KubeEye: An Automatic Diagnostic Tool That Provides a Holistic View of Your Kubernetes Cluster
We review an open source platform that allows developers to automatically monitor the health of their Kubernetes cluster and track the changes.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeKubeEye is an open-source diagnostic tool for identifying various Kubernetes cluster issues automatically, such as misconfigurations, unhealthy components and node failures. It empowers cluster operators to manage and troubleshoot clusters in a timely and graceful manner. Developed in Go on the basis of Polaris and Node Problem Detector, KubeEye is equipped with a series of built-in rules for exception detection. Besides pre-defined rules, KubeEye also supports customized rules.

Why Open Source
As the de facto standard in container orchestration, Kubernetes features a powerful and flexible architecture which supports various cloud-native add-ons. That said, there are some obstacles and problems which have haunted cluster operators and engineers for so long, such as:
- CPU, memory, or disk exceptions.
- Kernel deadlock and filesystem damage.
- Container runtime daemon not responding.
- Unhealthy etcd.
- Request and limit blackbox.
- Pod failures.
- Certificates expiring.
- Docker service failures.
- OOM (Out of Memory).
In fact, the problems listed here are just the tip of the iceberg. The majority of the cluster issues lies below the surface as they are not directly detectable from the cluster control plane. In other words, even with these potential issues, Kubernetes may continue to schedule Pods onto malfunctioning nodes, thus posing a greater threat to the stability and security of your cluster.
To identify these issues in time, the KubeSphere team developed KubeEye with over three years of expertise in Kubernetes cluster management and maintenance in production for both community users and commercial customers.
What Can KubeEye Do
- Identify and detect problems in your Kubernetes cluster control plane, including
kube-apiserver,kube-controller-manager, andetcd. - Identify and detect various node problems, including memory, CPU and disk pressure, and unexpected kernel issues.
- Validate YAML specifications of your workloads for best practices and compliance in the industry, thus improving cluster stability.
KubeEye Architecture
By calling the Kubernetes API, KubeEye gets diagnostic data as it matches key error messages in logs with rules of container syntax on a regular basis. See the architecture graph below:
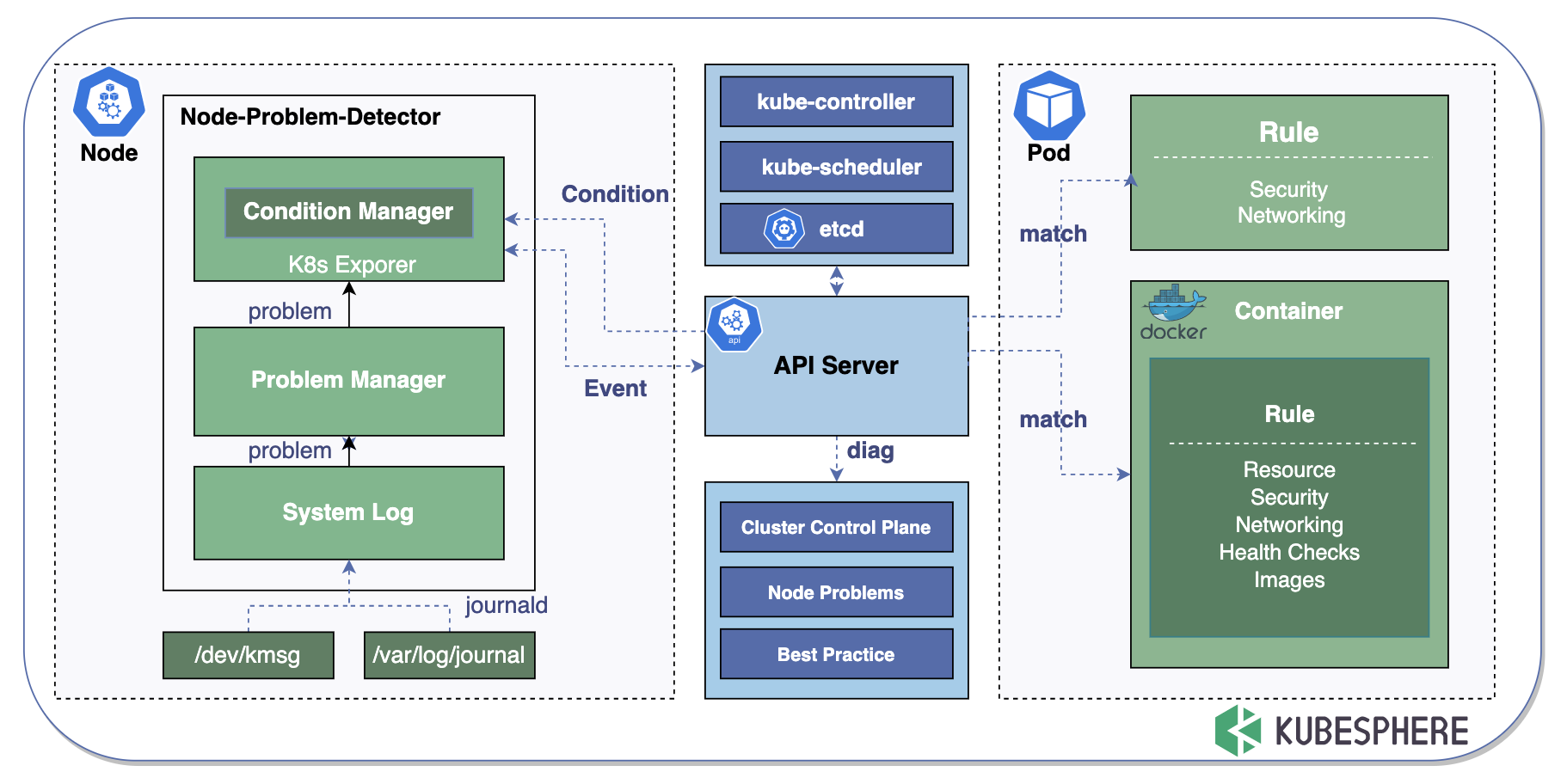
Checklist
Here is a list including built-in items that will be checked by KubeEye. Unmarked items are still in development.
| YES/NO | CHECK ITEM | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Yes | ETCDHealthStatus | If etcd is up and running |
| Yes | ControllerManagerHealthStatus | If Kubernetes kube-controller-manager is up and running |
| Yes | SchedulerHealthStatus | If Kubernetes kube-scheduler is up and running |
| Yes | NodeMemory | If node memory usage is above the threshold |
| Yes | DockerHealthStatus | If Docker is up and running |
| Yes | NodeDisk | If node disk usage is above the threshold |
| Yes | KubeletHealthStatus | If kubelet is active and running normally |
| Yes | NodeCPU | If node cpu usage is above the threshold |
| Yes | NodeCorruptOverlay2 | Overlay2 is not available |
| Yes | NodeKernelNULLPointer | The node displays NotReady |
| Yes | NodeDeadlock | A deadlock happens when two or more processes are waiting for each other as they compete for resources |
| Yes | NodeOOM | Monitor processes that consume too much memory, especially those consuming plenty of memory very quickly. The kernel kills them to prevent them from running out of memory |
| Yes | NodeExt4Error | Ext4 mounting error |
| Yes | NodeTaskHung | Check if there is a process in state D for more than 120s |
| Yes | NodeUnregisterNetDevice | Check the corresponding network |
| Yes | NodeCorruptDockerImage | Check Docker images |
| Yes | NodeAUFSUmountHung | Check storage |
| Yes | NodeDockerHung | As Docker hangs, you can check Docker logs |
| Yes | PodSetLivenessProbe | If the liveness probe is set for every container in a Pod |
| Yes | PodSetTagNotSpecified | The mirror address does not declare a tag or the tag is latest |
| Yes | PodSetRunAsPrivileged | Running a Pod in a privileged mode means that the Pod can access the host’s resources and kernel capabilities |
| Yes | PodSetImagePullBackOff | The Pod cannot pull the image properly, so it can be pulled manually on the corresponding node |
| Yes | PodSetImageRegistry | Check if the image form is in the corresponding registry |
| Yes | PodSetCpuLimitsMissing | No CPU resource limit is declared |
| Yes | PodNoSuchFileOrDirectory | Check if the corresponding file exists inside the container |
| Yes | PodIOError | Caused by file IO performance bottlenecks |
| Yes | PodNoSuchDeviceOrAddress | Check the corresponding network |
| Yes | PodInvalidArgument | Check the corresponding storage |
| Yes | PodDeviceOrResourceBusy | Check the corresponding directory and PID |
| Yes | PodFileExists | Check existing files |
| Yes | PodTooManyOpenFiles | The number of open files or socket connections exceeds the system set value |
| Yes | PodNoSpaceLeftOnDevice | Check disk and inode usage |
| Yes | NodeApiServerExpiredPeriod | Check if the apiserver certificate expires in less than 30 days |
| Yes | PodSetCpuRequestsMissing | No CPU resource request is declared |
| Yes | PodSetHostIPCSet | Set the host IP |
| Yes | PodSetHostNetworkSet | Set the host network |
| Yes | PodHostPIDSet | Set the host PID |
| Yes | PodMemoryRequestsMiss | No memory resource request is declared |
| Yes | PodSetHostPort | Set the host port |
| Yes | PodSetMemoryLimitsMissing | No memory resource limit is declared |
| Yes | PodNotReadOnlyRootFiles | The file system is not set to read-only |
| Yes | PodSetPullPolicyNotAlways | The image pulling policy is not Always |
| Yes | PodSetRunAsRootAllowed | Executed as the root user |
| Yes | PodDangerousCapabilities | You have the dangerous option in capabilities such as ALL, SYS_ADMIN and NET_ADMIN |
| Yes | PodlivenessProbeMissing | The readiness probe is not set |
| Yes | privilegeEscalationAllowed | Privilege escalation is allowed |
| NodeNotReadyAndUseOfClosedNetworkConnection | http2-max-streams-per-connection | |
| NodeNotReady | Fail to start ContainerManager; cannot set the property TasksAccounting, or unknown properties |
Get Started With KubeEye
Clone the KubeEye GitHub repository and install the tool.
git clone https://github.com/kubesphere/kubeeye.gitcd kubeeyemake installNote: You can also download the executable file from the GitHub release page of KubeEye.
Install Node Problem Detector (Optional), which will run as a DaemonSet in your cluster. You only need to install NPD when you want detailed reports.
ke install npdUse KubeEye to make a diagnosis of your cluster.
$ ke diag NODENAME SEVERITY HEARTBEATTIME REASON MESSAGE node18 Fatal 2020-11-19T10:32:03+08:00 NodeStatusUnknown Kubelet stopped posting node status. node19 Fatal 2020-11-19T10:31:37+08:00 NodeStatusUnknown Kubelet stopped posting node status. node2 Fatal 2020-11-19T10:31:14+08:00 NodeStatusUnknown Kubelet stopped posting node status. node3 Fatal 2020-11-27T17:36:53+08:00 KubeletNotReady Container runtime not ready: RuntimeReady=false reason:DockerDaemonNotReady message:docker: failed to get docker version: Cannot connect to the Docker daemon at unix:///var/run/docker.sock. Is the docker daemon running? NAME SEVERITY TIME MESSAGE scheduler Fatal 2020-11-27T17:09:59+08:00 Get http://127.0.0.1:10251/healthz: dial tcp 127.0.0.1:10251: connect: connection refused etcd-0 Fatal 2020-11-27T17:56:37+08:00 Get https://192.168.13.8:2379/health: dial tcp 192.168.13.8:2379: connect: connection refused NAMESPACE SEVERITY PODNAME EVENTTIME REASON MESSAGE default Warning node3.164b53d23ea79fc7 2020-11-27T17:37:34+08:00 ContainerGCFailed rpc error: code = Unknown desc = Cannot connect to the Docker daemon at unix:///var/run/docker.sock. Is the docker daemon running? default Warning node3.164b553ca5740aae 2020-11-27T18:03:31+08:00 FreeDiskSpaceFailed failed to garbage collect required amount of images. Wanted to free 5399374233 bytes, but freed 416077545 bytes default Warning nginx-b8ffcf679-q4n9v.16491643e6b68cd7 2020-11-27T17:09:24+08:00 Failed Error: ImagePullBackOff default Warning node3.164b5861e041a60e 2020-11-27T19:01:09+08:00 SystemOOM System OOM encountered, victim process: stress, pid: 16713 default Warning node3.164b58660f8d4590 2020-11-27T19:01:27+08:00 OOMKilling Out of memory: Kill process 16711 (stress) score 205 or sacrifice child Killed process 16711 (stress), UID 0, total-vm:826516kB, anon-rss:819296kB, file-rss:0kB, shmem-rss:0kB insights-agent Warning workloads-1606467120.164b519ca8c67416 2020-11-27T16:57:05+08:00 DeadlineExceeded Job was active longer than specified deadline kube-system Warning calico-node-zvl9t.164b3dc50580845d 2020-11-27T17:09:35+08:00 DNSConfigForming Nameserver limits were exceeded, some nameservers have been omitted, the applied nameserver line is: 100.64.11.3 114.114.114.114 119.29.29.29 kube-system Warning kube-proxy-4bnn7.164b3dc4f4c4125d 2020-11-27T17:09:09+08:00 DNSConfigForming Nameserver limits were exceeded, some nameservers have been omitted, the applied nameserver line is: 100.64.11.3 114.114.114.114 119.29.29.29 kube-system Warning nodelocaldns-2zbhh.164b3dc4f42d358b 2020-11-27T17:09:14+08:00 DNSConfigForming Nameserver limits were exceeded, some nameservers have been omitted, the applied nameserver line is: 100.64.11.3 114.114.114.114 119.29.29.29 NAMESPACE SEVERITY NAME KIND TIME MESSAGE kube-system Warning node-problem-detector DaemonSet 2020-11-27T17:09:59+08:00 [livenessProbeMissing runAsPrivileged] kube-system Warning calico-node DaemonSet 2020-11-27T17:09:59+08:00 [runAsPrivileged cpuLimitsMissing] kube-system Warning nodelocaldns DaemonSet 2020-11-27T17:09:59+08:00 [cpuLimitsMissing runAsPrivileged] default Warning nginx Deployment 2020-11-27T17:09:59+08:00 [cpuLimitsMissing livenessProbeMissing tagNotSpecified] insights-agent Warning workloads CronJob 2020-11-27T17:09:59+08:00 [livenessProbeMissing] insights-agent Warning cronjob-executor Job 2020-11-27T17:09:59+08:00 [livenessProbeMissing] kube-system Warning calico-kube-controllers Deployment 2020-11-27T17:09:59+08:00 [cpuLimitsMissing livenessProbeMissing] kube-system Warning coredns Deployment 2020-11-27T17:09:59+08:00 [cpuLimitsMissing]
Add Custom Check Rules
In addition to the pre-defined diagnostic items and rules, KubeEye also supports customized rules. For example:
Make sure you have installed NPD.
ke install npdEdit its ConfigMap using Kubectl.
kubectl edit cm -n kube-system node-problem-detector-configAdd regular expression rules in the ConfigMap for exceptional logs.
Customize Best Practice Rules
Create a rule in YAML. For example, the rule below checks your Pod specification to make sure images only come from the authorized registry.
checks: imageFromUnauthorizedRegistry: warning customChecks: imageFromUnauthorizedRegistry: promptMessage: When the corresponding rule does not match, show that image from an unauthorized registry. category: Images target: Container schema: '$schema': http://json-schema.org/draft-07/schema type: object properties: image: type: string not: pattern: ^quay.ioSave the file, such as
rule.yaml.Run KubeEye with the YAML file.
$ ke diag -f rule.yaml --kubeconfig ~/.kube/config NAMESPACE SEVERITY NAME KIND TIME MESSAGE default Warning nginx Deployment 2020-11-27T17:18:31+08:00 [imageFromUnauthorizedRegistry] kube-system Warning node-problem-detector DaemonSet 2020-11-27T17:18:31+08:00 [livenessProbeMissing runAsPrivileged] kube-system Warning calico-node DaemonSet 2020-11-27T17:18:31+08:00 [cpuLimitsMissing runAsPrivileged] kube-system Warning calico-kube-controllers Deployment 2020-11-27T17:18:31+08:00 [cpuLimitsMissing livenessProbeMissing] kube-system Warning nodelocaldns DaemonSet 2020-11-27T17:18:31+08:00 [runAsPrivileged cpuLimitsMissing] default Warning nginx Deployment 2020-11-27T17:18:31+08:00 [livenessProbeMissing cpuLimitsMissing] kube-system Warning coredns Deployment 2020-11-27T17:18:31+08:00 [cpuLimitsMissing]
Roadmap
Going forward, KubeEye will add support for:
- Fine-grained diagnostic items, such as the slow response time of Kubernetes clusters.
- The diagnosis of KubeSphere components, such as DevOps and service mesh.
- The diagnosis of cluster network and storage.
References
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments