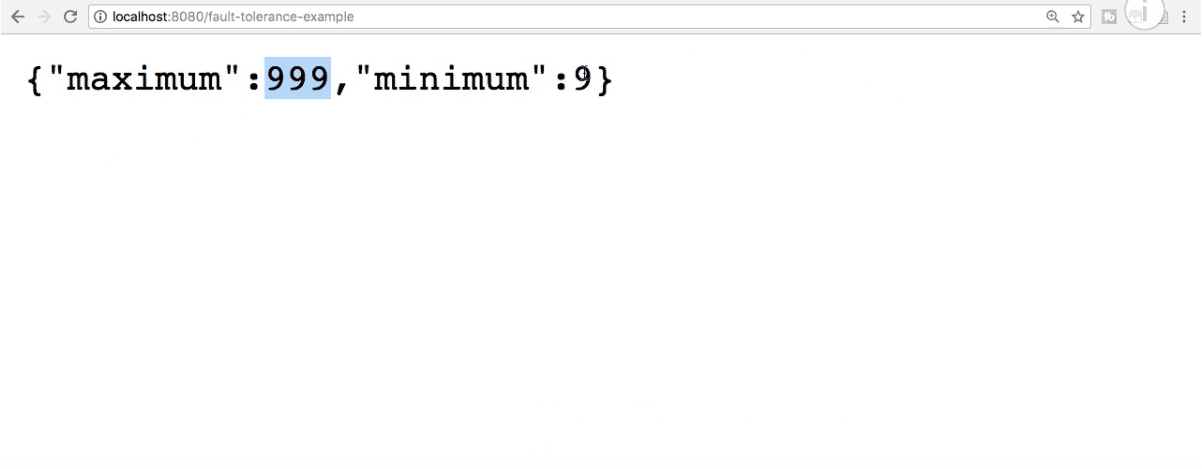
return new LimitConfiguration(999, 9);
} Hystrix enables you to specify the fallback method for each of your service methods. If the method throws an exception, what should be returned to the service consumer?
Here, if retrieveConfiguration() fails, then fallbackRetrieveConfiguration is called, which returns a hardcoded LimitConfiguration instance:
Hystrix and Alerts
With Hystrix, you can also configure alerts at the backend. If a service starts failing continuously, you can send alerts to the maintainance team.
Hystrix Is Not a Silver Bullet
Using Hystrix and fallback methods is appropriate for services that handle non-critical information.
However, it is not a silver bullet.
Consider, for instance, a service that returns the balance of a bank account. You cannot provide a default hardcoded value back.
Using Sufficient Redundancy
It is important to design critical services in a fail safe manner. It is important to build enough redundancy into the system to ensure that the services do not fail.
Have Sufficient Testing
It is important to test for failure. Bring a microservice down. See how your system reacts.
Chaos Monkey from Netflix is a good example of this.
Summary
In this article, we discussed fault tolerance. We saw how fault tolerance is essential in a microservices architecture. We then saw how it can be implemented at the code level using frameworks such as Hystrix.
Published at DZone with permission of Ranga Karanam, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments