Kubernetes Updates and Maintenance: Minimizing Downtime Challenges
Discover the strategies and best practices for Kubernetes updates and maintenance to minimize downtime and streamline your Kubernetes management with Atmosly.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeThe power and flexibility of managed Kubernetes platforms like EKS, GKE, and AKS can't be understated, but even the best tools require upkeep. Navigating the essential world of Kubernetes updates and maintenance to ensure your cluster enjoys the latest security patches, improved performance, and access to new features, all while minimizing downtime and disruptions. This article delves into the specific considerations and best practices for maintaining a healthy and secure Kubernetes environment within these managed cloud providers, helping you navigate the update process with confidence. As we journey through this guide, we'll explore:
- Understanding the update landscape: Differentiating between Kubernetes versions, patch releases, and specific offerings within each managed platform.
- Planning and preparation: Strategizing your update approach, considering the impact on workloads, and leveraging platform-specific tools for seamless transitions.
- Execution best practices: Rolling updates, blue/green deployments, and leveraging platform automation for a smooth and efficient update experience.
- Post-update considerations: Verification, monitoring, and rollback strategies to ensure everything runs smoothly after the update.
In this comprehensive article, we'll delve deep into the critical aspects of Kubernetes updates and maintenance, with a particular focus on minimizing downtime – a challenge that every DevOps professional encounters.
Understanding Kubernetes Update Challenges
Kubernetes Complexity in Managed Environments
Kubernetes clusters, particularly managed ones like EKS, AKS, and GKE provided by cloud services, present a unique set of complexities. While these managed services simplify certain aspects of Kubernetes management, they also introduce challenges, especially when integrating additional tools and applications. Each Kubernetes version has its own lifecycle, making it crucial for DevOps teams to stay ahead of update schedules to maintain compatibility and functionality.
The complexity isn't just in the core components like the API server etc., but also in the numerous plugins and integrations that Kubernetes supports. These elements can vary significantly in their update and compatibility requirements. Successfully managing a Kubernetes cluster, therefore, involves a careful balance of understanding the managed service's features and the additional layers added through tools and applications.
Predicting Updates With Kubernetes Version Lifecycle
Understanding each Kubernetes version's lifecycle is vital in predicting and planning for necessary upgrades. Kubernetes versions typically have a defined maintenance period, after which they no longer receive updates. Staying within this maintenance period is critical to ensure continued support, security patches, and compatibility. This foresight is essential in a managed Kubernetes environment to prepare for and implement updates without causing service disruptions.
Maintaining Uninterrupted Service During Updates
One of the key challenges in updating Kubernetes, particularly in a managed environment, is ensuring uninterrupted service. Downtime can significantly impact customer experience and revenue. Therefore, it's imperative for DevOps teams to strategize updates meticulously. This involves understanding the specific nuances of managed Kubernetes services and the additional tools and applications in use, ensuring all components work harmoniously during and after an update.
Strategies for Minimising Downtime
Rolling Updates
Rolling updates are a favored strategy in the Kubernetes world. They enable the gradual deployment of changes across the cluster, one node at a time. This approach minimizes the impact on running services by ensuring that a portion of the cluster is always operational. It's akin to changing the wheels of a moving car without bringing it to a halt.
Rolling updates are particularly effective because they maintain a level of redundancy within the cluster. During an update, Kubernetes schedules pods onto nodes that are not being updated, allowing the application to continue running. This approach ensures that even though some nodes are undergoing maintenance, the application remains available.
Blue/Green Deployment
Blue/Green deployment is another technique employed to reduce risks during updates. In this approach, two identical environments, known as "Blue" and "Green," coexist. Updates are applied to the inactive environment while the active one continues to serve traffic. Once the update is complete and verified, traffic is switched to the updated environment. This strategy offers a seamless transition in case issues arise during the update.
Blue/Green deployments are valuable when you want to have a completely new environment ready for testing and validation before switching over. It provides a rollback mechanism in case something unexpected occurs, as you can instantly switch back to the previous environment (Blue) without extensive downtime.
Canary Releases
Canary releases introduce a level of control into the update process. They involve deploying updates to a small subset of users or nodes, allowing DevOps teams to monitor and test the changes in a controlled environment. If no issues arise, the update can be progressively rolled out to a larger audience. Canary releases enable early detection of problems and mitigate their impact.
Canary releases are like sending a few scouts ahead before the entire troop embarks on a journey. By exposing a limited set of users or nodes to the update, you can gather valuable feedback and assess the update's performance under real-world conditions. If issues arise, you can contain the impact to a smaller subset, minimizing the overall downtime.
Best Practices in Kubernetes Maintenance
Regular Backups and Disaster Recovery
One of the fundamental aspects of Kubernetes maintenance is regular backups and disaster recovery planning. Backups ensure that critical data and configurations are protected. In the event of an update gone awry or a catastrophic failure, backups serve as a lifeline, facilitating the swift recovery of systems.
Backups are not just about data; they encompass the entire cluster's state, including configurations, secrets, and persistent volumes. Kubernetes provides tools like Velero and Kasten K10 for comprehensive backup and recovery solutions. Regularly testing your backups is equally important to ensure their reliability when needed.
Thorough Testing and Staging Environments
Testing is an integral part of Kubernetes maintenance. Updates should be thoroughly tested in staging environments that mirror the production setup. This practice helps identify potential issues before they affect live services. Testing encompasses everything from validating compatibility to assessing the impact on application performance.
Staging environments should be as close to the production environment as possible. They should replicate the same configurations, dependencies, and scale. Kubernetes allows you to create and manage multiple clusters, making it feasible to maintain a staging environment that closely mimics your production setup.
Automation for Streamlined Updates
Automation plays a pivotal role in streamlining the Kubernetes update process. Automation tools can orchestrate the deployment, monitor the update's progress, and perform rollback actions if necessary. By reducing manual intervention, automation minimizes the risk of human errors and accelerates the update process.
Automation not only applies to the update itself but also to the entire lifecycle of Kubernetes management. Tools like Helm, Ansible, and Kubernetes Operators can be used to automate routine tasks, making it easier to ensure consistent configurations and reduce the chance of misconfigurations during updates.
Leveraging Atmosly for Efficient Kubernetes Management
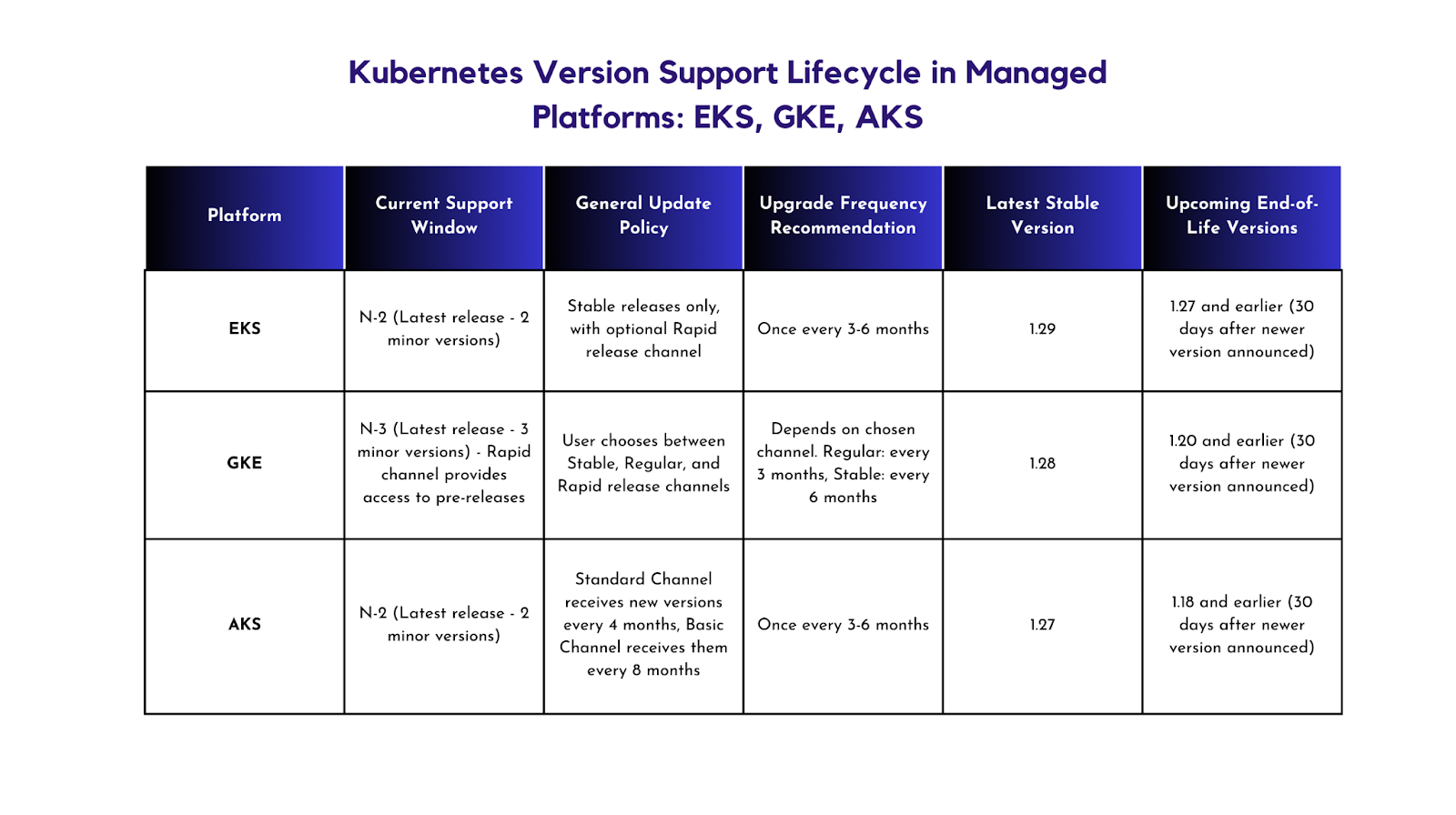
Note:
- Specific dates and details for each version may
- "N" refers to the latest minor version of Kubernetes at the time of writing this article.
- "Pre-releases" in GKE's Rapid channel may have limited support and stability.
- Upgrade frequency recommendations are suggestions and may need to be adjusted based on specific needs and risk tolerance.
- Always refer to the official documentation of each platform for the most up-to-date information.
- Kubernetes Docs
- Kubernetes User Guide
- Microsoft Kubernetes Versions
How Atmosly Helps in Easy Upgrades and Maintenance
While cloud providers offer streamlined upgrade processes for Kubernetes itself, ensuring compatibility with specific add-ons (e.g., CNI plugins, logging agents) and application stability requires careful planning and consideration. This complexity stems from the diverse offerings and varying support lifecycles of add-ons, coupled with the need to assess potential impacts on running applications. Atmosly takes care of these intricacies of managing the add-on version as per the upgrade version to keep it compatible, along with managing any impact on the applications. Nevertheless, all this is done with infrastructure as a code (IAC) to keep GitOps principles aligned.
What Atmosly Simplifies Your Cluster Journey
- Streamlined journey: Atmosly handles everything from cluster creation to updates, including effortless add-on management and rollouts. No more juggling complex tasks – focus on your applications.
- Fortress built-in: Implement robust Cluster Guardrails to ensure unwavering security and compliance at every level. Sleep soundly, knowing your clusters are protected.
- Cost clarity and savings: Gain granular insights into your cluster costs with detailed breakdowns. Leverage Spot Instances seamlessly to optimize expenses and maximize savings.
- Disaster-proof ready: Enjoy peace of mind with built-in backup and disaster recovery capabilities. Be prepared for anything and ensure business continuity.
- Marketplace of possibilities: Deploy custom or open-source Helm charts from a curated marketplace, simplifying the addition of new tools and functionalities.
Conclusion
In the world of Kubernetes, updates and maintenance are inevitable challenges. However, by understanding the complexities, employing downtime-minimizing strategies, adhering to best practices, and leveraging tools like Atmosly, DevOps professionals can conquer these challenges effectively. Kubernetes updates and maintenance need not be synonymous with prolonged downtime. Instead, they can be executed with precision and minimal disruption, ultimately enhancing system reliability and performance.
Published at DZone with permission of Ankush Madaan. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments