Imputing Missing Data Using Sklearn SimpleImputer
In this post, learn how to use Python's Sklearn SimpleImputer for imputing/replacing numerical and categorical missing data using different strategies.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIn this post, you will learn about how to use Python's Sklearn SimpleImputer for imputing/replacing numerical and categorical missing data using different strategies. In one of the related articles posted sometime back, the usage of fillna method of Pandas DataFrame is discussed. Here is the link, Replace missing values with mean, median and mode. Handling missing values is a key part of data preprocessing and hence, it is of utmost importance for data scientists/machine learning engineers to learn different techniques in relation imputing / replacing numerical or categorical missing values with appropriate value based on appropriate strategies.
The following topics will be covered in this post:
- SimpleImputer explained with Python code example
- SimpleImputer for imputing numerical missing data
- SimpleImputer for imputing categorical missing data
SimpleImputer Explained With Python Code Example
SimpleImputer is a class found in package sklearn.impute. It is used to impute / replace the numerical or categorical missing data related to one or more features with appropriate values such as following:
Each of the above type represents strategy when creating an instance of SimpleImputer. Here is the Python code sample representing the usage of SimpleImputor for replacing numerical missing value with the mean.
First and foremost, let's create a sample Pandas Dataframe representing marks, gender and result of students.
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
students = [[85, 'M', 'verygood'],
[95, 'F', 'excellent'],
[75, None,'good'],
[np.NaN, 'M', 'average'],
[70, 'M', 'good'],
[np.NaN, None, 'verygood'],
[92, 'F', 'verygood'],
[98, 'M', 'excellent']]
dfstd = pd.DataFrame(students)
dfstd.columns = ['marks', 'gender', 'result']
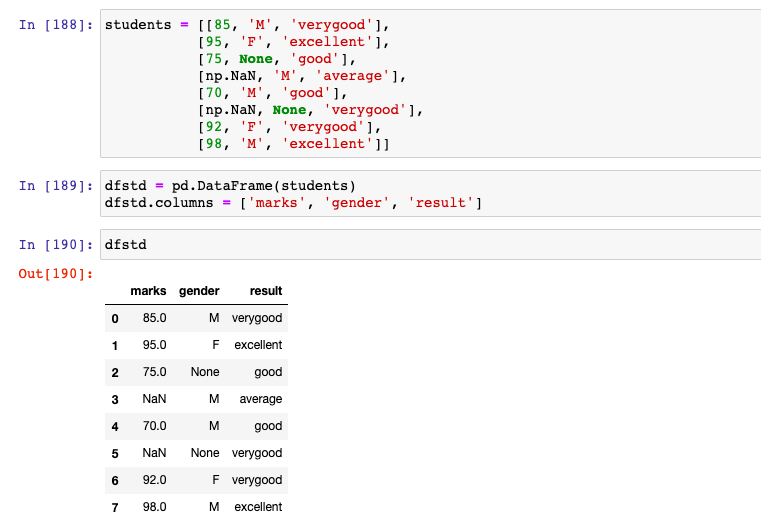
There are two columns / features (one numerical - marks, and another categorical - gender) which are having missing values and need to be imputed. In the code below, an instance of SimpleImputer is created with strategy as "mean". The missing value is represented using NaN. Note some of the following:
- sklearn.impute package is used for importing SimpleImputer class.
- SimpleImputer takes two argument such as missing_values and strategy.
- fit_transform method is invoked on the instance of SimpleImputer to impute the missing values.
xxxxxxxxxx
from sklearn.impute import SimpleImputer
#
# Missing values is represented using NaN and hence specified. If it
# is empty field, missing values will be specified as ''
#
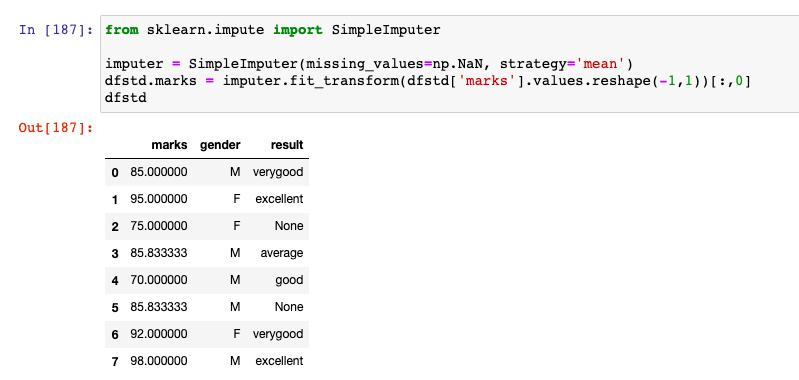
imputer = SimpleImputer(missing_values=np.NaN, strategy='mean')
dfstd.marks = imputer.fit_transform(dfstd['marks'].values.reshape(-1,1))[:,0]
dfstd
Here is how the output would look like. Note that missing value of marks is imputed / replaced with the mean value, 85.83333
SimpleImputer for Imputing Numerical Missing Data
For the numerical missing data, the following strategy can be used.
The code example below represents the instantiation of SimpleImputer with appropriate strategies for imputing numerical missing data
xxxxxxxxxx
#
# Imputing with mean value
#
imputer = SimpleImputer(missing_values=np.NaN, strategy='mean')
#
# Imputing with median value
#
imputer = SimpleImputer(missing_values=np.NaN, strategy='median')
#
# Imputing with most frequent / mode value
#
imputer = SimpleImputer(missing_values=np.NaN, strategy='most_frequent')
#
# Imputing with constant value; The command below replaces the missing
# value with constant value such as 80
#
imputer = SimpleImputer(missing_values=np.NaN, strategy='constant', fill_value=80)
SimpleImputer for Imputing Categorical Missing Data
For handling categorical missing values, you could use one of the following strategies. However, it is the "most_frequent" strategy which is preferably used.
- Most frequent (strategy='most_frequent')
- Constant (strategy='constant', fill_value='someValue')
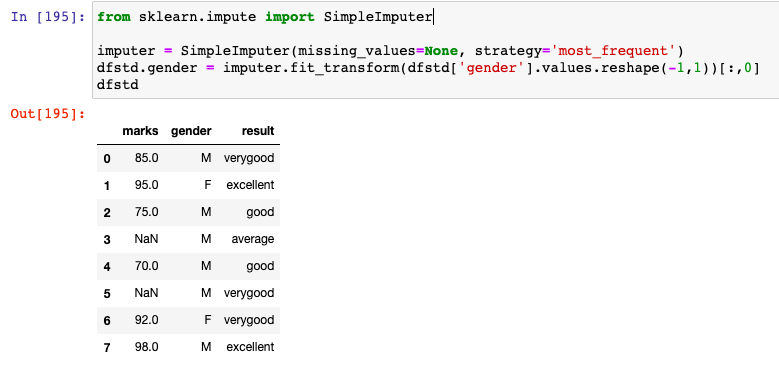
Here is how the code would look like when imputing missing value with strategy as most_frequent. In the code sample used in this post, gender is having missing values. Note how the missing value under gender column is replaced with 'M' which occurs most frequently.
xxxxxxxxxx
from sklearn.impute import SimpleImputer
imputer = SimpleImputer(missing_values=None, strategy='most_frequent')
dfstd.gender = imputer.fit_transform(dfstd['gender'].values.reshape(-1,1))[:,0]
dfstd
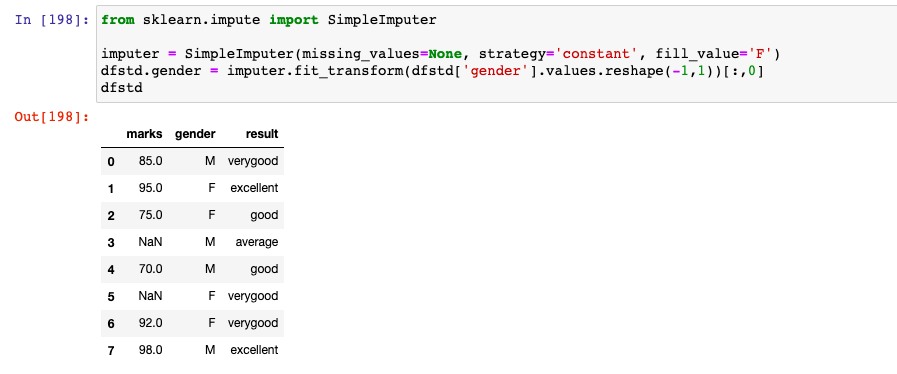
Here is how the code would look like when imputing missing value with strategy as constant. Note how the missing value under gender column is replaced with 'F' which is assigned using fill_value parameter.
xxxxxxxxxx
from sklearn.impute import SimpleImputer
imputer = SimpleImputer(missing_values=None, strategy='constant', fill_value='F')
dfstd.gender = imputer.fit_transform(dfstd['gender'].values.reshape(-1,1))[:,0]
dfstd
Conclusions
Here is the summary of what you learned in this post:
- You can use Sklearn.impute class SimpleImputer to impute/replace missing values for both numerical and categorical features.
- For numerical missing values, a strategy such as mean, median, most frequent, and constant can be used.
- For categorical features, a strategy such as the most frequent and constant can be used.
Published at DZone with permission of Ajitesh Kumar, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments