Java Immutable Explained. Immutable Objects With Examples.
In this article, find answers about immutability and its best practices. Practical examples demonstrate the advantages of immutability and related tricks.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeWhat This Article About
Immutability is a broad concept and has many angles. Immutability is a set of practices that potentially might reduce the number of bugs in your application. As a consequence, this subject invokes confusion. Here, we review it from a different perspective. I'll explain the most important immutability aspects in clear language.

Mutability Problems Examples
Before we start, let's review two examples. They are pretty artificial but explain potential problems with mutable code:
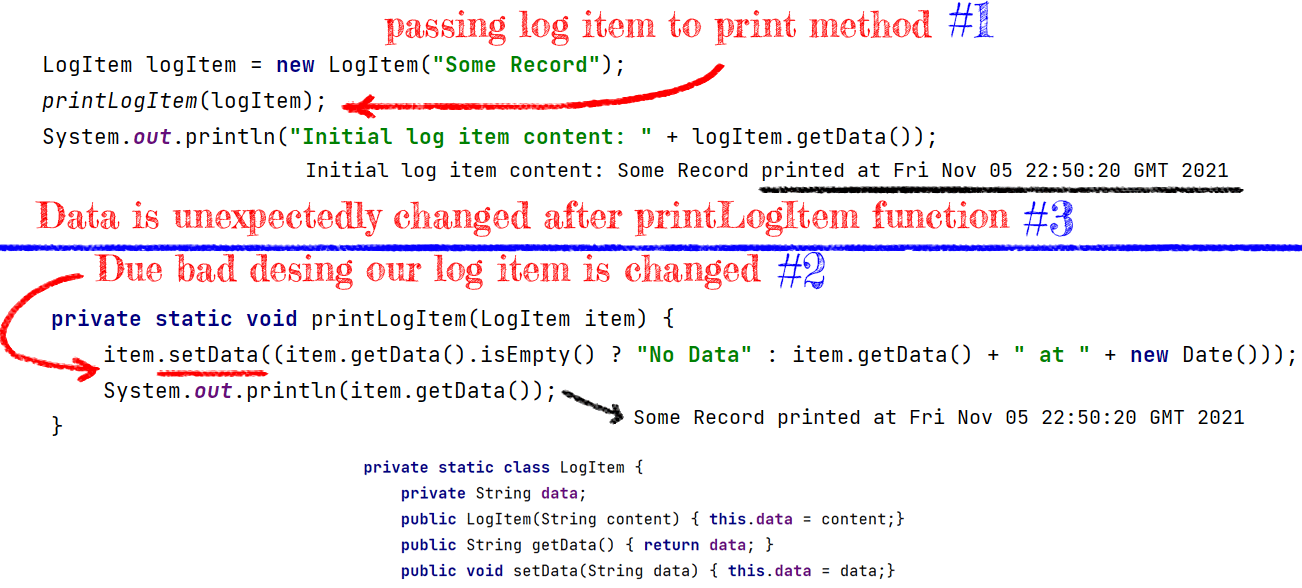
Data Is Changed When It Is Passed to a Function
In this example, we pass the logItem object to the printLogItem function. Expecting that it will be just printed, we later find out that the content of our logItem object has been changed.
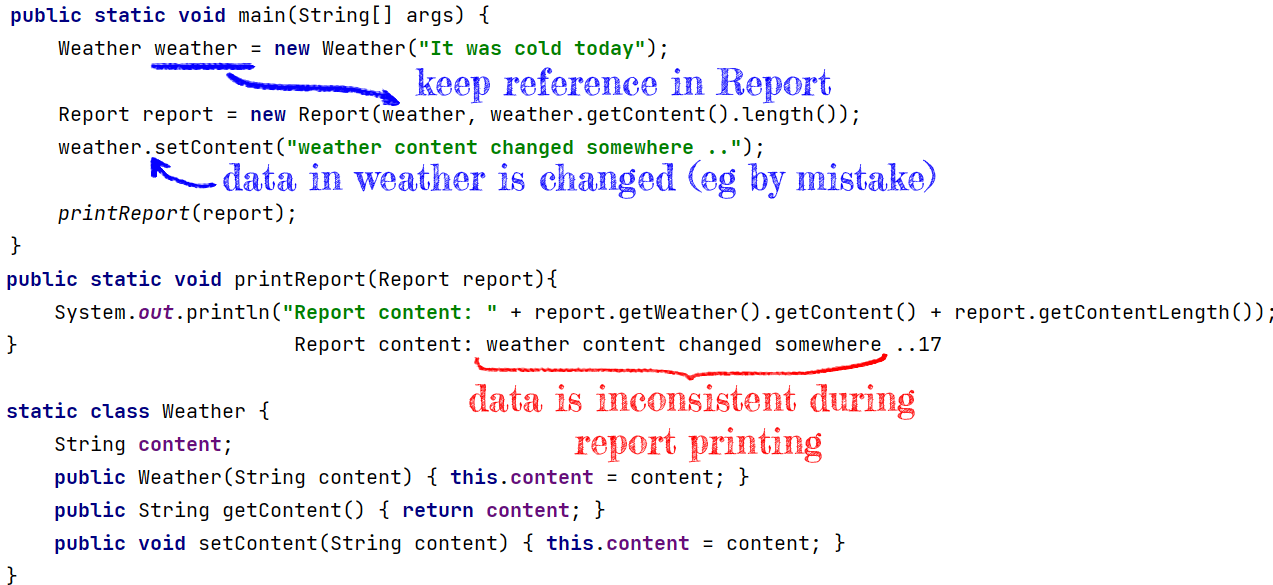
Build Report Became Inconsistent Due Internal Object Change
In this example, we built a report assuming that internal data (Weather object) won't be changed. Later we printed a report and saw that it became inconsistent (due to internal object change).
You Might Say, “What Stupid Examples!”

The provided examples might look extremely silly. Who would write such code? Well, the code looks obvious just because it's small. In real projects with a hundred complex classes, you can miss such problems.
Fixing Provided Examples
The core problem of the mentioned examples is that the object that shouldn't be changed was changed. Now when we identify the problem we can fix it. But how? There are a couple of ways. Let's start with the most obvious one:
Making Fields Final
First of all, if we forget to put private visibility, then data still would be accessible. To make it immutable, we need to make it final as below:

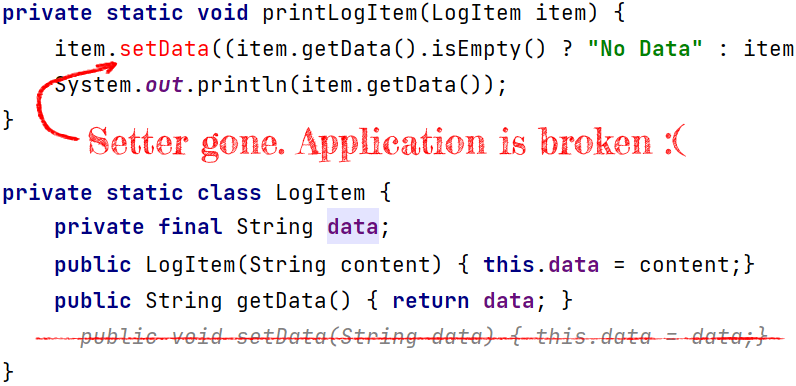
Removing the Setter
The easiest way we keep the same state is by removing the setter. Would it be enough?
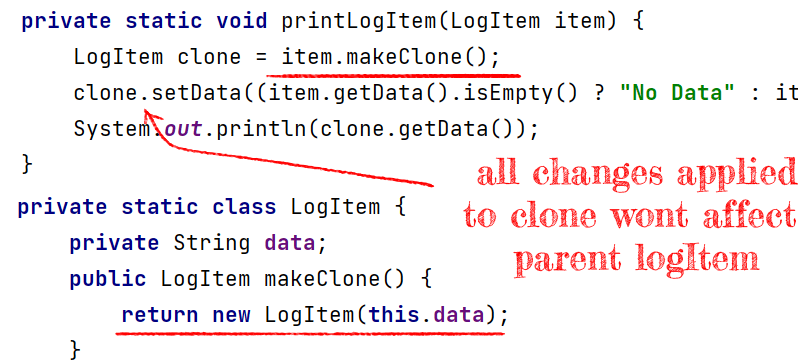
Passing Clone Instead of Real Instance
If we want to keep old implementation and setter alive we can solve it from 2 sides:
- We can pass a clone of the object.
- We can clone passed objects inside printLogItem function.
Immutable Primitives in Java
By default in Java, there are a couple of primitives such as int, long, and char. All primitives can't change their value unless you reassign them. Therefore, having them marked as final will make them perfectly immutable. 
Immutable String in Java
String in Java is the same as all other primitives. Once it's created it can't change its value. In order to make it immutable, it's enough to make it final. Easy peasy. 
Immutable Class in Java
Class in Java is nothing but a template. Once any class has an implementation, it becomes an Object. Therefore, saying "Immutable Class" is not precisely correct. But in general, it means that all instances of this Class would be immutable.
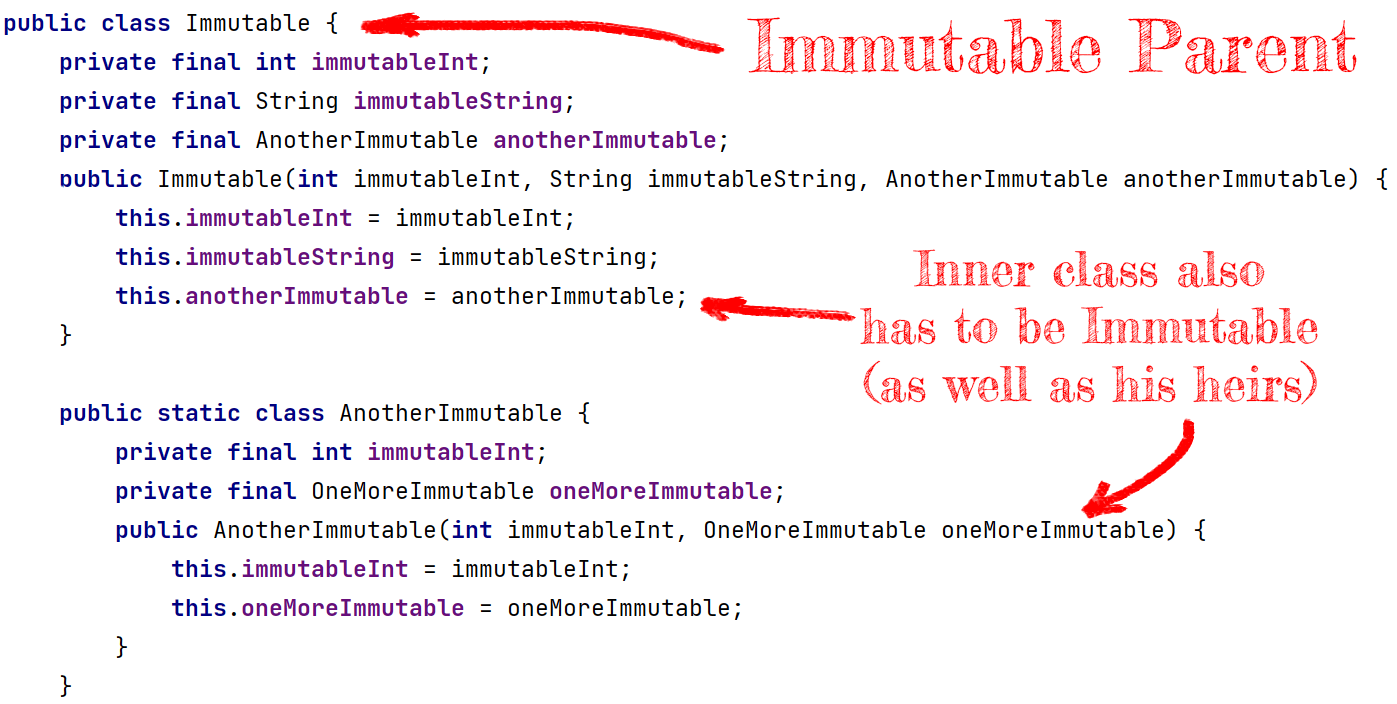
Okay, so what are the criteria of Class Immutability?
- Each field of this Class has to be immutable.
- Each field and Class has to be immutable as well.
Making Immutable Java Class
According to the previously explained rules, we can make a simple Immutable Class:
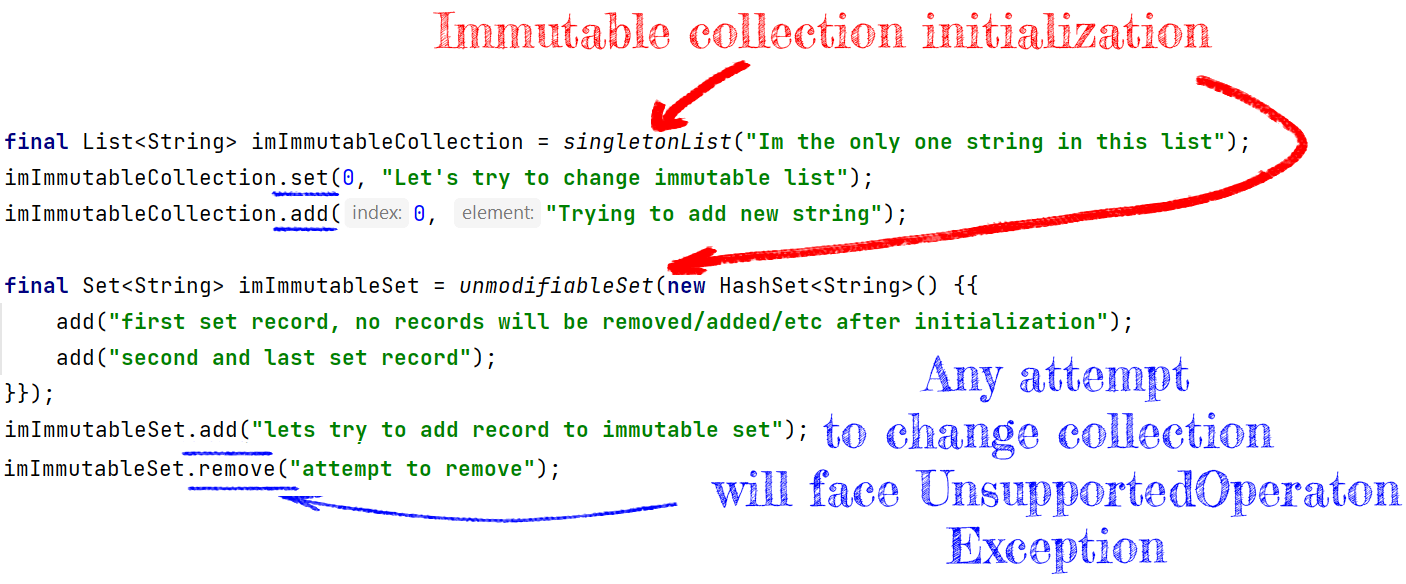
Immutable Collections in Java
Collections are also Objects, so if they follow the explained requirements, they are immutable. In practice, it means they are initialized only once and forever. Any changes are disabled or will face exceptions thrown.
In the next example, I'll show how to make an immutable collection using public Java API (java.util.Collections.*):
Using Lombok for Generating Immutable Code
Lombok is a framework that provides annotation that allows you to generate Java classes using annotations. Lombok provides options for immutable classes (but you have to take care of all immutability requirements: e.g. all internal fields also have to be immutable).
Lombok @Value Annotation: Immutable Boilerplate Bean
To quickly generate immutable Java Bean with final fields and hashcode/equals, you need to use @Value annotation:
Also, @Value annotation provides an option with static factory method: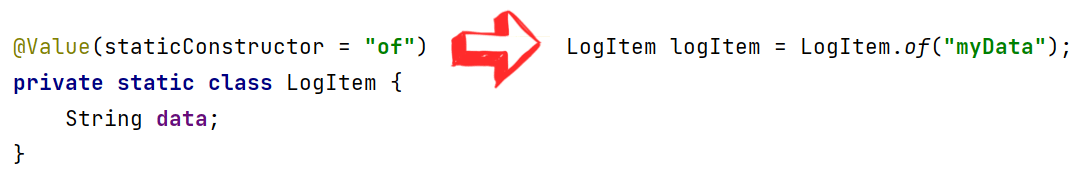
Is Singleton Immutable?
No. Singleton pattern defines that for a given class, only one instance can exist. If this class follows all immutability requirements, it can be immutable.
Is Enum Immutable?
This question is pretty similar to the previous one. Enum is a class that has a pre-defined number of instances. Inside each enum, we might have mutable data, but if internal fields of enum are immutable, then enum is immutable as well.
Main Advantages of Immutability Practices
Among all existent positive sides of immutability there are two main benefits:
- Application becomes more predictable and won't face inconsistency (for immutable data).
- Immutable parts of the application will be Thread Safe (IT'S VERY VALUABLE!).
Conclusion
The described practice is not mandatory, and you still can write reliable applications without immutable tricks. However, the explained recommendations are not just a "good tone," but a practical way to make stable and less buggy applications. In an enterprise world with huge applications, its practice should be mandatory. Thanks for reading!
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments