How To Run Ganache in a Browser
Test your app frontend with a local blockchain instance running in your browser using Ganache.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeWhen developing Web3 projects, it helps to have a local blockchain devnet for testing. Ganache is one of the most popular tools for this in the Ethereum ecosystem and part of Truffle. Ganache allows you to set up a local blockchain with different settings to thoroughly test your smart contracts before deployment.
Seeing a local blockchain’s output in the terminal helps you to understand how your project will behave in a live environment. The ability to set the output to variables to manipulate some front-end code is even more useful. Some users may not know that you can do this by running Ganache in your browser.
This article explores how to run Ganache in your browser and highlights three great new features that make developing your Web3 projects easier.
Ganache in the Browser
Running a local blockchain instance to test your smart contracts is an essential step in the Web3 development process. By testing in this manner, you confirm things are working correctly before using a node service, such as Infura, to deploy your contracts to a testnet or mainnet. This minimizes the risk of ramping up daily limits and ensures you only need to deploy once. Ganache is an excellent tool that simulates the Ethereum network and allows developers to:
- Fork any Ethereum network without waiting to sync
- Establish block mining rules (instant, on-demand, intervals)
- Impersonate any real account without needing their private keys
- Make function calls with Ethereum JSON-RPC support
However, many who use this tool may be unaware that, since v7.0.0.0, Ganache can also run in your browser. Running in the browser allows you to set the local blockchain’s output to variables, which you can then use to test your frontend code. This visual process helps you to understand how your users will interact with your project and also enables you to test your dapp entirely offline (when using a local instance).
By first running Ganache in the browser and fine-tuning how your dapp reacts, you can easily switch the provider to your node service API once things are working as intended. Additionally, since Ganache’s latest update (v7.3.2 at the time of writing), you can now fork the Ethereum main net when running Ganache in the browser. This allows you to interact with real accounts and contracts through your front-end code.
The Project
In this section, we will create a basic smart contract using Truffle and its VS Code extension. Then, we’ll first deploy our contract to Ganache via the command line. Afterwards, we will create a simple front end to use Ganache in the browser and interact with our deployed contract.
Requirements
For this project, we will use the following:
Step 1 – Installation
First, we can run the command node --version in our terminal to ensure NodeJS and NPM are properly installed on our machine.
Next, we will install Truffle and Ganache by running the following command:
npm install -g truffle ganache
Checking the version number for Truffle and Ganache with truffle --version and ganache --version respectively will tell us if both tools were installed successfully.
The next step is to install VS Code, then navigate to the Extensions tab in the editor and search for Truffle for VS Code.
With everything now installed, we are ready to start working on the project.
Step 2 – Set up the Project
With the Truffle for VS Code extension, we can easily create a new Truffle project through the VS Code command palette. Press ctrl + shift + P in the editor to open up the command palette and type truffle to see a list of commands we can use. Select Truffle: New Solidity Project and then create a basic project to create a new project in the desired folder.
This creates an initialized project with a simple folder structure and example code we can use if we wish.
The ability to use console.log in our smart contract code is another great new feature recently available for Ganache. Before we create the smart contract for our project, let’s set that up by installing the required package. Navigate to the project folder in the terminal and type the following command:
npm install @ganache/console.log
Step 3 – Write the Smart Contract
The smart contract for our project will be a basic one we can donate some ETH and request to see the balance.
In the contracts folder, create a new file and call it SimpleContract.sol. Next, fill it with the following smart contract code:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: UNLICENSED
pragma solidity ^0.8.13;
import '@ganache/console.log/console.sol';
contract SimpleContract {
constructor() {
console.log('\n\n#################################################\n'
'#### Now Deploying Contract ####\n'
'#################################################'
);
}
function donate() public payable {
console.log('Successfully Donated ', msg.value);
}
function getBalance() public view returns (uint256) {
console.log("This contract's balance is:", address(this).balance);
return address(this).balance;
}
// Needed in order to receive payments
receive() external payable {}
}
The code in our smart contract is relatively simple. It displays a message in the console when we deploy our smart contract, provides the functionality to donate ETH and query the balance, and prints messages in the console when calling the functions.
Step 4 – Deploy to Ganache
After installing the Truffle for VS Code Extension, we can easily deploy by right-clicking the smart contract file and choosing Deploy Contracts. However, if we want to see our console messages, we will have to use our own terminal rather than the one built into VS Code. This could potentially change in the future, but for now, we will have to create a simple migration script to carry out the deployment.
In the migrations folder, create a new script called 1_SimpleContract.js and input the following code:
const SimpleContract = artifacts.require("SimpleContract");
module.exports = function (deployer) {
deployer.deploy(SimpleContract);
};Next, open up a new terminal window and start Ganache:
ganache
This terminal window is where we will see our console messages when they appear. We now have two terminal windows open: one running Ganache and the other open in the folder of our Truffle project.
In the terminal window that’s open in our Truffle project’s location, type the following command to initiate the deployment:
truffle migrate --network development
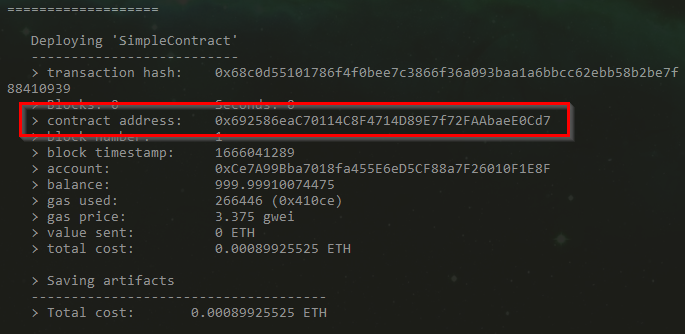
If the deployment is successful, we can see our console message printed in the terminal:
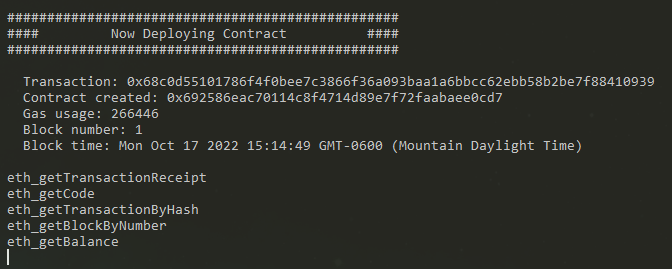
Great! Our contract is live on our local Ganache instance! We’ll leave Ganache running for now so we can interact with our contract using the browser. Before we get to that, copy the contract address from the output in the terminal where we typed the migrate command. We will use this address to point our front end to our smart contract.
Step 5 – Build the Frontend
Setup
For the front end of this project, we will use React. Navigate to a new empty folder and type:
npx create-react-app ganache-browser-test
Next, we will install Web3.JS to easily interact with our smart contract. Navigate into our new project folder and install Web3.JS with this command:
cd ganache-browser-test
npm install web3
Newer versions of create-react-app don’t play nicely with Web3.JS, so we need to install a specific version of React Scripts. We can do so with this command:
npm install --save-exact react-scripts@4.0.3
Finally, to use Ganache in our browser, we will install it directly as a dependency:
npm install ganache
Alternatively, you can add the CDN link in the HTML to access Ganache from the browser:
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/ganache@7.3.2/dist/web/ganache.min.js"></script>Before we start working on the frontend code, we need to create a file containing our contract’s ABI so that we can interact with our smart contract. We can copy that file directly from our Truffle project. Navigate to the build/contracts folder in our Truffle project and copy the SimpleContract.json file.
Next, open up our frontend project in the editor and create a new folder called abi. In that folder, paste the SimpleContract.json file. The file structure for our front end now looks like this:
The Frontend Code
With all the setup out of the way, we can start working on our front end. First, open the App.js file in the src folder and replace the boilerplate code with this:
import { useState } from 'react';
import './App.css';
import SimpleContract from './abi/SimpleContract.json';
const ganache = require('ganache');
const Web3 = require('web3');
const options = {}
const provider = ganache.provider(options);
const web3 = new Web3('http://127.0.0.1:8545');
const CONTRACT_ADDRESS = 'YOUR_CONTRACT_ADDRESS'
const USER_ADDRESS = web3.utils.toChecksumAddress('YOUR_ACCOUNT_ADDRESS');
const contractInstance = new web3.eth.Contract(SimpleContract.abi, CONTRACT_ADDRESS);
const App = () => {
const [contractBalance, setContractBalance] = useState(0);
const donate = async () => {
const donationAmount = document.querySelector('#donationAmount').value;
const response = await contractInstance.methods.donate().send({
from: USER_ADDRESS,
value: web3.utils.toWei(donationAmount)
});
console.log('donate response:', response);
};
const getBalance = async () => {
const response = await contractInstance.methods.getBalance().call();
console.log('getBalance response:', response);
setContractBalance(web3.utils.fromWei(response));
}
return (
<div className="App">
<header className="App-header">
<h1>Ganache In The Browser</h1>
<div>
<input
type='number'
id='donationAmount'
defaultValue={0.01}
/>
<label htmlFor='donationAmount'>ETH</label>
<br></br>
<button
id='donate'
type='button'
onClick={donate}
>
Donate
</button>
</div>
<div>
<button
id='getBalance'
type='button'
onClick={getBalance}
>
Get Contract Balance
</button>
</div>
<div>
<p>
{contractBalance} ETH
</p>
</div>
</header>
</div>
);
}
export default App;Be sure to change CONTRACT_ADDRESS to the address, we received when deploying our smart contract back in Step 4. As well, USER_ADDRESS is the account that will call the functions. We can get this from the list of accounts that displays when we first started our Ganache instance in the terminal:

Any of these account addresses will work.
Before we move on, let’s take a second to walk through the code we wrote:
- We import our dependencies and
SimpleContractJSON file. - Set the
ganacheandWeb3variables. - Create an empty
optionsvariable that we initialize ourproviderinstance with.- Note: This
optionsvariable is where we would set any of the options we would like our local blockchain instance to include, such as forking Mainnet or Goerli, when running Ganache strictly in the browser (without it running in our other terminal window).
- Note: This
- Initialize our
web3object using ourlocalhost URLand port8545, where our Ganache instance is already running.- Note: You can run Ganache strictly in the browser at this point by using the
providervariable instead of localhost. We are usinglocalhostin this case, since we want to interact with our already deployed smart contract and see ourconsole.logmessages in the terminal output.
- Note: You can run Ganache strictly in the browser at this point by using the
- Set our
CONTRACT_ADDRESSandUSER_ADDRESSvariables. - Create a contract instance we can use to call our functions in the
Appcode. - Create the
contractBalanceReact state variable and itssetmethod. - Define our
donateandgetBalancefunctions. - Finally, we return the
htmlfor our front end.
Run the Project
Now we can run our app with npm start to display our front end, which looks like this:

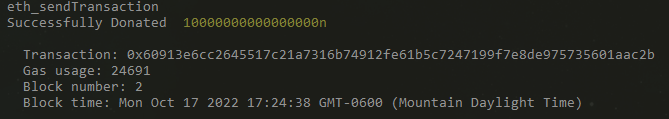
When we test our project, we can see the results and our console.log messages displayed on the terminal window which is running Ganache, and the ETH balance on our front end successfully updates with the new balance.

Step 6 – Fork Goerli or Mainnet With Ganache in the Browser
Now that we know our project functions properly on a locally running instance of Ganache, the next step is to run it on a forked version of a testnet and then mainnet. We won’t run through the actual process of doing that in this article, but setting it up to do so is simple. All we need to do is change a few lines of our frontend code.
First, the options variable needs to specify which network we wish to fork:
const options = { fork: { network: 'goerli' } };
Or:
const options = { fork: { network: 'mainnet' } };
Then we need to update our web3 variable declaration:
const web3 = new Web3(options);
Finally, we need to make sure that we update CONTRACT_ADDRESS with our address on whichever network we are forking. We also need to update USER_ADDRESS to an account address on the same network that has sufficient funds to donate to our contract.
When forking mainnet, that section of code could look something like this:
const options = { fork: { network: 'mainnet' } };
const provider = ganache.provider(options);
const web3 = new Web3(provider);
const CONTRACT_ADDRESS = '0x692586eaC70114C8F4714D89E7f72FAAbaeE0Cd7'
const USER_ADDRESS = web3.utils.toChecksumAddress('0xCe7A99Bba7018fa455E6eD5CF88a7F26010F1E8F');And with that, we could test our project with a forked version of mainnet using Ganache in our browser.
Conclusion
Testing projects by creating an interface helps to visualize how your dapp is running and gives you a better idea of how it will perform for users once on mainnet. Running in your browser while testing your frontend code is one of the features that make Ganache such a powerful tool in your development toolkit. For more information about working with Ganache or contributing to the project, check out their GitHub or documentation.
Published at DZone with permission of Paul McAviney. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments