How to Use IBM App Connect's ‘Mapping Assist’ to Automatically Map Your Integration Flows
This tutorial explains IBM App Connect Mapping Assist's capability to reduce integration flow building time and enable developers to build flows confidently.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIBM App Connect includes AI-powered Mapping Assist to dramatically accelerate the speed of development, shorten time to value, and improve your overall user experience. Mapping Assist uses a pre-trained AI algorithm to securely provide users with intelligent, customized data mapping suggestions.
The need for digital transformation is more important than ever before, with 56% of CEOs reporting that their digital improvements have led to revenue growth. Businesses are recognizing the need to focus on creating convenient, digital solutions both internally for employees and externally for their customers to stay ahead of the competition. Integration is key to digital transformation efforts — by harnessing the power of your existing data you can extend the reach of your digital IT assets, whether you're providing an existing service through a new digital channel or tapping into an entirely new market via APIs surfaced through partner applications.
When building integrations, data mapping is the process by which a user specifies how data elements from a source application correspond to elements in a target application. For example, mapping the 'Post Code' field from Application A to the 'Zip Code' field in Application B. Data mapping is the first step of a wide variety of integration tasks, including data transformation or data mediation between data sources and a destination. But data mapping has long been a point of frustration for developers since mapping fields between different endpoints is complex and time-consuming, slowing the speed at which businesses can respond to changes and remain competitive.
What Makes Mapping Complex?
- An Increasing Number and Diversity of Endpoints
There is a steep learning curve when integrating a new application, particularly in understanding the application's metadata. This is especially challenging when integration development is not a primary role, for example, a marketing professional wanting to use a new SaaS application to simplify event management will need to map existing customer data from a CRM application. And the need for integration continues to grow as businesses are using an ever-increasing range of endpoints, from homegrown apps to off-the-shelf applications, databases, files, SaaS applications, Webservices, and more. In this environment, understanding how to map elements between many different applications and delivering at speed becomes a challenge for even the most experienced integration developers. - No Field Naming Standards
Applications are built by different vendors with no universally agreed-upon conventions for field naming. For instance, a PIN may refer to a pin-code (personal identification number) in one application while it may refer to a product identification number in another. This lack of standardization makes it very difficult for users to reuse knowledge when working on different applications. Users are thereby forced to spend valuable time learning every new application or endpoint before they can start to deliver business value through integration.Many application vendors also allow administrators to develop custom objects or to make schema changes in existing business objects. This customization generates additional overheads on the user to learn and understand field naming outside of the publicized documentation.
Additionally, making changes to integrations created by someone else poses a challenge, especially if design-related mapping decisions are not documented properly. Reviewing and understanding this additional documentation, where available, adds time and complexity.
- Field Structures Further Compounding Complexity
There are multiple examples of applications, for instance, MS Dynamics 365 and IBM Maximo, which have huge numbers of fields to map, in some cases more than one thousand fields. With so many fields to map, building integration flows that contain these applications can become especially time-intensive.Furthermore, applications can also provide data via nested fields. For example, the address field may be made up of multiple fields such as 'house number' and 'street'. As a result, field hierarchy must be a consideration while mapping objects. The user may need to repeatedly map the source flat structure to the target nested structure and vice versa — a time-consuming activity with a greater risk for errors.
Simplify Integration With IBM App Connect's Mapping Assist
Mapping Assist utilizes a pre-trained Artificial Intelligence (AI) algorithm which uses Natural Language Processing schema matching to find the closest match between source and target mappings. No pre-training is required to get started — Mapping Assist suggestions are provided by the algorithm as soon as you start building a flow. The algorithm assigns a percentage of confidence to each mapping suggestion based on semantic proximity to a target field, using business object metadata such as the field name, description, and display name to find the correct match. This means that Mapping Assist will also facilitate mapping fields from custom objects and schemas where there are no field naming standards.
Key Features of Mapping Assist:
- Automap all fields wherever the matching confidence is higher than 80%.
- Relevant and fine-grained field-level suggestions are provided when confidence is between 30%-100%.
- Suggestions are provided based on multiple sources, including all the previous nodes in the flow, for greater accuracy.
- Mapping suggestions for flat structures as well as complex, nested mapping fields are provided.
- Previously selected mappings are remembered and shown as top suggestions when a similar source and target mapping is attempted.
Demonstration
Sync the Salesforce Contacts with Microsoft 365 scenario is used to demonstrate this:
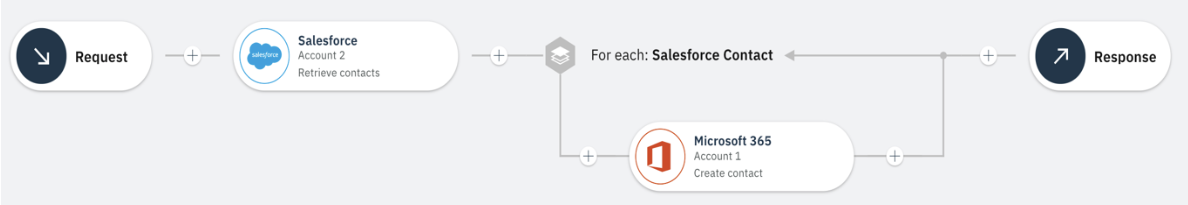 Figure 1: Sync the Salesforce Contacts with Microsoft 365
Figure 1: Sync the Salesforce Contacts with Microsoft 365
Once the Microsoft 365 Create Contact node is added, mapping suggestions will be generated and the best possible matches (top suggestions) are presented which can be automatically inserted into fields with a single click.
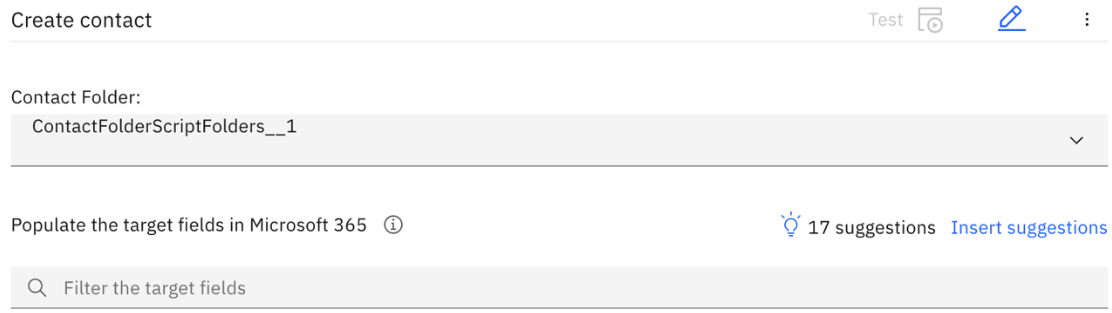
Figure 2: Top suggestions with Insert suggestions
These top suggestions have an 80% (or higher) accuracy rate, and the count (N suggestions) identifies the total number of fields that will be populated with mappings. Mapping Assist Insert suggestions won't count or apply mapping for the fields which have:
- Existing mappings that are manually populated.
- Multiple suggestions for a field with the same confidence rating. In that case, all suggestions have an equal chance to be mapped. Those suggestions will be provided in field-level suggestions and can be mapped manually by selecting an appropriate mapping.
By clicking on Insert Suggestions, all suggestions with a confidence score of above 80% will be automatically inserted into the Microsoft 365 Create Contact node.

Figure 3: Populated mappings for simple and nested fields
Figure 3, demonstrates all the fields that are automatically mapped by Insert Suggestions. Note the suggestions for simple fields as well as the nested fields.
For remaining unpopulated fields, a click on textbox will present the suggestions if Mapping Assist found suggestions for that field in the form of a Suggested mappings list. This displays up to five suggestions with percentages that are above 30% from all previous nodes.
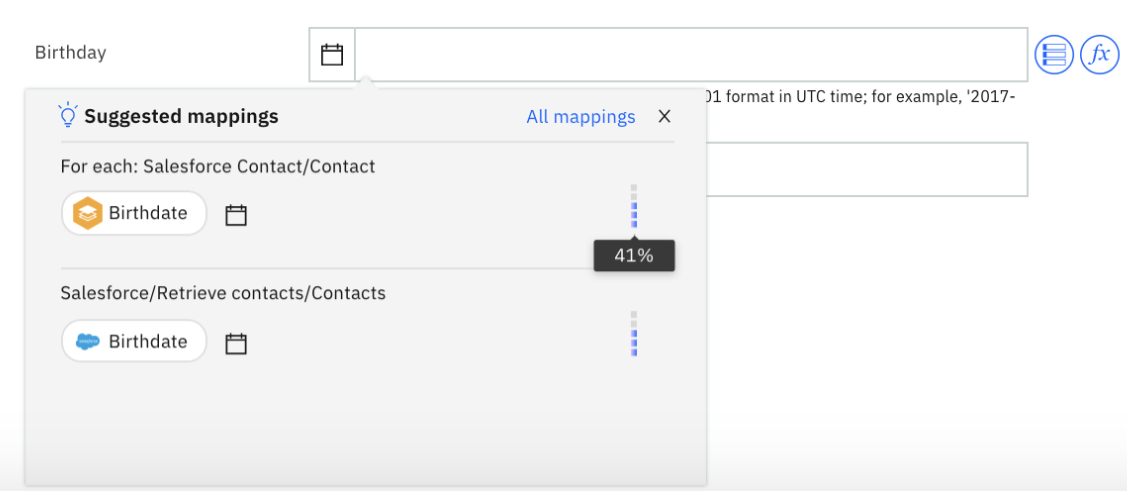
Figure 4: Field Level Suggestions for a simple field
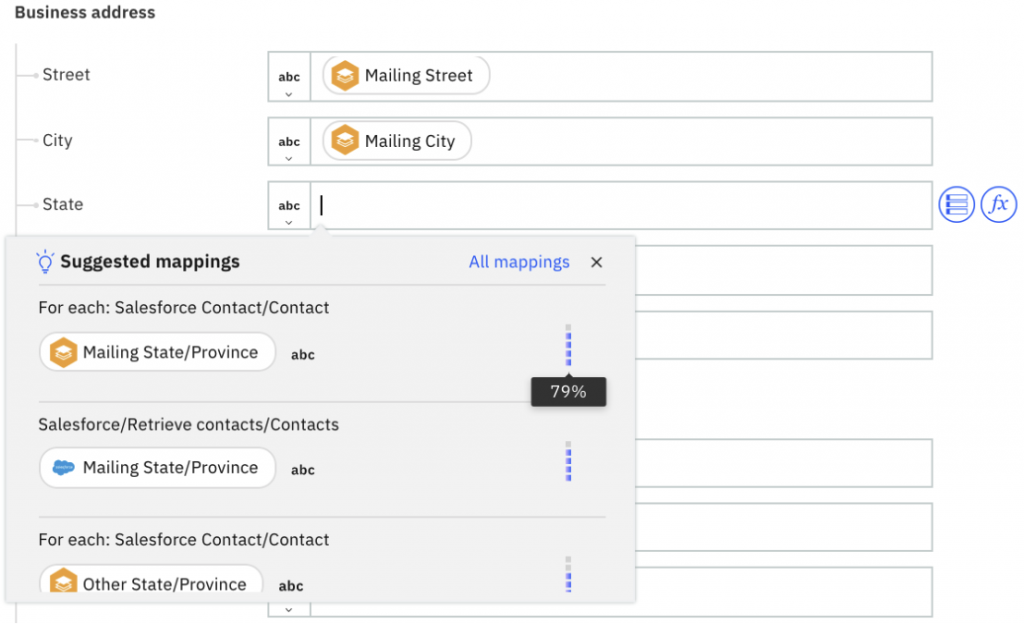
Figure 5: Field Level Suggestions for a nested field
In figure 5, suggestions are from two nodes — For each node and Salesforce node. For each mapping, the field hierarchy identifies the origin of the content, such as the application or node name, action, and object.
If you wish to map the fields that are not suggested by Mapping Assist, you can do so by clicking on All mappings, which displays all inputs available for the target field (figure 6).
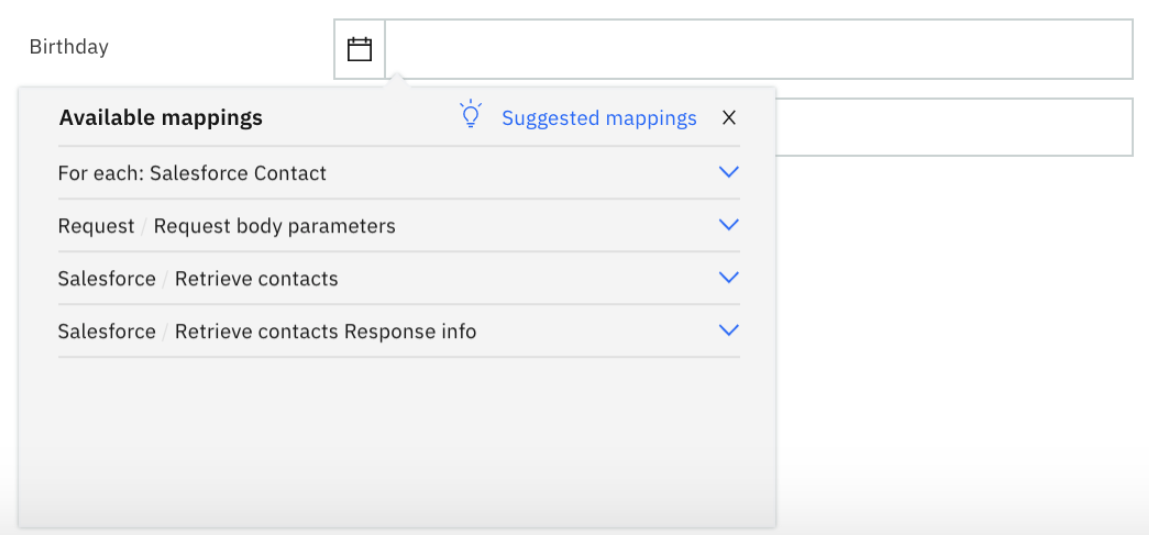
Figure 6: All available mappings are shown for a target field
Clicking on Suggested mappings will switch back to the Suggested mappings list.
To improve accuracy in future mappings, Mapping Assist collects and stores the mapping data in an internal database by tracking the mapping history of flows that are started. For example, if you mapped Birthdate to Birthday, this mapping will be remembered and Mapping Assist will suggest it in future flows with a 100% confidence rating and be mapped any time a user chooses to Insert Suggestions.
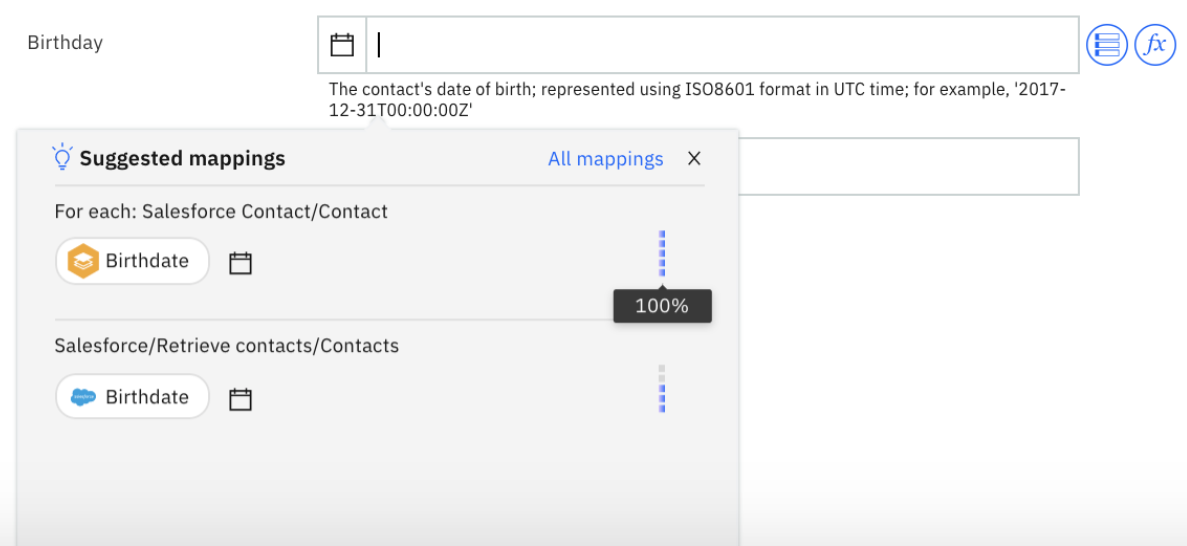
Figure 7: Suggestion from user history
Mapping suggestions for nested array fields are supported for exact schema matches only. This means root element names should exactly match in the source and destination array and fields that have the same field name under the root element will be mapped.
To illustrate this feature, let's consider a scenario to Sync data from one account to another account in Microsoft 365.
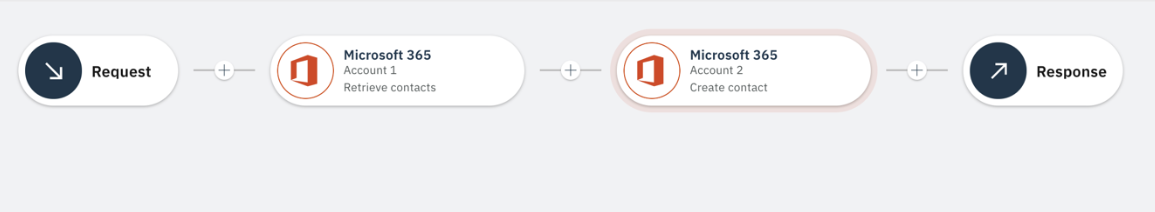
Figure 8: Sync data between two different accounts
Clicking the Insert Suggestions will populate the fields with mappings, including nested array fields.
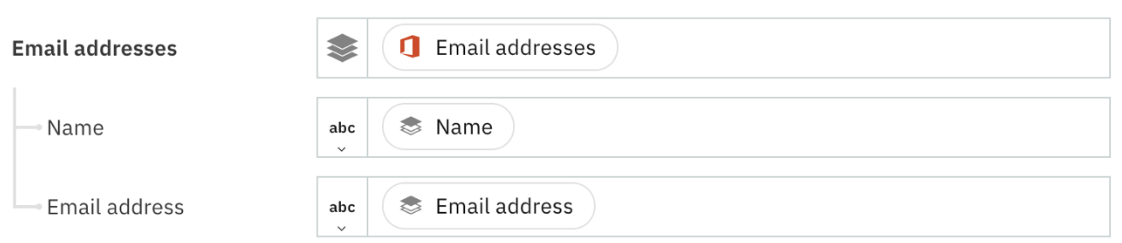
Figure 9: Populated mappings for nested array fields
You can also use the field level suggestions available for nested array fields as shown in Figure 10.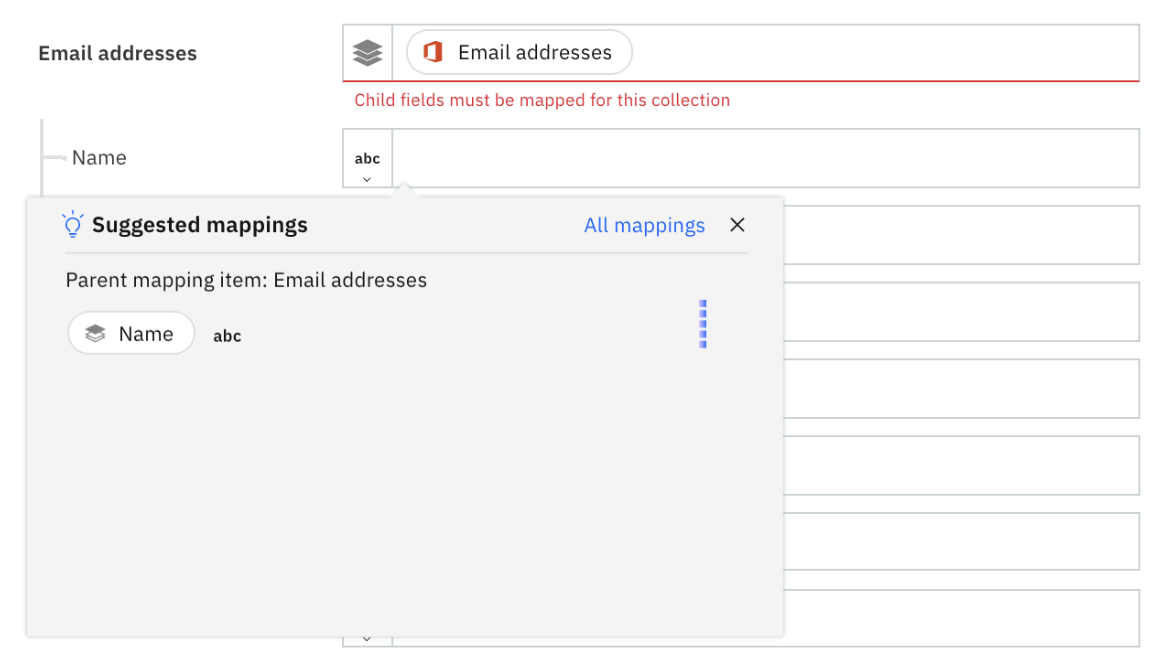
Figure 10: Suggestion for child element field in nested array fields
This tutorial explains IBM App Connect Mapping Assist's capability to reduce integration flow building time and enable developers to build flows confidently.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments