IoT in Agriculture: Five Technology Uses for Smart Farming and Challenges to Consider
Want to learn more about improving farming practices? These IoT solutions can help increase crop yields and overall efficiency in the AgriTech industry.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeWith the growing adoption of the Internet of Things (IoT), connected devices have penetrated every aspect of our life, from health and fitness, home automation, automotive and logistics, to smart cities and industrial IoT.
Thus, it is only logical that IoT, connected devices, and automation would find its application in agriculture and, as such, tremendously improve many facets of the farming practice. How could one still rely on horses and plows when self-driving cars and virtual reality are no longer a sci-fi fantasy but an everyday occurrence?
Farming has seen a number of technological transformations in the last decades, becoming more industrialized and technology-driven. By using various smart agriculture gadgets, farmers have gained better control over the process of raising livestock and growing crops, making it more predictable and efficient.
In this article, we will explore the IoT use cases in agriculture and examine their benefits. If you are considering investing in smart farming or planning to build an IoT solution for agriculture, dive right in.
What Is Smart Agriculture? The Definition and Market Size
There are many ways to refer to modern agriculture. For example, AgriTech refers to the general application of technology to agriculture.
Smart agriculture, on the other hand, is mostly used to denote the application of IoT solutions in agriculture.
Although smart agriculture IoT, as well as industrial IoT, aren’t as popular as consumer connected devices, the market is still very dynamic. The adoption of IoT solutions for agriculture is constantly growing. Namely, BI Intelligence predicts that the number of agriculture IoT device installations will hit 75 million by 2020, growing 20% annually. At the same time, the global smart agriculture market size is expected to triple by 2025, reaching $15.3 billion (compared to being slightly over $5 billion back in 2016).
Because the market is still developing, there are still ample opportunities for businesses willing to join in. Building IoT products for agriculture within the coming years can set you apart as an early adopter and, as such, help you pave the way to success.
But why should you consider building an IoT application for agriculture in the first place?

The Benefits of Smart Farming: How IoT Is Shaping Agriculture
Technologies and IoT have the potential to transform agriculture in many aspects. Namely, there are five ways IoT can improve agriculture:
- Data, tons of data, collected by smart agriculture sensors, e.g. weather conditions, soil quality, crop’s growth progress or cattle health. This data can be used to track the state of your business in general, as well as staff performance, equipment efficiency, etc.
- Better control over the internal processes and, as a result, lower production risks. The ability to foresee the output of your production allows you to plan for better product distribution. If you know exactly how much crops you are going to harvest, you can make sure your product won’t lie around unsold.

- Cost management and waste reduction thanks to the increased control over production. Being able to see any anomalies in the crop growth or livestock health, you will be able to mitigate the risks of losing your yield.
- Increased business efficiency through process automation. By using smart devices, you can automate multiple processes across your production cycle, e.g. irrigation, fertilizing, or pest control.
- Enhanced product quality and volumes. Achieve better control over the production process and maintain higher standards of crop quality and growth capacity through automation.
As a result, all of these factors can eventually lead to higher revenue.
Now that we have outlined how IoT can be advantageously applied in the sphere of agriculture, let’s take a look at how the listed benefits can find their application in real life.
IoT Use Cases in Agriculture
There are many types of IoT sensors and IoT applications that can be used in agriculture:
Monitoring of Climate Conditions
Probably the most popular smart agriculture gadgets are weather stations, combining various smart farming sensors. Located across the field, they collect various data from the environment and send it to the cloud. The provided measurements can be used to map the climate conditions, choose the appropriate crops, and take the required measures to improve their capacity (i.e. precision farming).
Some examples of such agriculture IoT devices are allMETEO, Smart Elements, and Pycno.

Greenhouse Automation
In addition to sourcing environmental data, weather stations can automatically adjust the conditions to match the given parameters. Specifically, greenhouse automation systems use a similar principle.
For instance, Farmapp and Growlink are also IoT agriculture products offering such capabilities among others.
GreenIQ is also an interesting product that uses smart agriculture sensors. It is a smart sprinklers controller that allows you to manage your irrigation and lighting systems remotely.

Crop Management
One more type of IoT product in agriculture and another element of precision farming is crop management devices. Just like weather stations, they should be placed in the field to collect data specific to crop farming; from temperature and precipitation to leaf water potential and overall crop health, these can all be used to readily collect data and information for improved farming practices.
Thus, you can monitor your crop growth and any anomalies to effectively prevent diseases or infestations that could harm your yield. Arable and Semios can serve as good representations of how this use case can be applied in real life.

Cattle Monitoring and Management
Just like crop monitoring, there are IoT agriculture sensors that can be attached to the animals on a farm to monitor their health and log performance. This works similarly to IoT devices for pet care.
For example, SCR by Allflex and Cowlar use smart agriculture sensors (collar tags) to deliver temperature, health, activity, and nutrition insights on each individual cow, as well as collective information about the herd.

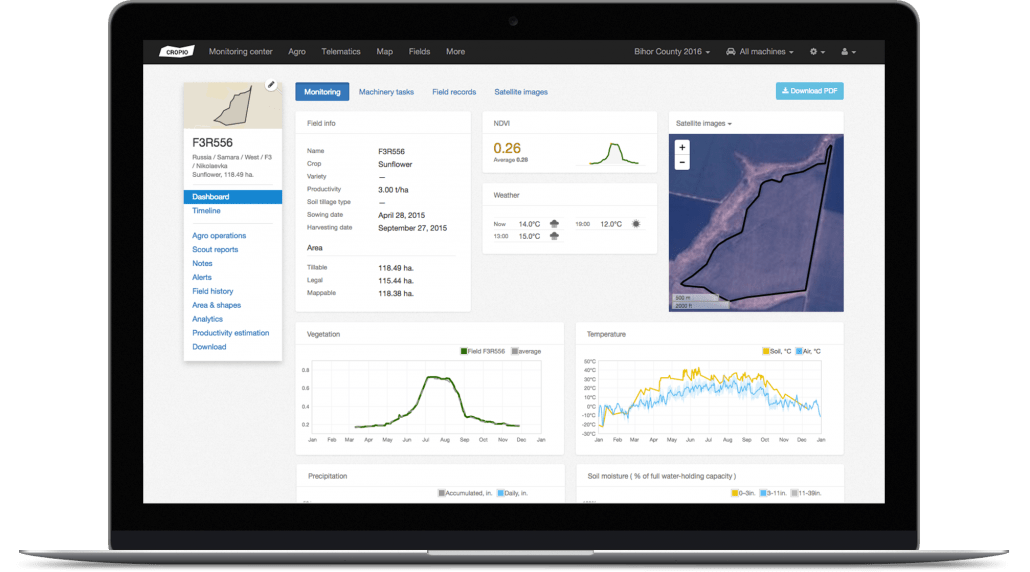
End-to-End Farm Management Systems
A more complex approach to IoT products in agriculture can be represented by the so-called farm productivity management systems. They usually include a number of agriculture IoT devices and sensors, installed on the premises as well as a powerful dashboard with analytical capabilities and in-built accounting/reporting features.
This offers remote farm monitoring capabilities and allows you to streamline most of the business operations. Similar solutions are represented by FarmLogs and Cropio.
In addition to the listed IoT agriculture use cases, some prominent opportunities include vehicle tracking (or even automation), storage management, logistics, etc.
Four Things to Consider Before Developing Your Smart Farming Solution
As we can see, the use cases for IoT in agriculture are endless. There are many ways smart devices can help you increase your farm’s performance and revenue. However, agriculture IoT apps development is no easy task. There are certain challenges you need to be aware of if you are considering investing in smart farming.
1. Hardware
To build an IoT solution for agriculture, you need to choose the sensors for your device (or create a custom one). Your choice will depend on the types of information you want to collect and the purpose of your solution. In any case, the quality of your sensors is crucial to the success of your product— it will depend on the accuracy of the collected data and its reliability.
2. The Brain
Data analytics should be at the core of every smart agriculture solution. The collected data itself will be of little help if you cannot make sense of it. Thus, you need to have powerful data analytics capabilities and apply predictive algorithms and machine learning in order to obtain actionable insights based on the collected data.
3. Maintenance
Maintenance of your hardware is a challenge that is of primary importance for IoT products in agriculture, as the sensors are typically used in the field and can be easily damaged. Thus, you need to make sure your hardware is durable and easy to maintain. Otherwise, you will need to replace your sensors more often than you would like.

4. Mobility
Smart farming applications should be tailored for use in the field. A business owner or farm manager should be able to access the information on site or remotely via a smartphone or desktop computer.
Plus, each connected device should be autonomous and have enough wireless range to communicate with the other devices and send data to the central server.
5. Infrastructure
To ensure that your smart farming application performs well (and to make sure it can handle the data load), you need a solid internal infrastructure.
Furthermore, your internal systems have to be secure. Failing to properly secure your system only increases the likeliness of someone breaking into it, stealing your data, or even taking control of your autonomous tractors.
Published at DZone with permission of Maria Aleksandrova, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments