GitHub Security for Repositories: Comparing WhiteSource Bolt, Snyk, Depshield, and GitHub Alerts
Make sure your repos are secure.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeMillions of repositories are hosted on GitHub, and lots of projects hosted there make their way into your project as dependencies. Developers can just look for modules that cover their use-case and import it into their project, which is actually great! The not-so-great part about importing third-party code is that developers usually just ignore the security aspects of it altogether.
According to GitHub, its security scan for vulnerabilities in Ruby and JavaScript unearthed more than four million bugs, which sparked a significant clean-up effort by project owners. As demonstrated by Equifax's massive data breach, vulnerable open-source software libraries may contain significant security repercussions. GitHub has made some improvements in terms of notifying the user about the security issues in their code, but the users are required to opt into their security alerts.
This article covers some popular tools that you can use to improve the security of your products hosted across GitHub repositories. Most of these tools are available in the GitHub Market and you can try integrating them with your repository for free. Let's get started.
WhiteSource Bolt
WhiteSource Bolt is a new GitHub app available in the GitHub Marketplace for free. It lets you discover vulnerable open-source libraries and dependencies in your project. It covers over 200 programming languages and offers continuous tracking of multiple open-source vulnerabilities databases. This includes the CVE/NVD, security advisories, and popular open-source project issue trackers.
Bolt lets you scan unlimited repositories per user, five scans a day. The scan is triggered when you push commits into your repository and one of the commits include an update to the package repository file. For instance, if you're running a JavaScript project, any change made to the package.json file will trigger a scan.
If Bolt finds a vulnerability within your code, a new Issue is created in your repo's Issue tracker and you'll be notified via email. The report will include a CVSS score of the issue and suggestions on fixing the issue. This includes upgrading to the latest version or trying an alternative library.
How to Set Up WhiteSource Bolt?
Head over to the GitHub page for WhiteSource Bolt. Press the install button. Make sure that you've enabled Issues for your repositories before getting started.
Next, select the account where you want to set up Bolt.
You can choose to install WhiteSource Bolt for all your repos or a few selected repositories.
You will be asked to create an account at WhiteSource. Go ahead and create one.
Verify the email and that's it. WhiteSource will add a .whitesource file to all the existing repos as follows:
The next time you push commits that involve a change to any of the files whitelisted by WhiteSource, Bolt will trigger a scan.
Sonatype Depshield
Sonatype DepShield is a free GitHub app which can automatically identify vulnerabilities in open source dependencies. Depshield enables GitHub developers to take essential governance and security measures in their own hands. Depshield is powered by Sonatype's OSS Index and integrates publicly available open source vulnerability data into GitHub's public repositories. This allows developers to identify, and eventually fix, possible issues as soon as possible. However, Sonatype doesn't offer the entire DB in the free app:
With the use of DepShield, organizations are empowered to move their security practices as far left as they see possible. This allows developers to usher in open-source hygiene into their GitHub repositories.
Sonatype DepShield monitors projects on an ongoing basis and automatically creates issues where security vulnerabilities exist. With the help of DepShield, developers can view an inventory of publicly known security vulnerabilities listed within GitHub's Issue Tracker.
Furthermore, you can click on an issue to view details on the specific vulnerability, which includes CVSS and CVE.
Determine vulnerable version ranges on every listed vulnerability
saDepShield is a fantastic first stage to start with open-source hygiene. However, it is based on vulnerability data gleaned from public sources.
Snyk for GitHub
Snyk is known to unearth and fix vulnerabilities in existing dependencies repeatedly.
Integrate GitHub to Test and Watch Your Repositories
Ruby, Scala, Node.js, Python, and Java GitHub repos can be added and easily checked. For instance, if you're running an express project, it will point out the security in issues associated with the NPM packages used in your express project. It notifies you of the possible security issues that you might come act.
Users also have the option to decide which of the languages they would like to watch with Snyk on an ongoing basis. However, unlike WhiteSource Bolt and DepShield, results are shown in Snyk's app and not in GitHub environment on the 'issues' tab.
The integration works with public and private repositories; however, the number of tests that you can run on private projects is limited to 200. Moreover, when it comes to private instances, users will be first required to set up using Snyk's Broker.
Here are the steps that need to be followed:
- Navigate to the integrations page and click "Connect to GitHub." Once here, grant Snyk additional GitHub permissions. Users may choose to allow access to private and public repositories or allow access only to public repositories.
- In the next stage, users should be able to view a complete list of GitHub repos across GitHub organizations that you're a part of. Here, users can select those repositories they want to test with Snyk. In case of supported manifest files at the root, or a couple of directories deep, Snyk automatically recognizes and initiates projects for them.
- Click the button towards the bottom of the page that says "Add selected repositories to Snyk." The repositories selected will appear in the user's projects, and will be regularly checked for vulnerabilities.
- When users click "View report" on a particular project, users can view as well as fix vulnerabilities almost immediately. Users should also be able to review any of the suggested remediations and create a PR using the corresponding patches or upgrades.
Integration features
Watch a Ruby, Python, Scala, Node.js, or Java GitHub repo and add it as a project to Snyk. Doing this allows users to:
- View Snyk tests in their pull requests where vulnerabilities are regularly checked
- Receive email alerts as well as a Snyk pull request along with relevant fixes whenever new vulnerabilities affecting the user's repo are made known
- Receive email alerts as well as a Snyk pull request whenever a new patch or upgrade is made available for a vulnerability that affects the user
- Manually trigger Snyk pull requests with the help of the test report page or the project page for the relevant repo on snyk.io
Disabling the GitHub Integration
If users no longer wish to watch a GitHub repo, the project settings page gives them a choice to stop watching the concerned project. The project is set to the inactive status.
Users will no longer receive alerts or Snyk tests based on their pull requests. The webhook that facilitates the GitHub integration for the repo will be removed. Users can still restart watching at any time they wish.
Authorizing GitHub Repository Access
When Snyk is granted access to GitHub, users have the choice to:
- allow access to private and public repositories
- allow access to public repositories only
This is applicable for every GitHub organization that the user has the required permissions for. However, access to private and public repositories is not available in the free version.
In case users wish to modify their permissions, they can navigate to Settings, Integrations, and select GitHub from the list.
Github Security Alerts
In October 2017, Github made it simpler for developers to keep track of the projects their code is dependent on, with the inclusion of dependency graphs that are currently supported in JavaScript and Ruby.
Now, a little over a year later, for the 75+ percent of GitHub projects that report dependencies, GitHub assists developers in identifying projects that may be negatively impacted.
With the dependency graph, Github notifies users when vulnerabilities are detected in one of the user's dependencies and proposes known fixes from among GitHub community. This works perfectly
Start Using Security Alerts
Whether projects are public or private, security alerts receive critical vulnerability information and pass it to the appropriate people.
Enable Your Dependency Graph
Public repositories automatically contain the user's dependency graph with security alerts pre-enabled. In the case of private repositories, users will be required to opt-in for the security alerts in their repository settings or grant access within the Dependency graph section of their repository's Insights tab.
Set Notification Preferences
When the dependency graph is enabled, admins will be able to receive security alerts by default. Admins will also be able to add individuals or teams as recipients for security alerts within the dependency graph settings.
Respond to Alerts
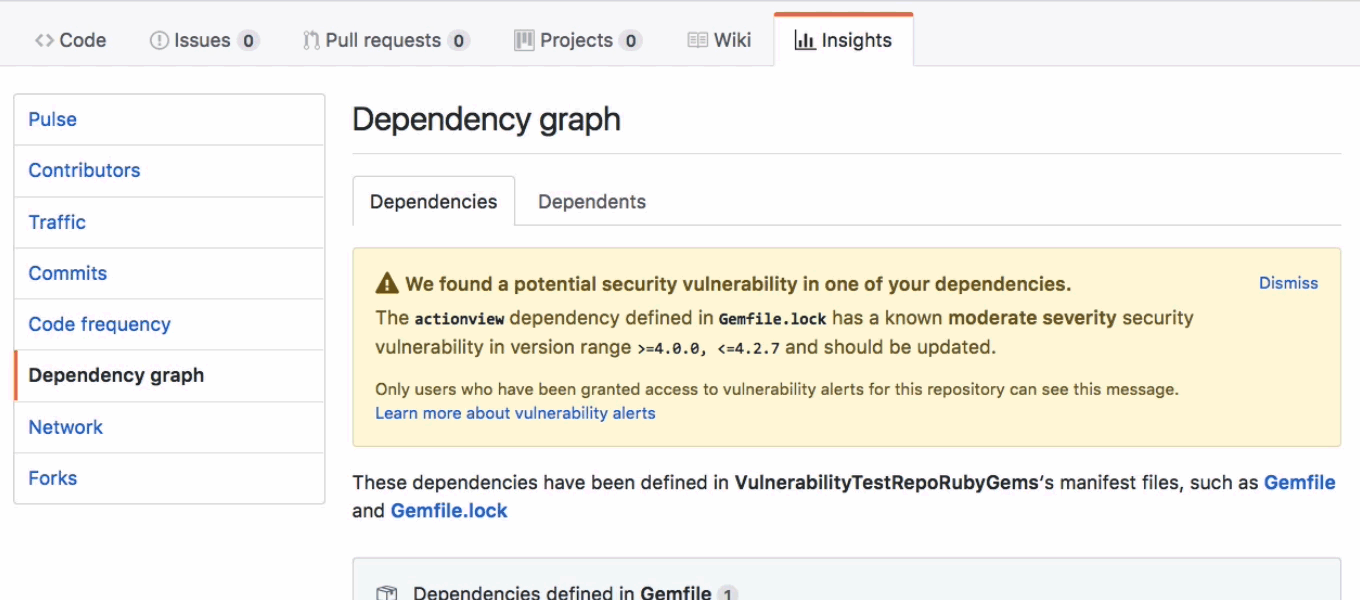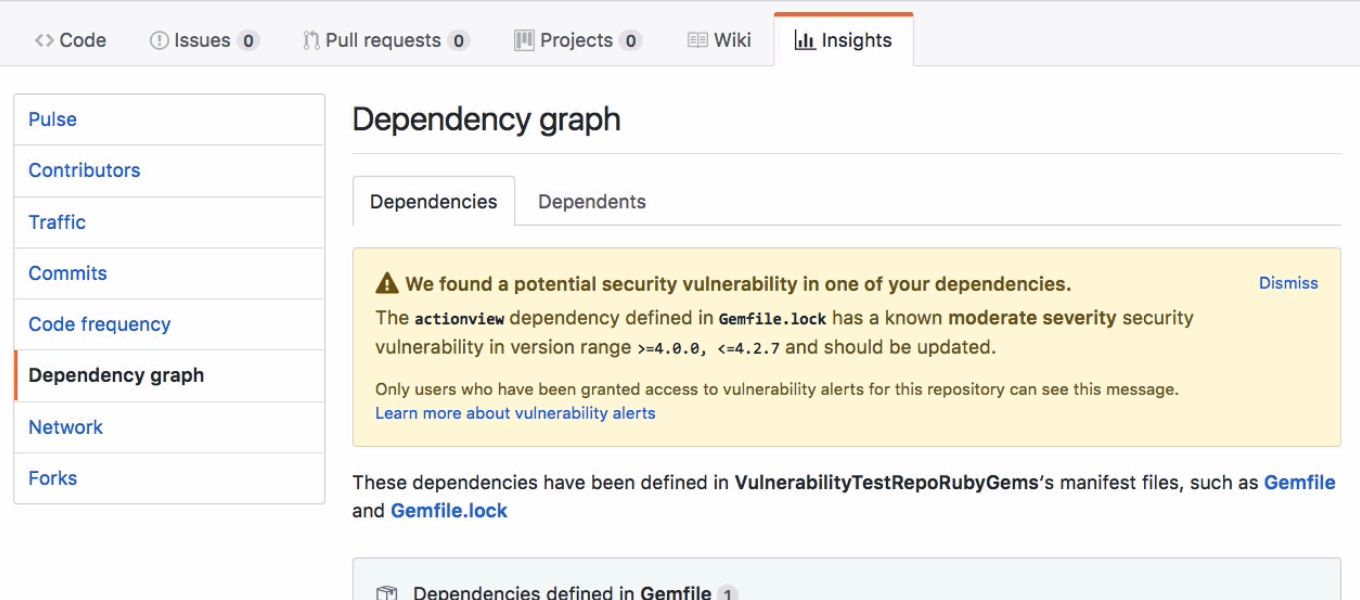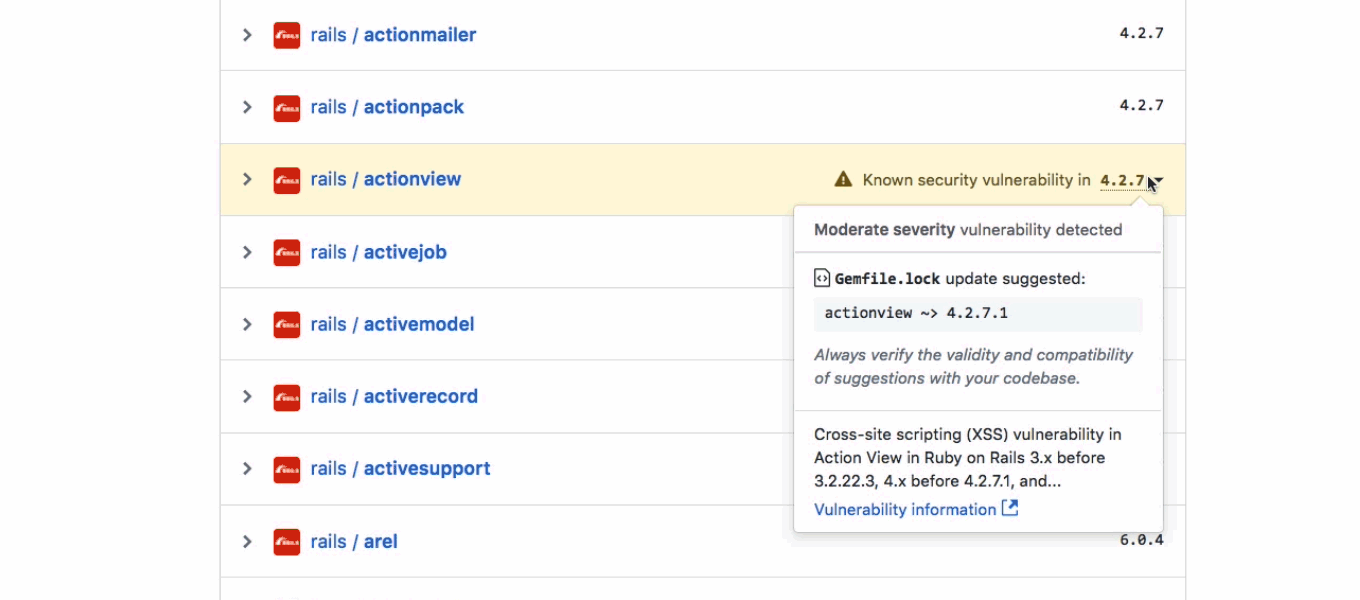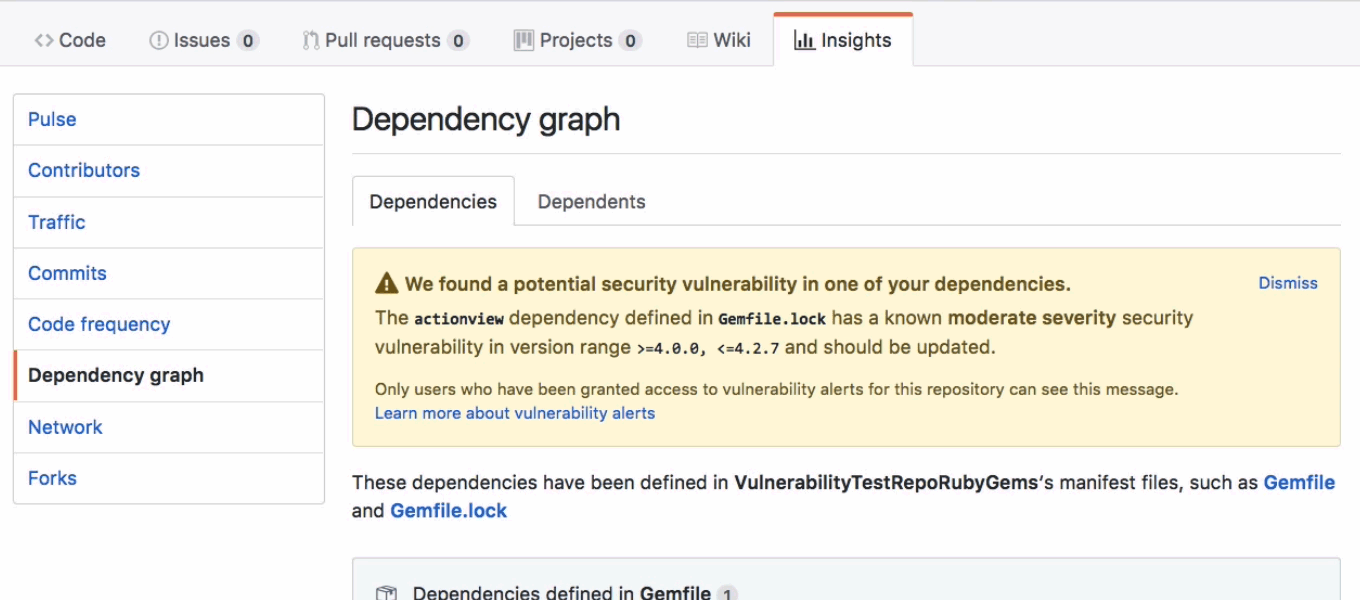
When GitHub notifies users about a possible vulnerability, GitHub will highlight dependencies that it recommends for updating. In case of the existence of a known safe version, Github will choose one that uses machine learning and publicly available data, to include in their suggestion.
Vulnerability Coverage
Vulnerabilities that contain CVE IDs, publicly known vulnerabilities extracted from the National Vulnerability Database, will be automatically included in security alerts.
However, all vulnerabilities do not have CVE IDs. Many publicly disclosed vulnerabilities don't have them either. The understanding is that Github will continue to improve at identifying vulnerabilities as its security data expands. To know more about assistance with managing security issues, you can have a look at security partners in the GitHub Marketplace.
This is perhaps the next logical step when it comes to utilizing the most extensive collection of open source data to assist developers in keeping their code safer.
Summary
Security tools are mostly purpose-built and aimed at delivering at the speed and scale that development teams need to secure applications while meeting build deadlines.
Automation is central to code security with application security tools. By the seamless integration of testing into the development lifecycle, security tools allow developers to locate flaws earlier in the process when it's most cost-effective to fix. This will enable teams to improve security without additional staff, expense or equipment.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments