How to Use Java Constructor and Collection in Mule 4
Java constructors of any Java class can be called from the mule configuration XML file using the “New” operation of the Java module.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeHow to Use Java Constructor in Mule 4
Java constructors of any Java class can be called from the mule configuration XML file using the “New” operation of the Java module.
For this tutorial, let’s consider the below Java class which has two constructors, i.e., one default and one constructor that takes input parameters to initiate the class.
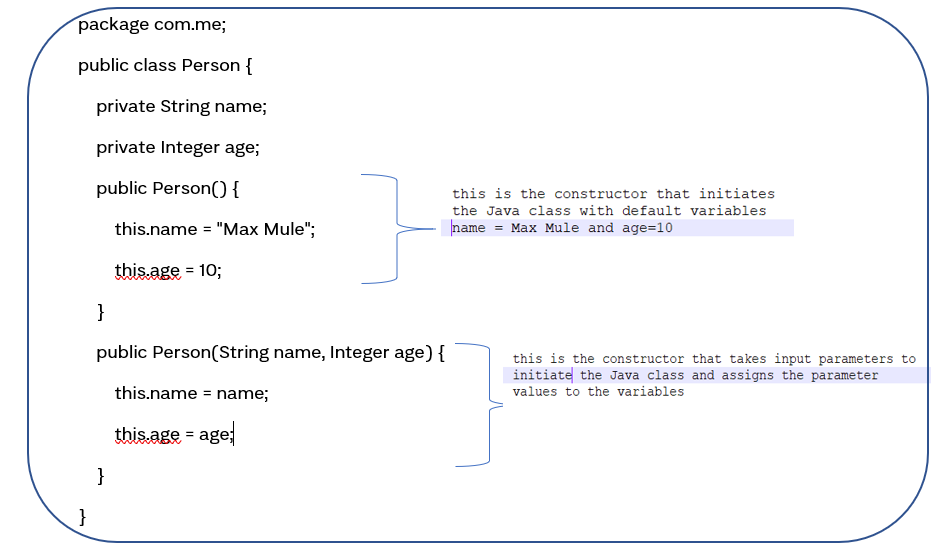
Initiate the Default Constructor
Initiate the default constructor using the “New” operation of the Java module. Specify the Java class name and constructor name in the connector configuration.
<java:new constructor="Person()" class="com.me.Person"/>
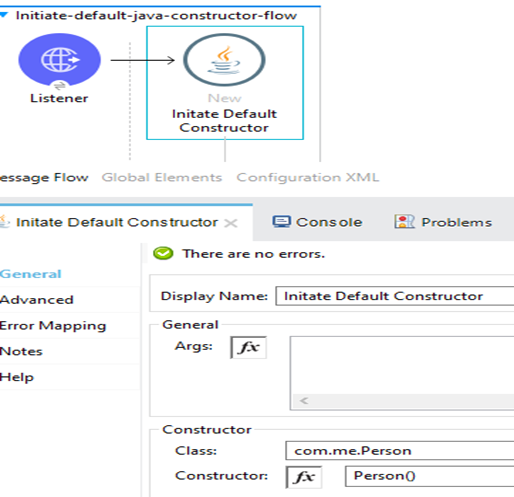
Initiate the Constructor That Takes Arguments
Initiate the constructor that takes input arguments using the ”New” operation of the Java module. Specify the Java class name and constructor name and the arguments in the connector configuration.
<java:new constructor="Person(java.lang.String,java.lang.Integer)" class="com.me.Person">
<java:args><![CDATA[#[{
name: "Priyabrata Dash",
age: 30
}]]]>
</java:args>
</java:new>

Below Maven compiler plugin must be configured in the pom.xml to compile Java classes with the -parameters flag:
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>x.x.x</version>
<configuration>
<compilerArgs>
<arg>-parameters</arg>
</compilerArgs>
</configuration>
</plugin>
How to Use Java Collection in Mule 4
Java collections can be initialized and used in mule code using New and Invoke operations of the Java module.
- Initialize java collection class using the above mentioned New operation
- Add data to the collection using Java Invoke
In this article, I am taking an example of initializing an ArrayList type of collection and storing values into it.
Initialize the ArrayList with java New operation:
- Initiate the ArrayList using the “New” operation of the Java module. Specify the Java class name as “java.util.ArrayList” and constructor name as “ArrayList()” in the connector configuration.
Define the target variable to store it

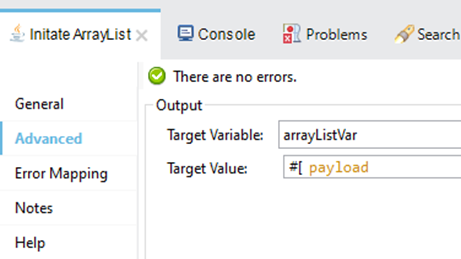
<java:new doc:name="Initate ArrayList" doc:id="e3c787f1-daa0-4ff5-b0f7-2913aa056156" class="java.util.ArrayList" constructor="ArrayList()" target="arrayListVar">
</java:new>Use the Java Invoke component for adding data to the collection:
- Drag the Java Invoke to the mule flow
- Configure the target as mentioned above variable ‘’arrayListVar’’ in the Instance section
- In the argument, pass the values that need to be stored in the ArrayList. Input to this argument field should be the number of parameters required to invoke a particular method. In this example, I have selected the method addAll(Collection arg), which takes only one argument of type Collection as below.
{
arg0: [10,20,30]
}Class should be java.util.ArrayList and Method, as mentioned above, is addAll(Collection arg).

<java:invoke method="addAll(java.util.Collection)" doc:name="Invoke" doc:id="0708d2c3-3325-476c-9b0c-ebe7949ed76d" class="java.util.ArrayList" instance="#[vars.arrayListVar]">
<java:args ><![CDATA[#[{
arg0: [10,20,30]
}]]]>
</java:args>
</java:invoke>
Output of the above Java invoke: The ‘arrayListVar’ will look like below which contains 3 numbers.

Published at DZone with permission of Priyabrata Dash. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments