How to Write an Effective Penetration Test Report
A quick guide on what a penetration testing report should consist of and how to make it perfect for both the tester and the business.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeWhat Is an Effective Penetration Testing Report?
Following the recent trend of cyberattacks against IT infrastructure, service organizations have a steady rise in demand to conduct penetration testing on IT resources to ensure all vulnerabilities are identified and mitigated. Penetration testing is a technical cybersecurity procedure targeted at finding security flaws in a company’s internal and external networks, web applications, and systems. After a penetration test is completed, the testers must provide a penetration test report that documents the security issues identified during the assessment.
A penetration testing report is issued to an organization to present the risk associated with the security vulnerabilities identified in the infrastructure and provide remediation steps to fix the identified risk exposure. The test objective can be fulfilled based on the adequacy of the penetration testing report. Hence, a well-documented penetration testing report is as important as the penetration test itself. Below you can see the difference between the two types of penetration testing reports:
-
Vulnerability report: A vulnerability report is a detailed description of the specific risks existing for the assets in the scope of the pen test; it is issued when a penetration test is completed. A vulnerability report is meant to guide the security and development teams, help them understand the findings and root causes, and define a remediation approach. The chart below illustrates the key components of a vulnerability report.

-
Final report: The purpose of the final report is to reach the executive management, describe the pen test process, and present a detailed summary. It is part of the executive summary which provides highlights of the main issues in a clear and concise non-technical manner, as well as the risk to the business, the impact, and the required remediation steps.
Executive Summary for Strategic Direction
Once the pen tester has completed the technical investigation of unknown vulnerabilities within the system, they must deliver a detailed executive summary or management report that is executed in clear and non-technical terms to explicitly highlight the significant risk observed during the test. For example, misconfiguration of a network port is a substantial risk that is most likely to be exploited by an attacker. This can be understood by both technical specialists and executives.
Business Impact
After testing, it is critical to help the executives make an informed decision on the remediation steps. Hence, the executive summary should contain an explicit high-level review of the risk and reflect the asset's state during the pen test. A visual representation of the risk as a graph or chart and risk rating is recommended.
See the sample below:
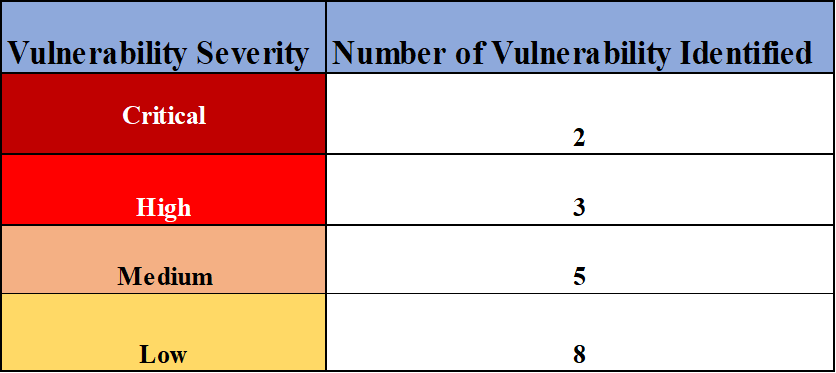
Walkthrough of Technical Risks
While risk ratings and evidence-gathering techniques are part of penetration testing, a penetration tester is expected to clarify each item. Doing so enables the client organization to understand the severity of the security issue and prioritize risk treatment according to the organization's risk appetite.
Let’s say a penetration tester discovered a lack of data encryption at rest and in transit in a banking organization that handles the personally identifiable information (PII) of its customers. It can be reported in a technical risk report in two ways:
- Technical correctness: Company A does not encrypt customer data, either at rest or in transit, using SSH, SSL, and TLS protocols.
- Technical correctness and context: Company A does not encrypt customer data, either at rest or in transit, using SSH, SSL, and TLS protocols. It can result in a breach of information security standards and regulations. Also, hackers are likely to intercept data which will compromise the integrity of the customer data.
Both analyses are helpful to the organization; however, the latter expresses the business risk. The lack of customer data encryption poses regulatory and data breach risks to the organization if an attacker gains access to customer data. Therefore, it is recommended that the penetration tester reports a vulnerability in the second format.
Probable Impact of Vulnerability
The scope of a penetration test is the likelihood and impact of a vulnerability to be exploited because of inadequate controls or lack of controls implemented. The likelihood could be minimal, but the impact could be high. In context, the likelihood of a user session being hijacked on a web application, if not securely protected against session hijack, will have a higher impact, such as privilege escalation and data confidentiality breach, as adequate controls to mitigate the risks have not been implemented.
A cyber-attack can cause a severe security concern and has a critical impact on the business and its reputation. To limit the impact and urgent treatment of a vulnerability, a penetration tester should utilize more refined ways to assign risk scores. In essence, a scoring system that assigns comparable scores (such as low, medium, high, and critical) and a reason concerning the severity level that each vulnerability poses for the business in a report should be adopted.
The following tools and mechanisms should help the pen tester provide adequate vulnerability details to the client.
- STRIDE: This is a model threat hunting tool that is useful for identifying computer security vulnerabilities on a target system. For example, privilege escalation and denial of service.
- CWE: Common weakness enumeration provides a mechanism for ranking software weaknesses and vulnerability to the tester using these tools for the purpose. With this tool, the pen tester gains adequate insight into the vulnerability and remediation steps.
- CAPEC: Common attack pattern enumeration and classification is a complete dictionary and classification repository of known attacks, which can be used by pen tester to understand and analyze identified vulnerabilities.
The higher the likelihood and impact of a vulnerability, the more willing the organization is to treat the risk.
Vulnerability Remediation Opportunities
Therefore, the organization should be provided with options for remediation efforts to treat each risk based on the identified vulnerabilities as it is applicable. The penetration tester must recommend purposeful and actionable ways of responding to risk in the penetration test report and not just a generic high-level fix.
Action plans and options include:
-
If a vulnerability detects that the servers are connected directly to the internet, recommending restricting internet access for all servers will impact other servers requiring internet access; instead, the penetration tester should suggest isolating and implementing control procedures on specific servers that require internet, such as patching servers for downloading patches and software updates.
-
Specific remediation action should be documented in the vulnerability report to ensure that information assets are not overprotected by enforcing generic controls. The responsibility of the pen tester is to report in detail where controls should be applied in granularity to ensure that each control is adequate for the specific vulnerability.
Concluding Thoughts
Adequate reporting upon concluding a penetration test is vital to the business's survival. It helps the organization redesign controls to meet business objectives and information security best practices.
- Reporting the result of a penetration test is far more demanding than the penetration test assessment. Therefore, there is more to this practice which includes communication, proper methodology, vulnerability description, customer business insight, deliverables, and client support.
- The pen tester should be specific about the risk and impact by explaining accurately why a particular severity is given.
- Adequate tools should be deployed to analyze the results and data of penetration tests.
- Using generic severity and remediation will be more daunting for the organization to understand and fix the issues.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments