Installing OpenVPN on AWS
Bring peer-to-peer connectivity to your cloud with this step-by-step guide to setting up OpenVPN on Amazon Web Services' free tier.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeOpenVPN is open source software that implements VPN and is used for creating peer-to-peer connections. OpenVPN is more than 16 years old — the first release was on 13 May 2001. So, with the history behind us, let's go through how to install OpenVPN on the cloud.
For this post, I am using the free tier provided by Amazon Web Services.
We are going to install an OpenVPN server and an OpenVPN client on your local machine, so first, you need an AWS account. Log into your AWS account and go to the EC2 dashboard, then launch an instance.
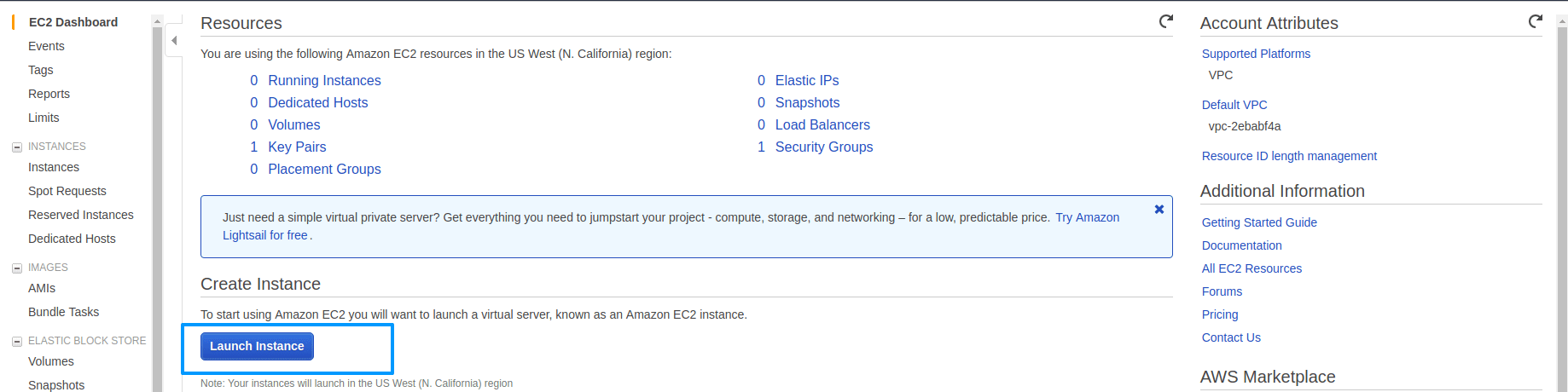
Then go to the AWS Marketplace and search for OpenVPN and select OpenVPN Access Server

I am going to select t2.micro, as it eligible for the free tier. Then, hit review and launch.

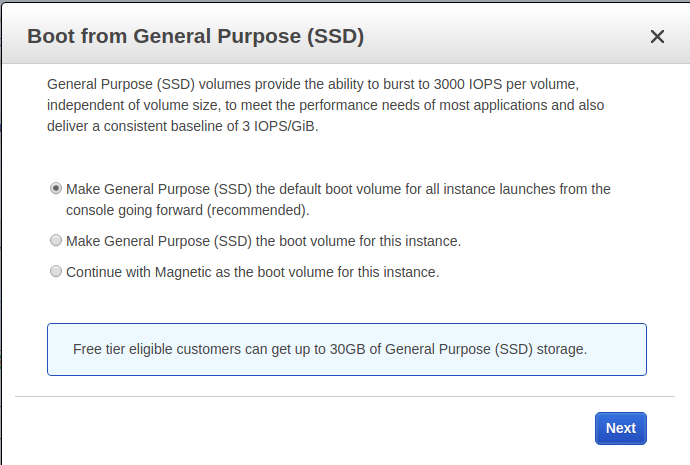
Here, I am going to select General Purpose (SSD) and hit next.
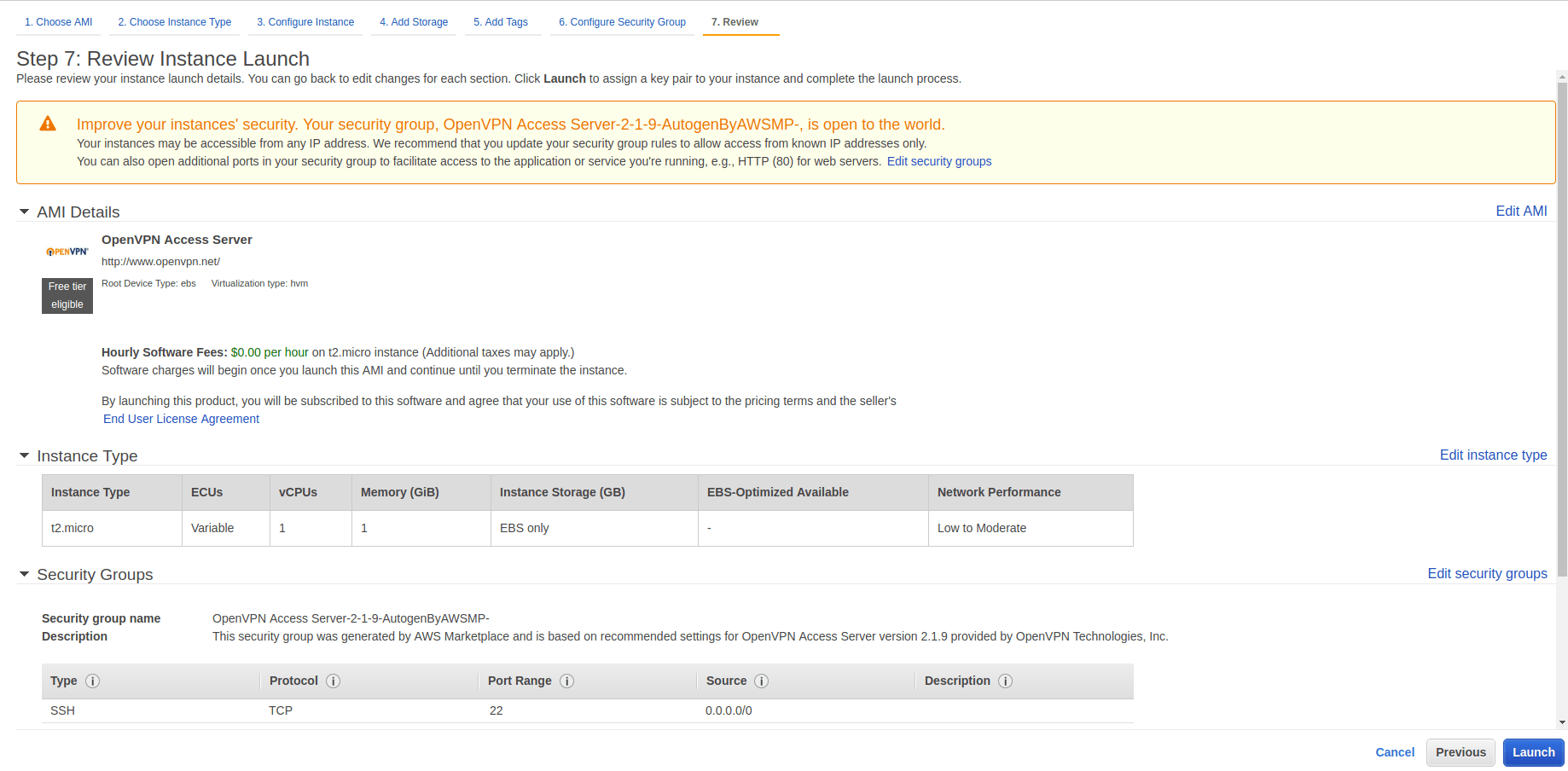
After that, AWS will skip to step number 7 in the process, where we need to review the instance. After reviewing it, hit launch.
It will take few minutes to reach a running state. Until then, we will create an elastic IP so that the IP will not get lost. In order to create elastic IP, hit Elastic IPs in the left panel of the EC2 dashboard. Hit Allocate New Address, and you will get an elastic IP.

Now associate that address with the instance you created earlier for OpenVPN.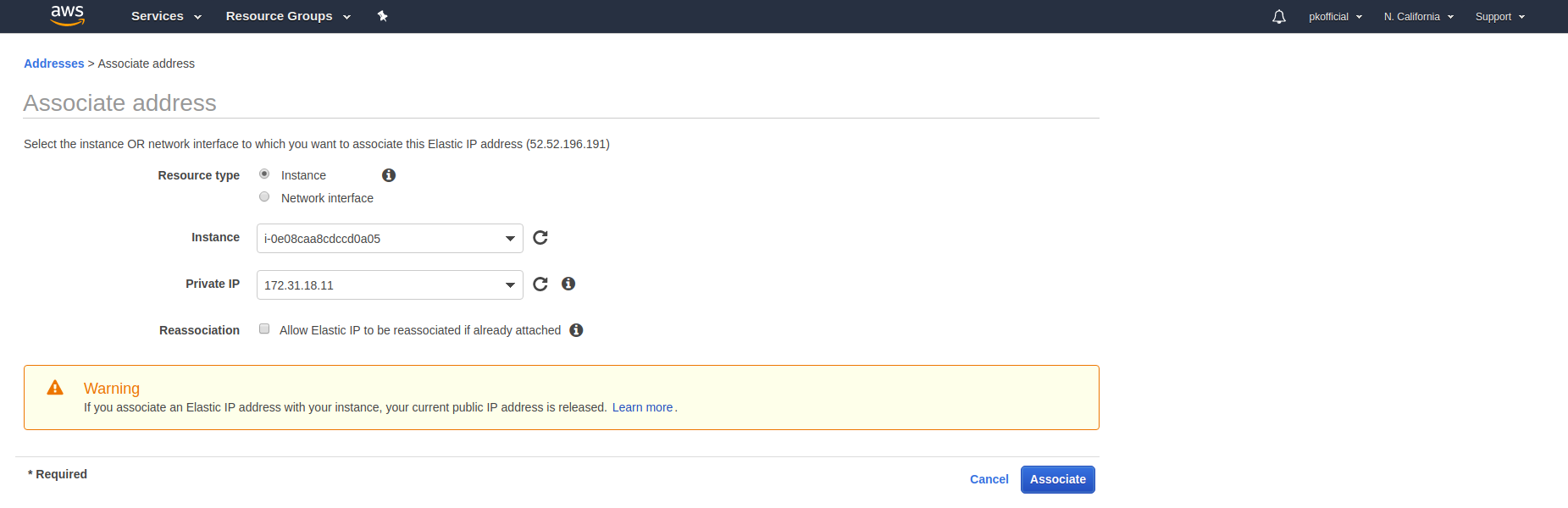
After that, Elastic IP will link to that instance and become the public IP of that instance.

Now we have to ssh into the instance. This is a one-time process. The user for ssh will be openvpnas.
When you enter into the instance, you will get the message below. Enter yes and hit enter to continue.
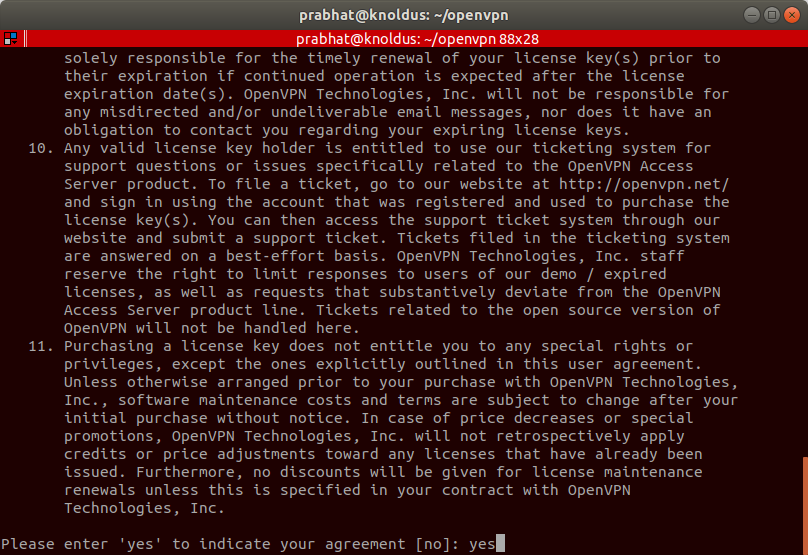
Now keep pressing enter until the initial configuration completes.
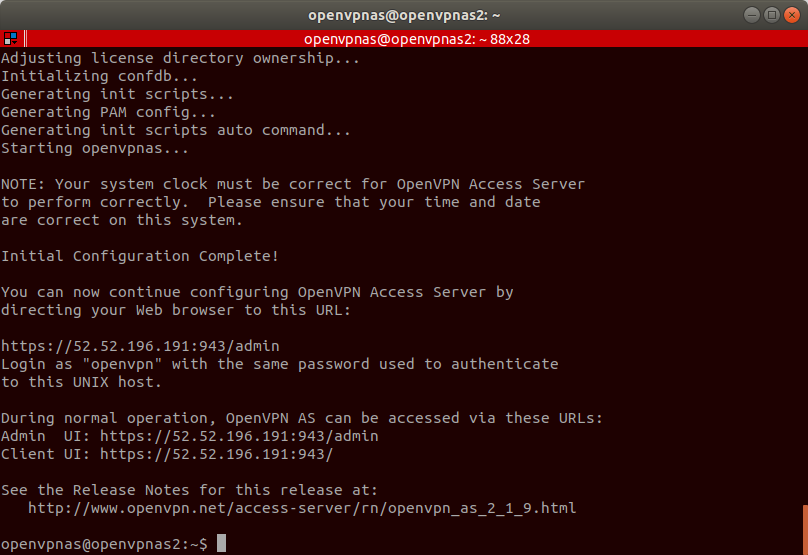
Once the configuration completes, change the password for the openvpn user. Enter
sudo passwd openvpn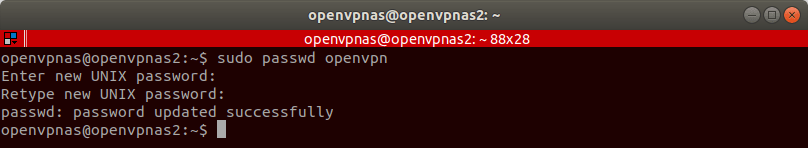
Now open the browser and go to the elastic IP address with the https protocol. For example, I am going to use https://52.52.196.191. This will prompt a warning message, as shown below. You just need to skip it and proceed to the URL.
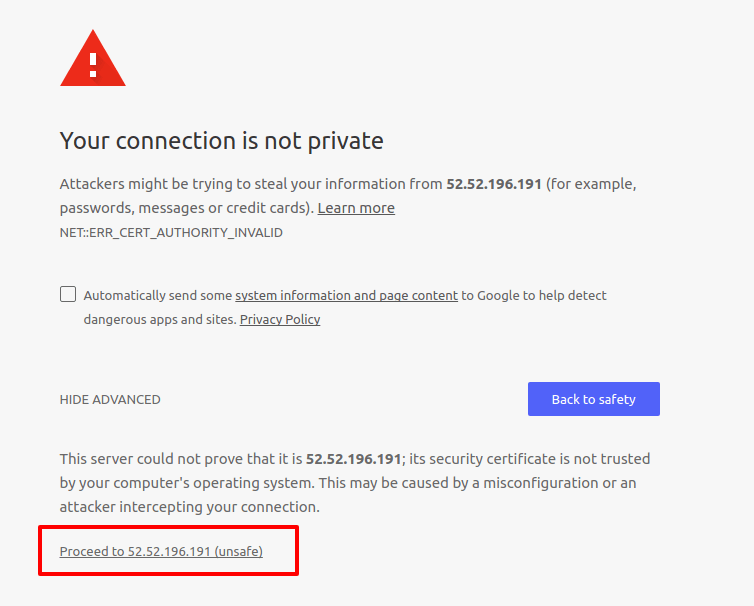
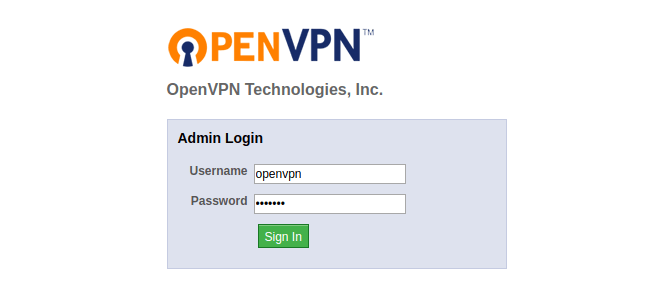
It will ask you to log in. Just can enter openvpn as the username and the password that you set earlier. Then, you need to install the OpenVPN client. As I am working on Linux, I am going select OpenVPN for Linux, which will take you to this page.
Just install the OpenVPN client on your machine and download the user-locked profile that will be used to connect to OpenVPN.

Connect to OpenVPN using the following command:
sudo openvpn --config client.ovpnNote: In order to connect, you must have root access.
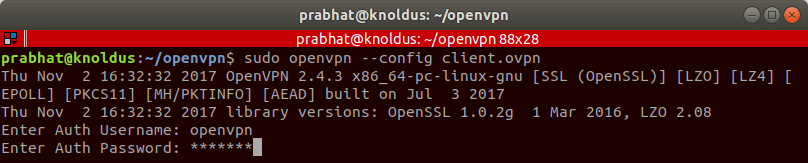
Once that is done, go to the admin panel by appending /admin after your URL (for example, https:///admin). It will take you to admin login page, where you need to enter the same credentials as before.
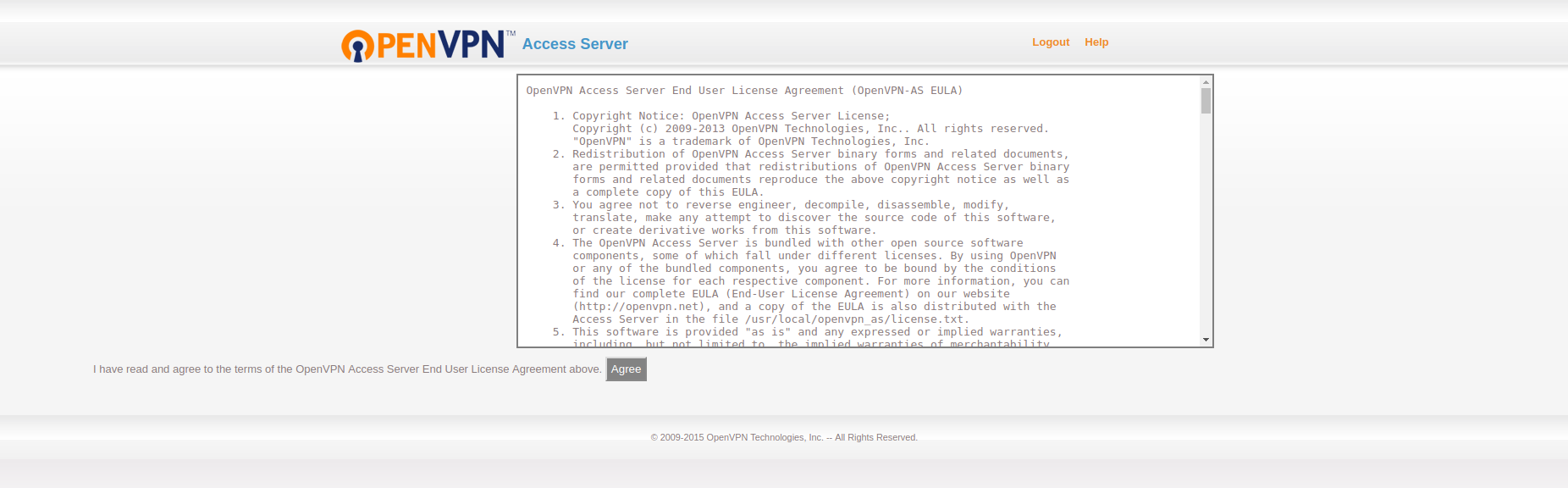
This first time, it will ask you to agree to its term. Once you agree, you will enter the admin panel.
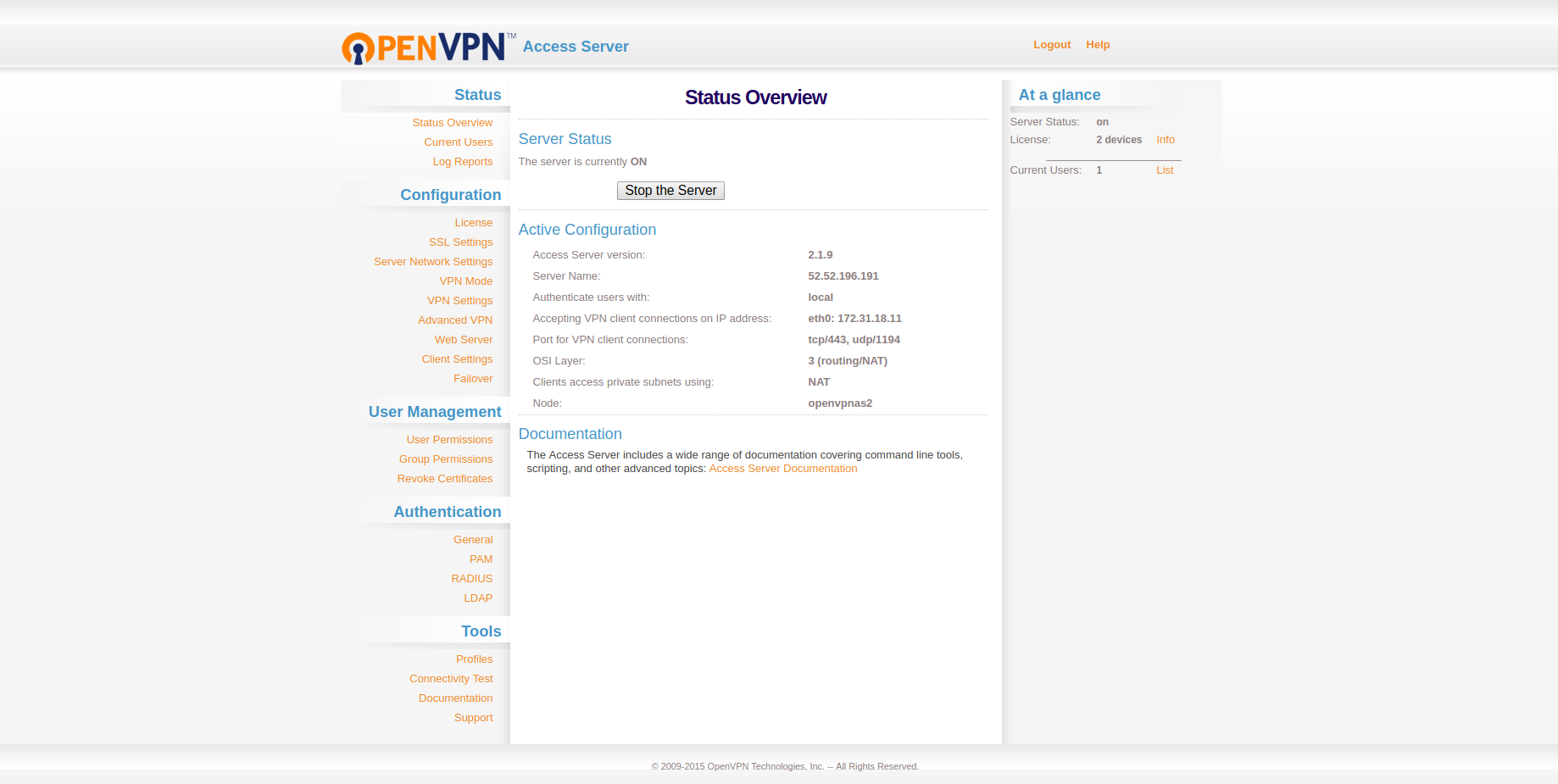
Then go to the Server Network Settings menu and uncheck Admin Web Server and Client Web Server. Then hit save. It will disable access to your web servers from public IPs.
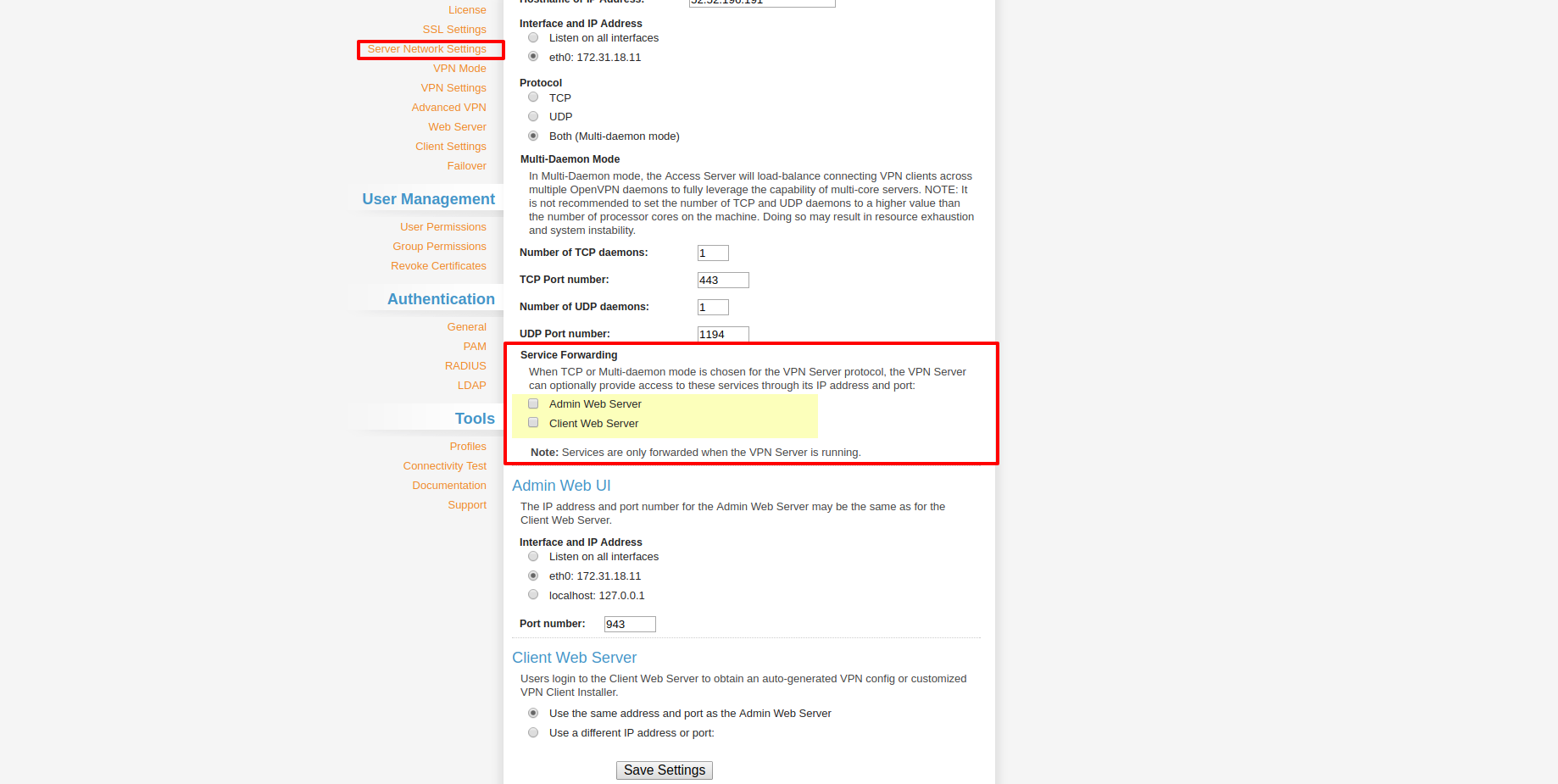
Now it will show a message saying Setting changed. Hit Update Running Server, and you will get a "Site cannot be reached" error — that is intended.

Now go to the EC2 dashboard and get the private IP of your instance.

Now go to your browser and replace the public IP withthe private IP and append :943 at the end of the IP. The URL should be like this: https://:943/admin. It will take you to the admin panel, and that’s it! Now, those who are connected to OpenVPN will able to access the server using a private IP. Your OpenVPN is now up and running.

One last note: For security, you can remove the ssh login from security groups.
This article was first published on the Knoldus blog.
Published at DZone with permission of Prabhat Kashyap, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments