How To Utilize NoSQL DB: Graph Database Examples
With the rising popularity of NoSQL databases among developers, read this post to explore their possibilities, with the focus on Graph Database utilization.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeSince NoSQL Databases are widely used and preferred among developers, because of their close relation to the Agile methodology, we decided to focus on their functionality in this article. At first, we need to define how we see NoSQL abbreviation, considering that there are several different versions for that. In the battle of the meanings, we have literally the database without SQL usage, and "not only SQL." Surely, we’d prefer to cognize the second option, but not anti-definition, given that SQL is running in any backend and traditionally is not eliminated.
The NoSQL databases create more intuitive methods of storing data, allowing to model the structured linkage that will be closer to the application’s form. They require fewer transformations when saving or retrieving with NoSQL APIs. Furthermore, NoSQL databases can fully utilize the Cloud to ensure minimal outage. As you can notice, NoSQL DB seems to be beneficial and more flexible than traditional storing. Let’s discover this difference in further detail.
Merits of NoSQL DB Compared With SQL
Comparing two types of databases, we will highlight the NoSQL approach with its advantages in relation to SQL. The difference appears in each and every way, so we are going to break down some of the most apparent ones.
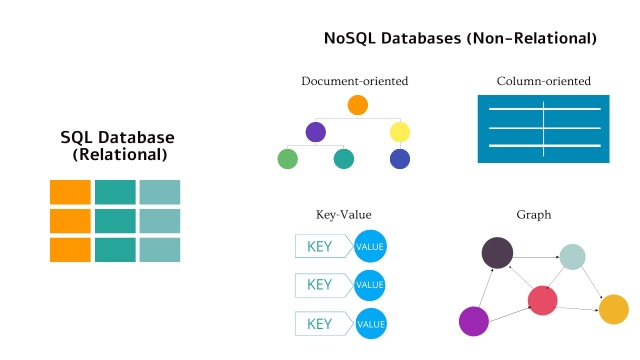
Non-Relational vs Relational
While relational databases (SQL approach) store data using tables, non-relational DB (NoSQL approach) incorporates a storage model that is designed for the particular needs of the data nature that is being stored. Within tables, linking works by getting "keys" (identifiers that may be applied to a row of data). Such "keys" could be primary and foreign, depending on the addition to the record, and altogether they create the relations, which are defining the whole concept of SQL databases.
For the non-relational databases, there is no unified form and usage. There are various types of databases, namely: column-oriented, key-value, graph, and document data stores, which are built differently with their own specific linking methods. The benefit of such flexibility is apparently obvious when you want to develop some complex ideas, requiring a more intuitive structure.
Horizontally vs Vertically Scalable
Vertical scaling (SQL approach) means adding more power to a present structure; however, horizontal scaling applies to adding new machines to the resource pool. Horizontal scalability (NoSQL approach) is typically focused on data segmentation (each node only contains part of the data). That said, in principle, integrating additional machines into an existing pool makes it easy to manage with less downtime because you are no longer constrained by the performance of a single unit. However, in this case, it also increases the cost of sharing, copying, or updating data because copies of the data should be passed.
Dynamic vs Predefined Scheme
With unstructured data, SQL databases employ a predetermined schema, whereas NoSQL databases utilize a dynamic model. Until you can add data to a relational database, you need to design schemas at first. The structure and data types are set in stone ahead of time. The structure of your database updates every minute you add an extra element to your application. This is an extremely lengthy procedure that causes significant downtime if the database is massive.
NoSQL databases are designed to store data without having to adhere to a strict schema. That provides the flexibility to make major real-time adjustments in applications. NoSQL databases have offered a solution to the scale and data format difficulties. So they are worth considering, undoubtedly.
Now that we have completed a look at the core differences between SQL and NoSQL databases and determined the internal operational capacities that offer NoSQL solutions, we can move to the exploration of practical implementation.
Example #1: The Platform for API Building
The first idea is the platform, which offers a user-friendly interface for creating various APIs. Since this SaaS platform is a technical solution for non-technical people, it uses graphs to visualize the structure and relations within the future users’ APIs. Though the platform is not confined to the integration of graphs in the interface, our developers’ team uses Graph database, in particular, Neo4j (which is the most common among Graph database environments).
When choosing the database for this project, there were no other applicable options, other than Graph database, since this type of NoSQL DB generates the whole network between data. Simply said, Neo4j creates nodes (entities, criteria, and other valuable data) and establishes relations between each of them. Neo4j additionally offers the possibility to monitor changes that are rendered from the modifications the user contributes to the platform.
Let’s return to the core of the idea itself: while the user generates API in the graph form with the same relations and nodes, the platform automatically adopts everything to the code, converting it at the same time to a more comprehensible form for the machine. However, if you take a look at the Neo4j dashboard where the database is displayed, the scheme would be as intuitive for the human as for the machine.
Example #2: The Data Analytics Platform for DAOs
A second idea is an analytics software that ranks and examines the top Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) based on a variety of criteria. The platform collects and aggregates a range of statistical metrics on DAOs, then shows them in an interactive map used for the community to explore. You are probably wondering how and where NoSQL DB could be implemented here. Briefly, since the platform is something like a social network for DAOs, there is a real-time interaction between users, so we used Graph database (Neo4j) particularly for two features, that require complex link building.
The first feature is called "Collaboration" and it is used to display users the results of the voting pattern, existing on the platform (the users can vote for different DAOs, and their ideas to invest or something else). In the panel "Collaboration", you can find matches between users that voted for the same DAOs. To make these relations work, we needed the Graph database, which allows us to simplify the structure of connections.
The other one is "Similar DAOs," which helps to find DAOs somehow related or connected within different criteria. Graph Database here is necessary to bring out each criterion separately on the graph scheme, in order to find correlations between them. Surely, it is easier than going through each entity in the table’s rows and columns, to find similarities.
Why Should You Consider Utilizing a Graph Database?
When we shared our insights on some of the projects we are working on, and they are both utilizing Graph Databases, we should check out this approach and Graph Database examples on a general scale. How often are they used? Why Graphs? How are they better than traditional relational databases? Let’s discover together.
Being multi-relational by nature, Graph Databases are opposed to relational ones, which have loosely affiliated tables. Navigating relationships is quick because they are already stored in the database and don’t need to be calculated. Data is saved in the same way that thoughts are scribbled on board. The information is kept letting you conceive and use it in a variety of ways. In contrast, relational databases can’t handle anymore the quantity, pace, and diversity of current data spreading. Acknowledging ways for NoSQL databases to address these issues is merely the first step in determining which database is best for your business.
Considering the fact that there are a variety of database approaches, and available tools for each of them, searching for the right solution could be tough. But if the ranking by the types of databases could somehow help you to decide, you can find it here. Graph databases are anticipated to gain ground on other types of databases, especially the still-dominant relational database. Even though they are not suitable for each and every app idea.
A graph database is suitable for any environment that enables social networking. This concept may be applied to any project where you’d have to find out people’s behavior in order to suggest new offerings for them. Besides, these types of databases enable defining the shortest route between entities. Hence, they are commonly used for social networks, platforms with communities, logistics, and spatial dimensions (for example, in real-time maps, flight booking platforms, or Transportation Management Systems).
In Conclusion
As NoSQL DB beneath its concept has the relation to Agile, these types of databases might be the right solution for your software. They could increase the performance, by eliminating the chances of "Nulls" (deadlocks of requests). They could be flexible and adapt to the purposes. Lastly, they could build intuitive interfaces from complex data, even though NoSQL DB is not a panacea. Every idea differs and requires a custom perspective, whether it would be a Graph database or Key-Value.
Published at DZone with permission of Tetiana Stoyko. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments