Jenkins Log Monitoring With ELK
In this article, we demonstrated Jenkins log and Job builds log monitoring using Filebeat and ELK Stack greater visibility, tracking, and monitoring.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreePurpose
A build log of a Jenkins Job contains a full set of records for a job, including the build name, number, execution time, the result (success or fail), and other things.
In this article, we have demonstrated Jenkins log and Job builds log monitoring using Filebeat and ELK Stack greater visibility, tracking, and monitoring.
Filebeat will ship the Jenkins logs to Elasticsearch for indexing and then we can see it in Kibana Dashboard.
In this tutorial, we are going to install and configure Jenkins, Elasticsearch, Filebeat, and Kibana and configure them on Ubuntu 16.04 to demonstrate this.
The installation packages may differ in the case of other Ubuntu versions.
Jenkins
It is an open-source automation server that can be used to automate tasks related to build, test, deliver, deploying projects.
Installation
You need to follow the below steps to install Jenkins in Ubuntu 16.04
Step1: Add the repository key to the system
wget -q -O - https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian/jenkins-ci.org.key
| sudo apt-key add –
Step2: Add the Jenkins source to the server source list
echo deb https://pkg.jenkins.io/debian-stable binary/
| sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/jenkins.list
Step3: Run an update to use the new repository
sudo apt-get update
Step4: Install Jenkins and dependencies
sudo apt-get install jenkins
Start and Status Check of Jenkins Server
Use systemctl for start/stop Jenkins instance.
Start server:
sudo systemctl start jenkins.service
Stop server:
sudo systemctl stop jenkins.service
Status check:
sudo systemctl status
Access and Setup Jenkins in Browser
Open your browser and you can access Jenkins by using either IP Address http://ipaddess:8080
OR
by domain name http://domainname:8080
Jenkins by default runs on a port 8080.
At the start, you will get an “Unlock Jenkins” screen.
You can find your initial password under “/var/lib/jenkins/secrets/initialAdminPassword”.
Login to the server command prompt (using putty or other tools) and do a cat on the above file to get the password.
Put the password in the “Administrator Password” field in the browser and click on the Continue button.

Next page select/click on “Install suggested plugins” option and it will start the Jenkins plugin installation. 
Once the installation process is complete, you will get a prompt to Create First Admin user and password and click on Save and Finish.
Your Jenkins is up and ready to use.
Configure JDK and Maven
To configure JDK and Maven globally for any project build, you can configure then under the Global Tool Configuration in Jenkins.
Log in to Jenkins and click on Manage Jenkins
Then click on Global Tool Configuration and configure any build tools you.
Below you can see how to configure JDK and Maven. You can use a similar approach to configure the other build tools, like Gradle or ANT
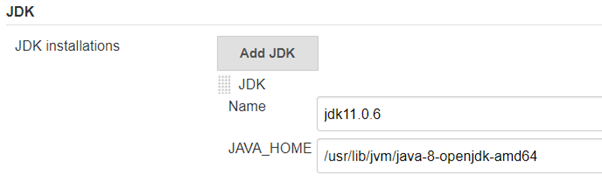
JDK Configure
Click on the Add JDK button under JDK and then put your JAVA_HOME (The JDK installation directory in your server)
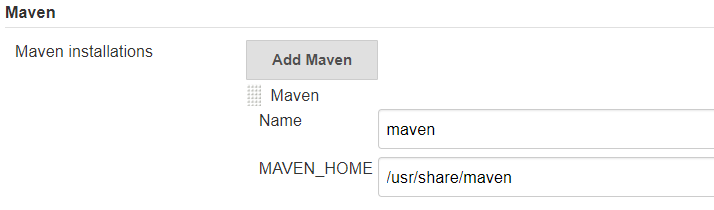
Maven Configure
Click on the Add Maven button under Maven and then put your MAVEN_HOME (The MAVEN installation directory in your server)
Click on the Apply button at the end of the page to save the above setting.
Elasticsearch
Elasticsearch is a search engine based on the Lucene library. Elasticsearch is developed in Java.
Installation
You need to follow the below steps to install elastic search
Step1: Add the repository key to the system
wget -qO - https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch
| sudo apt-key add –
Step2: Add the Elastic source to the server source list
echo "deb https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/6.x/apt stable main"
| sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/elastic-6.x.list
Step3: Run an update to use the new repository
sudo apt-get update
Step4: Install Elasticsearch
sudo apt-get install elasticsearch
Configure Elasticsearch
After Elasticsearch installation is complete, we need to open elasticsearch.yml under “/etc/elasticsearch” and configure network.host property.
You can set it a network.host: localhost
Or,
You can set it as network.host: 0.0.0.0 (0.0.0.0 IP address will bind to all network interfaces)
Start Server and Test
Now you can restart the elastic search instance by sudo service elasticsearch start
Elastic search by default runs on 9200 port. You can test your elastic search is up and running by doing a CURL or hitting the http://<ip_address>:9200/ URL in your browser.
It will give you a response something like this mentioned below,
xxxxxxxxxx
{
"name" : "dRb9-zU",
"cluster_name" : "elasticsearch",
"cluster_uuid" : "sxP-yPqIS4uMogJFEIa_yw",
"version" : {
"number" : "6.8.9",
"build_flavor" : "default",
"build_type" : "deb",
"build_hash" : "be2c7bf",
"build_date" : "2020-05-04T17:00:34.323820Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "7.7.3",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "5.6.0",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "5.0.0"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
}
Kibana
Kibana provides visualization capability for indexed content of Elasticsearch.
Installation
Step1: Install Elasticsearch
sudo apt-get install kibana
Configure and Start
After Elasticsearch installation is complete, we need to open kibana.yml under “/etc/kibana” and configure elasticsearch.hosts property and server.host property.
Property server.host is the server IP address where Kibana is running.
Property elasticsearch.hosts are where the location of the elasticsearch server running. The default value is http://localhost:9200
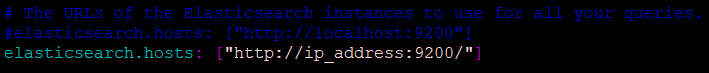
Also, check the server. port property, the value should be 5601 (Default Kibana server port)
Now you can restart the elastic search instance by sudo systemctl start kibana
Filebeat
Filebeat is a lightweight software which forwards and centralizes log data
Installation
Step1: Add the repository key to the system
wget -qO - https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch
| sudo apt-key add –
Step2: Add the Elastic source to the server source list
echo "deb https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/6.x/apt stable main"
| sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.list.d/elastic-7.x.list
Step3: Run an update to use the new repository
sudo apt-get update
Step4: Install Filebeat with dependencies
sudo apt-get install filebeat
Configure
Go to the configuration directory of Filebeat under location “/etc/filebeat” in the server using putty or other tools.
Here you can see the filebeat.yml file which holds all the configuration.
Now we will configure the Jenkins Server logs and Jenkins Job build logs inside the yml file.
Define Input Log Type and Enable Log Input
First, we have to set the type of the Filebeat inputs, and also, we need to enable the input configuration. It tells which type of file inputs we are passing to Filebeat and it will enable Filebeat to accept that logs. (Refer screen below)
Initially, the “enabled” property will be by default false. Set the value to true.

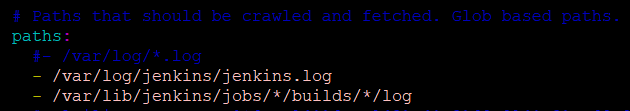
Define the Jenkins Log Location
Then set the path of the log files which you want to monitor. Here we want to monitor Jenkins logs as mentioned above,
Enable the Kibana Dashboard
Set the flag to true, so that logs will be visible to Kibana dashboard.

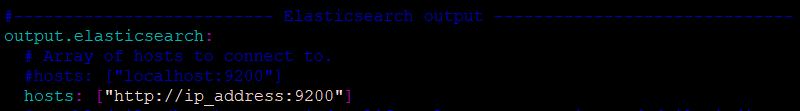
Define Kibana and Elasticserach Server
Define the host and port name of the Kibana server

Another important part where you define the elastic search, where your logs will be routed for indexing.
Configure Logging
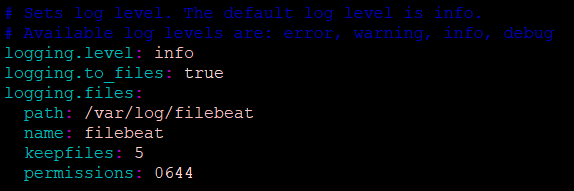
Another important part is to configure the logging in Filebeat. By default, the below settings will be commented out.
Here we have set the log level to INFO and gave the log file name as filebeat1, and also set the number of files to 5.
Verify YML File Configuration
You can now go to “/usr/share/filebeat/bin” where the Filebeat has been installed and use the following command to check if your YML file configuration is correct or not.
root@myvm:/usr/share/filebeat/bin# ./filebeat test config -e -c /etc/filebeat/filebeat.yml
If everything is fine you can see the “Config OK” message at the end after executing the above command.
Start Filebeat and Import Kibana Dashboard
You can restart the elastic search instance by sudo service filebeat start
Now as our main intention is to show these logs into the Kibana dashboard, so we will create an index from the command prompt using the following command.
Go to the “/usr/share/filebeat/bin” directory where Filebeat is installed.
Command to create the index:
filebeat setup --dashboards -E setup.dashboard.kibana_index=filebeat-*
This will set up and index called “filebeat-*” under which the log data will be stored in elastic and also the same indexed data will be visible in the Kibana dashboard.
Jenkins Project Build and Test Log in Kibana
You can log in to Jenkins (http://ip_address:8080/) and start building a Job.
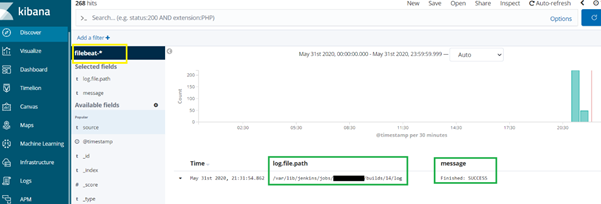
Now you open the Kibana(http://ip_address:5601) and click on the Discover link.
You should be able to see your index filebeat-*
You can see the Jenkins build log file path properly and also you can see the SUCCESS message for the build. (Marked in Screenshot)
Sample Kibana log screenshot
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments