Java: Migrating From Java 8 to Java 17
In this article, I will highlight some extremely important features available which can be learned and implemented quickly when migrating from directly Java 8 to Java 17.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeThis article focuses on the features to use when moving directly from Java 8 to Java 17. If your application is still running on Java 8 in production, then It’s difficult to track the features developed after version 8 onwards but there are quite a few easy to use and extremely important features available which can be learned and implemented quickly when migrating from directly Java 8 to Java 17.
In this article I will try to highlight some of them, I will also try to highlight the versions on which the specific feature is available for us to use but not necessarily in the sequential order of release.
NullPointerException Variable Identification
Precise identification of variables which was null when the NullPointerException is generated by JVM. All we need to do is to add “XX:+ShowCodeDetailsInExceptionMessages” to enable this feature. Let’s understand by a simple example:
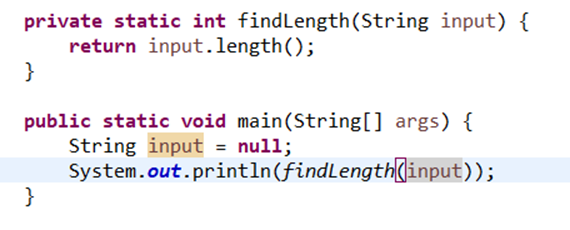
Results in:

Released version: Java 14
Switch Expression
From Java 14 onwards, switch expression can return values, this was the preview feature in 12 and 13. This enhancement is extremely important from a Pattern Matching perspective, all the features which have been released in every release are the building blocks of a complete feature that will be released in the future. For example, this feature is the building block for Pattern matching which is a preview feature as of Java 17.
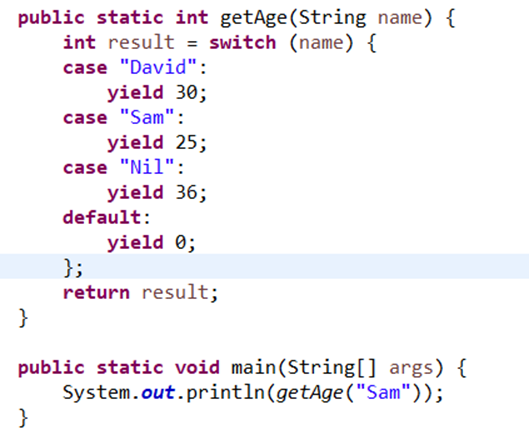
Please note:
- The ‘yield’ keyword should be used to return the value from the switch expression.
- All the blocks inside every case statement are multiline blocks.
Released version: Java 14
Record Type
Record types are the container classes that come with implicit getters/setters, constructor, equals/hashcode, and toString methods, also record container classes are Immutable in nature and are identical to Lombok. If your application is running on Java 16 onwards you can easily use record classes as DTO’s, to begin with. Use the keyword ‘record’ to create the record classes.
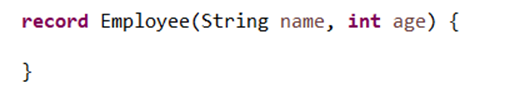

Released version: Java 16
The Enhanced instanceof Operator
Prior to Java 16 we must check the type of Object first then we have to cast the object to a variable, but the enhanced ‘instanceof’ can check the type and implicitly cast the object to a variable. I feel this enhancement is required for ‘Pattern Guards’, in the pattern matching section we will see how enhanced instanceof operator will play a role.
Prior to Java 16:

Java 16 onwards:

Released version: Java 16
CompactNumberFormat
CompactNumberFormat class is the subclass of NumberFormat class in java.text package, NumberFormat class formats a number in compact form.
The NumberFormat Style, SHORT would display 1000 as 1K and 10000 as 10K. Whereas the Style LONG will display 1000 as 1 thousand and 10000 as 10 thousand.

Output: 1K
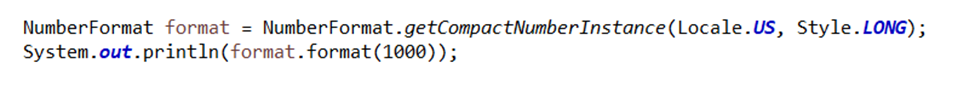
Output: 1 thousand
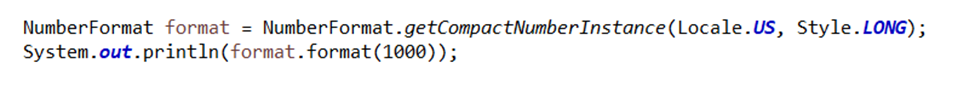
Similarly, the parse method should be used to parse the compact number to a long pattern

Released version: Java 12
Pattern Matching
As of Java 17, Pattern matching is a preview feature. To understand and execute this feature use –enable-preview option, or if you are an Eclipse user then the “Enable the preview features” option.

Two features that we saw earlier, “Switch Expression” and “Enhanced Instanceof Operator” were the building blocks for the Pattern matching feature. First, we will execute a simple program using the Switch Expression then will utilize the “Enhanced Instanceof” as a Pattern Guard in our program.
With the enhanced pattern matching coming up in the upcoming versions, we can avoid using instanceof and instead can write:


Since we are passing double the result is Double. If we pass integer 10 then the output will be Integer.
The enhanced ‘instanceof’ can check the type and implicitly cast the object to a variable, the same feature now can be used for pattern guard.

We have put a guard in the Integer block, that returns “Integer” only if the value is greater than 20.

Released version: Java 17 (preview) Java 18 (complete)
Text Block
From Java 15 onwards text block is available to use, with Text Block we can easily express multi-line Strings which enhances the code readability. Text block uses tripe quotes (“””).
Prior to Java 15:

Java 15 onwards:

Released version: Java 15
New String Methods
In Java 11 and 12 versions, there are certain new String methods are added that are extremely useful.
repeat |
11 |
isBlank |
11 |
strip |
11 |
lines |
11 |
indent |
12 |
transform |
12 |
I hope you like the article, this is the first of the Series, in further articles I will try to cover more such features.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments